Numeric Response (Value 5)
|
|
|
1.
|
Use the periodic table to determine the number of neutrons in
nitrogen-14.
|
|
|
2.
|
What is the relative charge of a proton?
|
|
|
3.
|
Use the periodic table to determine the number of electrons in a neutral atom of
lithium.
|
|
|
4.
|
Calculate the number of neutrons in 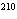 Pb.
|
|
|
5.
|
What is the atomic number for an element with 41 neutrons and a mass number of
80?
|
Matching (Value 10)
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | proton | d. | electron | b. | nucleus | e. | neutron | c. | atom |
|
|
|
6.
|
the central part of an atom, containing protons and neutrons
|
|
|
7.
|
a positively charged subatomic particle
|
|
|
8.
|
a subatomic particle with no charge
|
|
|
9.
|
the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that
element
|
|
|
10.
|
a negatively charged subatomic particle
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | mass number | d. | atomic mass | b. | atomic mass unit | e. | isotope | c. | atomic
number |
|
|
|
11.
|
the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of an element
|
|
|
12.
|
the number of protons in the nucleus of an element
|
|
|
13.
|
atoms with the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons in the
nucleus of an atom
|
|
|
14.
|
one-twelfth the mass of a carbon atom having six protons and six
neutrons
|
|
|
15.
|
the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
|
Multiple Choice (Value 25)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
16.
|
The comparison of the number of atoms in a copper coin the size of a penny with
the number of people on Earth is made to illustrate which of the following?
a. | that atoms are indivisible | b. | that atoms are very small | c. | that atoms are very
large | d. | that in a copper penny, there is one atom for every person on
Earth |
|
|
|
17.
|
The atomic number of an element is the total number of which particles in the
nucleus?
a. | neutrons | c. | electrons | b. | protons | d. | protons and
electrons |
|
|
|
18.
|
All atoms are ____.
a. | positively charged, with the number of protons exceeding the number of
electrons | b. | negatively charged, with the number of electrons exceeding the number of
protons | c. | neutral, with the number of protons equaling the number of
electrons | d. | neutral, with the number of protons equaling the number of electrons, which is equal
to the number of neutrons |
|
|
|
19.
|
If E is the symbol for an element, which two of the following symbols represent
isotopes of the same element? a. | 1 and 2 | c. | 1 and 4 | b. | 3 and 4 | d. | 2 and 3 |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which of the following is necessary to calculate the atomic mass of an
element?
a. | the atomic mass of carbon-12 | b. | the atomic number of the
element | c. | the relative masses of the element’s protons and neutrons | d. | the masses of each
isotope of the element |
|
|
|
21.
|
Select the correct symbol for an atom of tritium.
|
|
|
22.
|
How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated?
a. | Add the number of electrons and protons together. | b. | Subtract the number
of electrons from the number of protons. | c. | Subtract the number of protons from the mass
number. | d. | Add the mass number to the number of electrons. |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which hypothesis led to the discovery of the proton?
a. | When a neutral hydrogen atom loses an electron, a positively-charged particle should
remain. | b. | A proton should be 1840 times heavier than an electron. | c. | Cathode rays should
be attracted to a positively-charged plate. | d. | The nucleus of an atom should contain
neutrons. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following is correct concerning subatomic particles?
a. | The electron was discovered by Goldstein in 1886. | b. | The neutron was
discovered by Chadwick in 1932. | c. | The proton was discovered by Thomson in
1880. | d. | Cathode rays were found to be made of protons. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following was NOT among Democritus’s ideas?
a. | Matter consists of tiny particles called atoms. | b. | Atoms are
indivisible. | c. | Atoms retain their identity in a chemical reaction. | d. | Atoms are
indestructible. |
|
|
|
26.
|
Why do chemists use relative masses of atoms compared to a reference isotope
rather than the actual masses of the atoms?
a. | The actual mass of an electron is very large compared to the actual mass of a
proton. | b. | The actual masses of atoms are very small and difficult to work
with. | c. | The number of subatomic particles in atoms of different elements
varies. | d. | The actual masses of protons, electrons, and neutrons are not
known. |
|
|
|
27.
|
What does the number 84 in the name krypton-84 represent?
a. | the atomic number | c. | the sum of the protons and electrons | b. | the mass
number | d. | twice the number of
protons |
|
|
|
28.
|
Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 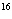 O.
|
|
|
29.
|
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
a. | Atoms of the same element can have different masses. | b. | Atoms of isotopes of
an element have different numbers of protons. | c. | The nucleus of an atom has a positive
charge. | d. | Atoms are mostly empty space. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Dalton hypothesized that atoms are indivisible and that all atoms of an element
are identical. It is now known that ____.
a. | all of Dalton's hypotheses are correct | b. | atoms of an element
can have different numbers of protons | c. | atoms are divisible | d. | all atoms of an
element are not identical but they must all have the same mass |
|
|
|
31.
|
Which of the following is NOT a part of Dalton's atomic theory?
a. | All elements are composed of atoms. | b. | Atoms are always in motion. | c. | Atoms of the same
element are identical. | d. | Atoms that combine do so in simple whole-number
ratios. |
|
|
|
32.
|
Who was the man who lived from 460B.C.–370B.C. and was among the first to
suggest the idea of atoms?
a. | Atomos | c. | Democritus | b. | Dalton | d. | Thomson |
|
|
|
33.
|
The atomic mass of an element depends upon the ____.
a. | mass of each electron in that element | b. | mass of each isotope of that
element | c. | relative abundance of protons in that element | d. | mass and relative
abundance of each isotope of that element |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which of the following equals one atomic mass unit?
a. | the mass of one electron | b. | the mass of one helium-4
atom | c. | the mass of one carbon-12 atom | d. | one-twelfth the mass of one carbon-12
atom |
|
|
|
35.
|
In which of the following sets is the symbol of the element, the number of
protons, and the number of electrons given correctly?
a. | In, 49 protons, 49 electrons | c. | Cs, 55 protons, 132.9
electrons | b. | Zn, 30 protons, 60 electrons | d. | F, 19 protons, 19
electrons |
|
|
|
36.
|
Why did J. J. Thomson reason that electrons must be a part of the atoms of all
elements?
a. | Cathode rays are negatively-charged particles. | b. | Cathode rays can be
deflected by magnets. | c. | An electron is 2000 times lighter than a
hydrogen atom. | d. | Charge-to-mass ratio of electrons was the same, regardless of the gas
used. |
|
|
|
37.
|
Dalton's atomic theory included which idea?
a. | All atoms of all elements are the same size. | b. | Atoms of different
elements always combine in one-to-one ratios. | c. | Atoms of the same element are always
identical. | d. | Individual atoms can be seen with a microscope. |
|
|
|
38.
|
What is the relative mass of an electron?
a. | 1/1840 the mass of a hydrogen atom | c. | 1/1840 the mass of a C-12
atom | b. | 1/1840 the mass of a neutron + proton | d. | 1/1840 the mass of an alpha
particle |
|
|
|
39.
|
How many protons, electrons, and neutrons does an atom with atomic number 50 and
mass number 125 contain?
a. | 50 protons, 50 electrons, 75 neutrons | c. | 120 neutrons, 50 protons, 75
electrons | b. | 75 electrons, 50 protons, 50 neutrons | d. | 70 neutrons, 75 protons, 50
electrons |
|
|
|
40.
|
The range in size of most atomic radii is approximately ____.
|