Matching (Value 15)
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | Boyle's law | d. | Graham's law | b. | Charles's law | e. | Gay-Lussac's law | c. | Dalton's
law | f. | ideal gas
law |
|
|
|
1.
|
For a given mass of gas at constant temperature, the volume of the gas varies
inversely with pressure.
|
|
|
2.
|
The volume of a fixed mass of gas is directly proportional to its Kelvin
temperature, if the pressure is kept constant.
|
|
|
3.
|
The pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its Kelvin temperature if the
volume is kept constant.
|
|
|
4.
|
P ´ V = n ´ R ´ T
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | effusion | c. | diffusion | b. | compressibility | d. | partial pressure
|
|
|
|
5.
|
a measure of how much the volume of matter decreases under pressure
|
|
|
6.
|
the pressure exerted by a gas in a mixture
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | solvation | e. | electrolyte | b. | weak electrolyte | f. | colloid | c. | aqueous
solution | g. | surfactant | d. | solvent |
|
|
|
7.
|
interferes with hydrogen bonding between water molecules
|
|
|
8.
|
Solute ions or molecules are surrounded by solvent molecules.
|
|
|
9.
|
compound that will conduct current in the liquid state or in aqueous
solution
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | dispersed phase | e. | Tyndall effect | b. | surface tension | f. | suspension | c. | Brownian
motion | g. | solute | d. | dispersion medium | h. | emulsion |
|
|
|
10.
|
inward force tending to minimize surface area of a liquid
|
|
|
11.
|
mixture in which particle size averages greater that 1000 nm in
diameter
|
|
|
12.
|
phenomenon observed when beam of light passes through a colloid
|
|
|
13.
|
colloid of a liquid in a liquid
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | Henry's law | d. | supersaturated solution | b. | immiscible | e. | concentration | c. | saturated
solution |
|
|
|
14.
|
solution containing maximum amount of solute
|
|
|
15.
|
At a given temperature, the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly
proportional to the pressure of the gas above the liquid.
|
Multiple Choice (Value 40)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
16.
|
Why does the pressure inside a container of gas increase if more gas is added to
the container?
a. | There is an increase in the number of collisions between particles and the walls of
the container. | b. | There is an increase in the temperature of the gas. | c. | There is a decrease
in the volume of the gas. | d. | There is an increase in the force of the
collisions between the particles and the walls of the container. |
|
|
|
17.
|
If a balloon is squeezed, what happens to the pressure of the gas inside the
balloon?
a. | It increases. | b. | It stays the same. | c. | It
decreases. | d. | The pressure depends on the type of gas in the
balloon. |
|
|
|
18.
|
What happens to the temperature of a gas when it is compressed?
a. | The temperature increases. | b. | The temperature does not
change. | c. | The temperature decreases. | d. | The temperature becomes
unpredictable. |
|
|
|
19.
|
As the temperature of the gas in a balloon decreases, which of the following
occurs?
a. | The volume of the balloon increases. | b. | The average kinetic energy of the gas
decreases. | c. | The gas pressure inside the balloon increases. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
20.
|
If 4 moles of gas are added to a container that already holds 1 mole of gas, how
will the pressure change inside the container?
a. | The pressure will be five times higher. | b. | The pressure will
double. | c. | The pressure will be four times higher. | d. | The pressure will
not change. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of these changes would NOT cause an increase in the pressure of a
contained gas?
a. | The volume of the container is increased. | b. | More of the gas is
added to the container. | c. | The temperature is
increased. | d. | The average kinetic energy of the gas in increased. |
|
|
|
22.
|
If a balloon is heated, what happens to the pressure of the air inside the
balloon if the volume remains constant?
a. | It increases. | c. | It decreases. | b. | It stays the same. | d. | The change cannot be
predicted. |
|
|
|
23.
|
What happens when a piston is used to decrease the volume of a contained
gas?
a. | Fewer gas particles exert a force on the piston. | b. | The piston’s
pressure on the gas becomes greater than the pressure exerted by the gas on the
piston. | c. | Gas particles become compressed. | d. | Gas particles leak out of the
container. |
|
|
|
24.
|
An ideal gas CANNOT be ____.
a. | condensed | c. | heated | b. | cooled | d. | compressed |
|
|
|
25.
|
If the atmospheric pressure on Mt. Everest is one-third the atmospheric pressure
at sea level, the partial pressure of oxygen on Everest is ____.
a. | one-sixth its pressure at sea level | c. | one-half its pressure at sea
level | b. | one-third its pressure at sea level | d. | equal to its pressure at sea
level |
|
|
|
26.
|
What happens to the partial pressure of oxygen in a sample of air if the
temperature is increased?
a. | It increases. | c. | It decreases. | b. | It stays the same. | d. | The change cannot be
determined. |
|
|
|
27.
|
If oxygen is removed from a sample of air as iron rusts, what happens to the
total pressure of the air?
a. | It increases. | c. | It decreases. | b. | It stays the same. | d. | The change cannot be
determined. |
|
|
|
28.
