Matching (Value 14)
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | dispersed phase | e. | Tyndall effect | b. | surface tension | f. | suspension | c. | Brownian
motion | g. | solute | d. | dispersion medium | h. | emulsion |
|
|
|
1.
|
Colloidal particles spread throughout a suspension.
|
|
|
2.
|
dissolved particle
|
|
|
3.
|
colloid of a liquid in a liquid
|
|
|
4.
|
inward force tending to minimize surface area of a liquid
|
|
|
5.
|
phenomenon observed when beam of light passes through a colloid
|
|
|
6.
|
mixture in which particle size averages greater that 1000 nm in
diameter
|
|
|
7.
|
chaotic movement of colloidal particles
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | solvation | e. | electrolyte | b. | weak electrolyte | f. | colloid | c. | aqueous
solution | g. | surfactant | d. | solvent |
|
|
|
8.
|
mixture in which particle size averages between 1 nm and 1000 nm
|
|
|
9.
|
compound that will conduct current in the liquid state or in aqueous
solution
|
|
|
10.
|
Solute ions or molecules are surrounded by solvent molecules.
|
|
|
11.
|
interferes with hydrogen bonding between water molecules
|
|
|
12.
|
dissolving medium
|
|
|
13.
|
compound that ionizes incompletely in aqueous solution
|
|
|
14.
|
homogeneous mixture of water and dissolved substances
|
Multiple Choice (Value 30) + 1 bonus
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
15.
|
Which symbol is used to connect the formula of the compound with the number of
water molecules in a hydrate?
a. | a dot | c. | a multiplication symbol | b. | an
asterisk | d. | a
parenthesis |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which of the following substances is the most soluble in water?
a. | carbon | c. | sodium chloride | b. | methane | d. | bromine |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following types of mixtures exhibit the Tyndall effect?
a. | suspensions and solutions | c. | colloids and
solutions | b. | suspensions and colloids | d. | colloids only |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of these would you expect to be soluble in the nonpolar solvent
carbon disulfide, CS 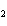 ? Hint: We talked about this compound in
class.
|
|
|
19.
|
Which compound changes color when it becomes a hydrate?
a. | potassium chloride | c. | sodium chloride | b. | copper(II) sulfate | d. | silicon dioxide |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which of the following is primarily responsible for holding water molecules
together in the liquid state?
a. | polar covalent bonds | c. | hydrogen bonds | b. | dispersion forces | d. | ionic bonds |
|
|
|
21.
|
What type of compound is always an electrolyte?
a. | ionic | c. | network solid | b. | nonpolar covalent | d. | polar covalent |
|
|
|
22.
|
The fact that ice is less dense than water is related to the fact that
____.
a. | the molecular structure of ice is much less orderly than that of
water | b. | ice has a molecular structure that is an open framework held together by hydrogen
bonds | c. | ice has a molecular structure in which water molecules are arranged
randomly | d. | the molecules of ice are held to each other by covalent
bonding |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the following mixtures is NOT a colloid?
a. | sugar water | c. | fog | b. | milk | d. | paint |
|
|
|
24.
|
What is the shape of the water molecule?
a. | linear | c. | trigonal planar | b. | bent | d. | tetrahedral |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following compounds is a nonelectrolyte?
a. | copper chloride | c. | sodium bromide | b. | carbon tetrachloride | d. | magnesium
sulfate |
|
|
|
26.
|
How does the surface tension of water compare with the surface tensions of most
other liquids?
a. | It is higher when a surfactant is added. | b. | It is about the
same. | c. | It is higher. | d. | It is lower. |
|
|
|
27.
|
What occurs in solvation?
a. | Solvent molecules surround solute ions. | b. | Solute ions separate
from solvent molecules. | c. | Ionic compounds are formed. | d. | Solvent molecules
bind covalently to solute molecules. |
|
|
|
28.
|
An emulsion is a colloidal dispersion of a ____.
