Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The endocrine system is made up of
a. | hormones. | c. | gonads. | b. | glands. | d. | prostaglandins. |
|
|
|
2.
|
The nervous system is to a telephone as the endocrine system is to a
a. | chemical message. | c. | radio broadcast. | b. | television set. | d. | hormone. |
|
|
|
3.
|
The endocrine system
a. | affects only the reproductive system. | b. | releases hormones into the
bloodstream. | c. | competes with the nervous system. | d. | is made up primarily of glands with
ducts. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Which of the following is a gland of the endocrine system?
a. | sweat gland | c. | pituitary gland | b. | tear gland | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
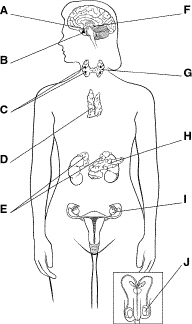
Figure
39–1
|
|
|
5.
|
Figure 39–1 shows the body’s
a. | hormones. | c. | endocrine glands. | b. | target cells. | d. | exocrine
glands. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which structure in Figure 39–1 regulates the level of calcium in the
blood?
|
|
|
7.
|
What is the function of the structure labeled H in Figure 39–1?
a. | to produce sex hormones | c. | to produce insulin and
glucagon | b. | to produce thyroxine | d. | to produce thymosin |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which structure in Figure 39–1 releases hormones that regulate many of the
other endocrine glands?
|
|
|
9.
|
Unlike endocrine glands, exocrine glands
a. | release secretions through ducts. | b. | release hormones. | c. | release secretions
directly into the bloodstream. | d. | are found throughout the
body. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Unlike nonsteroid hormones, steroid hormones
a. | remain outside the target cell. | c. | have no target
cells. | b. | bind to receptors inside the target cell. | d. | are made of
proteins. |
|
|
|
11.
|
A thermostat is a good example of a(an)
a. | hormone-receptor complex. | c. | prostaglandin. | b. | feedback
system. | d. | exocrine
gland. |
|
|
|
12.
|
One way the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis is by having
a. | each gland secrete only one hormone. | b. | two hormones with opposite effects regulate
certain things. | c. | only steroid hormones regulate important functions. | d. | the pituitary gland
regulate all the other glands. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Feedback inhibition means that an increase in a substance will
a. | decrease production of that substance. | b. | increase production of that
substance. | c. | increase the production of other substances. | d. | stop production of
another substance. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which endocrine gland secretes sex hormones?
a. | adrenal medulla | c. | hypothalamus | b. | testis | d. | pituitary |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which gland fails to produce enough of its hormone in the disease diabetes
mellitus?
a. | adrenal | c. | pancreas | b. | hypothalamus | d. | parathyroid |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which gland produces epinephrine and norepinephrine?
a. | parathyroid | c. | pituitary | b. | hypothalamus | d. | adrenal |
|
|
|
17.
|
Puberty usually begins between the ages of
a. | 5 and 8. | c. | 16 and 19. | b. | 9 and 15. | d. | 20 and 25. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which hormones stimulate the gonads to mature?
a. | FSH and LH | c. | androgens | b. | estrogens | d. | testosterone and
progesterone |
|
|
|
19.
|
The testes and the ovaries do not begin making active reproductive cells
until
a. | birth. | c. | gastrulation. | b. | fertilization. | d. | puberty. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Testosterone is needed for the development of
a. | eggs. | c. | the uterus. | b. | sperm. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
21.
|
Specialized sex cells are known as
a. | gametes. | c. | gonads. | b. | hormones. | d. | organs. |
|
|
|
22.
|
How many ova do the ovaries usually produce?
a. | one per day | c. | one between them each month | b. | about 20 per
year | d. | 200 million at a
time |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which structure produces sperm?
a. | scrotum | c. | seminiferous tubules | b. | epididymis | d. | vas deferens |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following is NOT a function of the female reproductive
system?
a. | to produce eggs | b. | to prepare the body to carry an
embryo | c. | to deliver sperm | d. | to release eggs into the Fallopian
tubes |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which organ system is responsible for making and delivering sperm?
