Matching (Value 14)
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | solvation | e. | electrolyte | b. | weak electrolyte | f. | colloid | c. | aqueous
solution | g. | surfactant | d. | solvent |
|
|
|
1.
|
interferes with hydrogen bonding between water molecules
|
|
|
2.
|
dissolving medium
|
|
|
3.
|
homogeneous mixture of water and dissolved substances
|
|
|
4.
|
Solute ions or molecules are surrounded by solvent molecules.
|
|
|
5.
|
compound that will conduct current in the liquid state or in aqueous
solution
|
|
|
6.
|
compound that ionizes incompletely in aqueous solution
|
|
|
7.
|
mixture in which particle size averages between 1 nm and 1000 nm
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | dispersed phase | e. | Tyndall effect | b. | surface tension | f. | suspension | c. | Brownian
motion | g. | solute | d. | dispersion medium | h. | emulsion |
|
|
|
8.
|
inward force tending to minimize surface area of a liquid
|
|
|
9.
|
dissolved particle
|
|
|
10.
|
mixture in which particle size averages greater that 1000 nm in
diameter
|
|
|
11.
|
Colloidal particles spread throughout a suspension.
|
|
|
12.
|
phenomenon observed when beam of light passes through a colloid
|
|
|
13.
|
chaotic movement of colloidal particles
|
|
|
14.
|
colloid of a liquid in a liquid
|
Multiple Choice (Value 25)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
15.
|
How does the surface tension of water compare with the surface tensions of most
other liquids?
a. | It is lower. | b. | It is about the same. | c. | It is
higher. | d. | It is higher when a surfactant is added. |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which of the following is primarily responsible for holding water molecules
together in the liquid state?
a. | dispersion forces | c. | ionic bonds | b. | hydrogen bonds | d. | polar covalent
bonds |
|
|
|
17.
|
What is primarily responsible for the surface tension of water?
a. | dispersion forces | c. | ionic attractions | b. | hydrogen bonding | d. | covalent
bonding |
|
|
|
18.
|
Surface tension ____.
a. | is the inward force which tends to minimize the surface area of a
liquid | b. | may be increased by detergents | c. | is decreased by hydrogen
bonding | d. | causes beads of water to spread out |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which is responsible for the high thermal energy required to melt ice?
a. | covalent bonding | c. | hydrogen bonding | b. | dispersion forces | d. | ionic
attractions |
|
|
|
20.
|
What is the term for the dissolving medium in a solution?
a. | solvent | c. | solvator | b. | solute | d. | emulsifier |
|
|
|
21.
|
A solution has which of the following properties?
a. | Gravity separates its parts. | b. | The top layer is different in composition than
the bottom layer. | c. | The average diameter of its solute particles
usually is less than 1 nm. | d. | A filter can remove the
solute. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which of the following substances dissolves most readily in gasoline?
a. | CH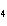 | c. | NH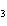 | b. | HCl | d. | NaBr |
|
|
|
23.
|
A solution is a mixture ____.
a. | from which the solute can be filtered | b. | that has the same properties
throughout | c. | that is heterogeneous | d. | in which a solid solute is always dissolved in
a liquid solvent |
|
|
|
24.
|
Why are two nonpolar substances able to dissolve in each other?
a. | They have similar attractive forces in their molecules. | b. | They combine to
produce a polar substance. | c. | There is no attractive force between
them. | d. | Nonpolar substances cannot dissolve in each other. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following substances dissolves most readily in water?
|
|
|
26.
|
What type of compound is always an electrolyte?
a. | polar covalent | c. | ionic | b. | nonpolar covalent | d. | network solid |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which of the following compounds conducts electricity only in the molten
state?
a. | sodium bromide | c. | calcium hydroxide | b. | magnesium sulfate | d. | barium sulfate |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which of the following compounds is an electrolyte?
a. | rubbing alcohol | c. | carbon tetrachloride | b. | sugar | d. | sodium
hydroxide |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which of the following compounds is a nonelectrolyte when pure, but an
electrolyte when dissolved in water?
a. | rubbing alcohol | c. | carbon tetrachloride | b. | sugar | d. | ammonia |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following are weak electrolytes in water?
a. | ionic compounds that partially dissociate in water | b. | ionic compounds that
are soluble | c. | polar compounds that ionize | d. | nonpolar compounds that do not
ionize |
|
|
|
31.
|
Which of the following compounds is a weak electrolyte?
a. | NaBr | c. | KOH | b. | HBr | d. | NH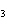 |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which of the following is NOT a common hydrate?
a. | Epsom salt | c. | sugar | b. | borax | d. | alum |
|
|
|
33.
|
Which symbol is used to connect the formula of the compound with the number of
water molecules in a hydrate?
a. | a parenthesis | c. | a multiplication symbol | b. | an
asterisk | d. | a
dot |
|
|
|
34.
|
What is another term for the water of hydration?
a. | water of solvation | c. | water of sublimation | b. | water of crystallization | d. | water of
efflorescence |
|
|
|
35.
|
Which of the following mixture types is characterized by the settling of
particles?
a. | solution | c. | colloid | b. | suspension | d. | hydrate |
|
|
|
36.
|
Which of the following mixture types can be filtered to remove solute?
a. | suspensions only | c. | suspensions and colloids | b. | colloids
only | d. | suspensions and
solutions |
|
|
|
37.
|
Which of the following materials is NOT a colloid?
a. | glue | c. | smoke | b. | alloy | d. | muddy water |
|
|
|
38.
|
Which of the following mixtures is NOT a colloid?
a. | fog | c. | paint | b. | milk | d. | sugar water |
|
|
|
39.
|
What is the size range of particles in a colloid?
a. | more than 1000 nm | c. | between 1 nm and 1000 nm | b. | between 100 nm and
1000 nm | d. | between 1 nm and 10
nm |
|
Numeric Response (Value 1)
|
|
|
40.
|
How many nonbonding pairs of electrons are in a water molecule?
|