|
If the volume of a container of air is reduced by one-half, what happens to the
partial pressure of oxygen within the container?
a. | It is reduced by one-half. | c. | It is doubled. | b. | It does not
change. | d. | It is reduced by
one-fourth. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which of the following atoms would have the greatest velocity if each atom had
the same kinetic energy?
a. | bromine | c. | ammonia | b. | chlorine | d. | hydrogen |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following gases is the best choice for inflating a balloon that
must remain inflated for a long period of time?
a. | argon | c. | hydrogen | b. | oxygen | d. | neon |
|
|
|
31.
|
Which of the following is primarily responsible for holding water molecules
together in the liquid state?
a. | dispersion forces | c. | ionic bonds | b. | hydrogen bonds | d. | polar covalent
bonds |
|
|
|
32.
|
The fact that ice is less dense than water is related to the fact that
____.
a. | the molecular structure of ice is much less orderly than that of
water | b. | the molecules of ice are held to each other by covalent bonding | c. | ice has a molecular
structure in which water molecules are arranged randomly | d. | ice has a molecular
structure that is an open framework held together by hydrogen bonds |
|
|
|
33.
|
Which is responsible for the high thermal energy required to melt ice?
a. | covalent bonding | c. | hydrogen bonding | b. | dispersion forces | d. | ionic
attractions |
|
|
|
34.
|
What is the term for the dissolving medium in a solution?
a. | solvent | c. | solvator | b. | solute | d. | emulsifier |
|
|
|
35.
|
Which of the following substances dissolves most readily in gasoline?
a. | CH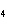 | c. | NH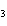 | b. | HCl | d. | NaBr |
|
|
|
36.
|
Predict which one of the following compounds would be insoluble in water.
a. | NaCl | c. | CF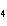 | b. | HCl | d. | CuSO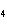 |
|
|
|
37.
|
Which of the following substances dissolves most readily in water?
|
|
|
38.
|
What type of compound is always an electrolyte?
a. | polar covalent | c. | ionic | b. | nonpolar covalent | d. | network solid |
|
|
|
39.
|
Which of the following is NOT a common hydrate?
a. | Epsom salt | c. | sugar | b. | borax | d. | alum |
|
|
|
40.
|
Which of the following mixture types is characterized by the settling of
particles?
a. | solution | c. | colloid | b. | suspension | d. | hydrate |
|
|
|
41.
|
Which of the following mixtures is NOT a colloid?
a. | fog | c. | paint | b. | milk | d. | sugar water |
|
|
|
42.
|
What is the size range of particles in a colloid?
a. | more than 1000 nm | c. | between 1 nm and 1000 nm | b. | between 100 nm and
1000 nm | d. | between 1 nm and 10
nm |
|
|
|
43.
|
Which of the following types of mixtures exhibit the Tyndall effect?
a. | suspensions and colloids | c. | colloids and
solutions | b. | suspensions and solutions | d. | colloids only |
|
|
|
44.
|
Which of the following usually makes a substance dissolve faster in a
solvent?
a. | agitating the solution | b. | increasing the particle size of the
solute | c. | lowering the temperature | d. | decreasing the number of
particles |
|
|
|
45.
|
What is the solubility of silver nitrate if only 11.1 g can dissolve in 5.0 g of
water at 20 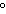 C?
|
|
|
46.
|
What happens to the solubility of a gas, in a liquid, if the partial pressure of
the gas above the liquid decreases?
a. | The solubility decreases. | c. | The solubility remains the
same. | b. | The solubility increases. | d. | The solubility cannot be determined. |
|
|
|
47.
|
What is the molarity of a solution that contains 6 moles of solute in 2 liters
of solution?
|
|
|
48.
|
In which of the following is the solution concentration expressed in terms of
molarity?
|
|
|
49.
|
What is the number of moles of solute in 250 mL of a 0.4M
solution?
a. | 0.1 mol | c. | 0.62 mol | b. | 0.16 mol | d. | 1.6 mol |
|
|
|
50.
|
What mass of Na 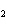 SO 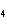 is needed
to make 2.5 L of 2.0 M solution? (Na = 23 g; S = 32 g; O = 16 g) a. | 178 g | c. | 356 g | b. | 284 g | d. | 710 g |
|
|
|
51.
|
What does NOT change when a solution is diluted by the addition of
solvent?
a. | volume of solvent | c. | number of moles of solute | b. | mass of
solvent | d. | molarity of
solution |
|
|
|
52.
|
How many mL of a 2.0M NaBr solution are needed to make 200.0 mL of
0.50M NaBr?
a. | 25 mL | c. | 100 mL | b. | 50 mL | d. | 150 mL |
|
|
|
53.
|
In which of the following is concentration expressed in percent by
volume?
a. | 10% (v/v) | c. | 10% (m/m) | b. | 10% (m/v) | d. | 10% |
|
|
|
54.
|
Which of the following is an expression of molality?
|
|
|
55.
|
To which of the following variables is change in boiling point directly
proportional?
a. | molarity of solution | c. | percent by volume of solution | b. | molality of
solution | d. | percent
(mass/mass) of solution |
|