a. | female reproductive system | c. | nervous system | b. | endocrine
system | d. | male reproductive
system |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which of the following is NOT a phase in the menstrual cycle?
a. | menstruation | c. | fertilization | b. | luteal | d. | ovulation |
|
|
|
27.
|
When during the menstrual cycle does an egg have the best chance of being
fertilized?
a. | during the follicular phase | c. | the beginning of the luteal
phase | b. | just before menstruation | d. | the day of ovulation |
|
|
|
28.
|
One menstrual cycle usually lasts about a
a. | day. | c. | month. | b. | week. | d. | year. |
|
|
|
29.
|
During the menstrual cycle, LH and FSH peak, causing the
a. | corpus luteum to disintegrate. | b. | follicle to release a mature
egg. | c. | uterine lining to detach from the uterus. | d. | the lining of the
uterus to thicken. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Menstruation does not occur if the
a. | uterine lining thickens. | c. | progesterone level
falls. | b. | estrogen level falls. | d. | egg is fertilized. |
|
|
|
31.
|
A zygote is a
a. | two-celled embryo. | c. | blastocyst. | b. | solid ball of about 50
cells. | d. | fertilized
egg. |
|
|
|
32.
|
The chances of fertilization are very good if sperm are present and a(an)
a. | blastocyst is already present. | c. | woman is
menstruating. | b. | egg is in the Fallopian tubes. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
33.
|
Which of the following are required for fertilization to occur inside the female
body?
a. | Sperm must swim into a Fallopian tube. | b. | An egg must be present in the Fallopian
tube. | c. | The nucleus of a sperm must enter an egg cell. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
34.
|
During the process of fertilization, which step happens first?
a. | The sperm’s nucleus enters the egg cell. | b. | Enzymes break down
the protective layer of the egg cell membrane. | c. | A sperm attaches to a binding site on the egg
cell membrane. | d. | The cell membrane of the egg cell changes. |
|
|
|
35.
|
Where does fertilization usually occur?
a. | Fallopian tube | c. | uterus | b. | ovary | d. | vagina |
|
|
|
36.
|
What is the result of gastrulation?
a. | a blastocyst | c. | the amnion | b. | a zygote | d. | germ layers |
|
|
|
37.
|
Which of the following forms during gastrulation?
a. | endoderm | c. | mesoderm | b. | ectoderm | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
38.
|
Which of the following processes happens last?
a. | gastrulation | c. | fertilization | b. | implantation | d. | ovulation |
|
|
|
39.
|
Which of the following is a function of the placenta?
a. | mixing the blood of the mother and the fetus | b. | protecting the fetus
from any drugs or alcohol in the mother’s body | c. | providing nutrients to the
fetus | d. | cushioning and protecting the fetus |
|
|
|
40.
|
The placenta connects the
a. | fetus to the mother’s uterus. | c. | umbilical cord to the
mother’s vagina. | b. | ectoderm to the endoderm. | d. | uterus to the
cervix. |
|
|
|
41.
|
If a woman is exposed to HIV during her pregnancy, the
a. | placenta will protect the fetus from the HIV viruses. | b. | HIV viruses can
cross the placenta and harm the fetus. | c. | HIV viruses could harm the
placenta. | d. | fetus will probably recover quickly from the disease. |
|
|
|
42.
|
Which of the following is characteristic of infancy?
a. | Teeth appear. | b. | Puberty begins. | c. | The first signs of
aging appear. | d. | An individual reaches 70 percent of her or his adult
height. |
|
|
|
43.
|
Which stage of the human life cycle occurs first?
a. | puberty | c. | adolescence | b. | adulthood | d. | childhood |
|
|
|
44.
|
Which of the following usually develop(s) during childhood?
a. | personality | b. | social skills | c. | long bones, to 80
percent of adult height | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
45.
|
All of the following usually occur during adolescence EXCEPT
a. | a growth spurt. | b. | secondary sex
characteristics. | c. | puberty. | d. | the appearance of first permanent
teeth. |
|
Modified True/False
Indicate
whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
the statement true.
|
|
|
46.
|
The endocrine system carries out its job by releasing target cells into
the bloodstream. _________________________
|
|
|
47.
|
Exocrine glands release their secretions into the bloodstream.