a. | solid in a liquid | c. | liquid in a gas | b. | liquid in a liquid | d. | gas in a liquid |
|
|
|
29.
|
What is the size range of particles in a colloid?
a. | between 100 nm and 1000 nm | c. | more than 1000
nm | b. | between 1 nm and 10 nm | d. | between 1 nm and 1000 nm |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following compounds is a strong electrolyte?
a. | acetic acid | c. | potassium sulfate | b. | sugar | d. | ammonia |
|
|
|
31.
|
A crystal that absorbs water vapor from the air is ____.
a. | deliquescent | c. | hygroscopic | b. | efflorescent | d. | aqueous |
|
|
|
32.
|
An emulsifying agent is typically characterized by having ____.
a. | two polar ends | c. | one nonpolar end | b. | one polar end and one nonpolar
end | d. | one polar
end |
|
|
|
33.
|
Predict which one of the following compounds would be insoluble in water.
a. | NaCl | c. | CF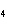 | b. | HCl | d. | CuSO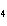 |
|
|
|
34.
|
The bonds between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms in a water molecule are
____.
a. | polar covalent bonds | c. | hydrogen bonds | b. | nonpolar covalent bonds | d. | ionic bonds |
|
|
|
35.
|
Which of the following substances dissolves most readily in gasoline?
a. | CH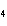 | c. | NaBr | b. | HCl | d. | NH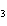 |
|
|
|
36.
|
An electric current can be conducted by ____.
a. | methane gas | c. | rubbing alcohol | b. | a salt solution | d. | a sugar
solution |
|
|
|
37.
|
Why are two nonpolar substances able to dissolve in each other?
a. | They combine to produce a polar substance. | b. | Nonpolar substances
cannot dissolve in each other. | c. | There is no attractive force between
them. | d. | They have similar attractive forces in their
molecules. |
|
|
|
38.
|
Which atom in a water molecule has the greatest electronegativity?
a. | There is no difference in the electronegativities of the atoms in a water
molecule. | b. | both hydrogen atoms | c. | the oxygen atom | d. | one of the hydrogen
atoms |
|
|
|
39.
|
A solution has which of the following properties?
a. | Gravity separates its parts. | b. | The average diameter of its solute particles
usually is less than 1 nm. | c. | The top layer is different in composition than
the bottom layer. | d. | A filter can remove the
solute. |
|
|
|
40.
|
What is the term for the dissolving medium in a solution?
a. | emulsifier | c. | solute | b. | solvent | d. | solvator |
|
|
|
41.
|
The bonds between adjacent water molecules are called ____.
a. | nonpolar covalent bonds | c. | ionic bonds | b. | hydrogen
bonds | d. | polar covalent
bonds |
|
|
|
42.
|
Which of the following mixture types can be filtered to remove solute?
a. | suspensions and colloids | c. | suspensions and
solutions | b. | suspensions only | d. | colloids only |
|
|
|
43.
|
Surface tension ____.
a. | is the inward force which tends to minimize the surface area of a
liquid | b. | is decreased by hydrogen bonding | c. | causes beads of water to spread
out | d. | may be increased by detergents |
|
|
|
44.
|
The solute in a colloidal suspension is called the ____.
a. | dispensing phase | c. | dispersed phase | b. | dissolving phase | d. | dispersion
medium |
|
|
|
45.
|
Which of the following mixture types is characterized by the settling of
particles?
a. | colloid | c. | suspension | b. | hydrate | d. | solution |
|
Numeric Response (Value 6)
|
|
|
46.
|
If 125 grams of Magnesium Sulfate heptahydrate is completely dehydrated, how
many grams of anhydrous magnesium sulfate will remain?
|
|
|
47.
|
How many hydrogen bonds can be formed between one hydrogen atom in a water
molecule and oxygen atoms of surrounding water molecules? (Value 1)
|
|
|
48.
|
How many nonbonding pairs of electrons are in a water molecule? (Value 1)
|
|
|
49.
|
How many phases are present in a colloid? (Value 1)
|