_________________________
|
|
|
48.
|
A nonsteroid hormone enters a target cell by passing across its cell
membrane. _________________________
|
|
|
49.
|
Thyroxine inhibits the secretion of TSH by the anterior pituitary gland,
which maintains homeostasis. _________________________
|
|
|
50.
|
The parathyroid glands secrete hormones that help the body deal with
stress. ______________________________
|
|
|
51.
|
The highest level of physical strength and development occurs during
adolescence. _________________________
|
|
|
52.
|
If a person’s thyroid gland is removed surgically and hormone
supplements are not taken, the person will probably lack energy, feel cold, and gain weight.
_________________________
|
|
|
53.
|
During puberty the reproductive system becomes fully functional.
_________________________
|
|
|
54.
|
The male reproductive system and the female reproductive system develop from
the same tissues in the embryo. _________________________
|
|
|
55.
|
A female is born with immature eggs and does not produce any new eggs
during her lifetime. _________________________
|
|
|
56.
|
In a 28-day menstrual cycle, menstruation usually begins on the 14th day
of the menstrual cycle. _________________________
|
|
|
57.
|
The process of a sperm joining an egg is called gastrulation.
_________________________
|
|
|
58.
|
If the primary germ layers fail to form normally during gastrulation, the
embryo could develop misshapen organs. _________________________
|
|
|
59.
|
If the placenta were to detach from the mother’s uterus early, the
embryo would stop receiving food and oxygen. _________________________
|
|
|
60.
|
Infancy ends at about two years of age. _________________________
|
Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
61.
|
The ____________________ system is made up of glands that release their products
into the ____________________.
|
|
|
62.
|
____________________ are chemicals that travel through the bloodstream and
affect the activities of other cells.
|
|
|
63.
|
Feedback ____________________ occurs when an increase in any substance inhibits
the process that produced the substance.
|
|
|

Figure
39–1
|
|
|
64.
|
If the structure labeled ____________________ in Figure 39–1 produces too
much of its hormone, the result is nervousness, elevated body temperature, and weight loss.
|
|
|
65.
|
If a child’s diet lacks iodine, the ____________________ gland cannot
produce its hormone and the child is likely to develop a condition called
____________________.
|
|
|
66.
|
____________________ is a period of rapid growth and sexual maturation during
which the reproductive system becomes fully functional.
|
|
|
67.
|
In the female body, each egg is surrounded by a ____________________, which
breaks open when the egg is mature.
|
|
|
68.
|
If the temperature of the scrotum increases by 5º Celsius,
____________________ may not develop properly.
|
|
|
69.
|
The shortest phase of the menstrual cycle is ____________________.
|
|
|
70.
|
The testes are contained in an external sac called the
_________________________.
|
|
|
71.
|
If a woman is not ovulating, there is no chance of ____________________.
|
|
|
72.
|
During ____________________, three germ layers form. They are called
____________________, ectoderm, and mesoderm.
|
|
|
73.
|
Almost everything that the mother takes into her body passes through the
____________________ to the embryo.
|
|
|
74.
|
The placenta is the connection between the ____________________ and the
developing fetus.
|
|
|
75.
|
The life cycle after birth is as follows: infancy, ____________________,
adolescence, and ____________________.
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
76.
|
How do the nervous and endocrine systems differ in the way they help to maintain
homeostasis?
|
|
|
77.
|
Compare endocrine glands and exocrine glands. Give an example of each kind of
gland.
|
|
|
78.
|
What determines whether a human embryo will develop into a male or a
female?
|
|
|
79.
|
List the three germ layers that result from gastrulation.
|
|
|
80.
|
Name and describe one of the four stages that follow birth.
|