Multiple Choice (Value 35)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Avery’s experiments showed that bacteria are transformed by
a. | RNA. | c. | proteins. | b. | DNA. | d. | carbohydrates. |
|
|
|
2.
|
What did Griffith observe when he injected a mixture of heat-killed,
disease-causing bacteria and live harmless bacteria into mice?
a. | The disease-causing bacteria changed into harmless bacteria. | b. | The mice developed
pneumonia. | c. | The harmless bacteria died. | d. | The mice were
unaffected. |
|
|
|

Figure
12–1
|
|
|
3.
|
Figure 12–1 shows the structure of a(an)
a. | DNA molecule. | c. | RNA molecule. | b. | amino acid. | d. | protein. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Which of the following is a nucleotide found in DNA?
a. | ribose + phosphate group + thymine | b. | ribose + phosphate group +
uracil | c. | deoxyribose + phosphate group + uracil | d. | deoxyribose + phosphate group +
cytosine |
|
|
|
5.
|
Because of base pairing in DNA, the percentage of
a. | adenine molecules in DNA is about equal to the percentage of guanine
molecules. | b. | pyrimidines in DNA is about equal to the percentage of purines. | c. | purines in DNA is
much greater than the percentage of pyrimidines. | d. | cytosine molecules in DNA is much greater than
the percentage of guanine molecules. |
|
|
|
6.
|
In eukaryotes, DNA
a. | is located in the nucleus. | c. | is located in the
ribosomes. | b. | floats freely in the cytoplasm. | d. | is circular. |
|
|
|
7.
|
During mitosis, the
a. | DNA molecules unwind. | b. | histones and DNA molecules
separate. | c. | DNA polymerase makes copies of DNA strands. | d. | nucleosomes become
more tightly packed. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which of the following include all the others?
a. | DNA molecules | c. | chromosomes | b. | histones | d. | nucleosomes |
|
|
|
9.
|
DNA replication results in two DNA molecules,
a. | each with two new strands. | b. | one with two new strands and the other with two
original strands. | c. | each with one new strand and one original
strand. | d. | each with two original strands. |
|
|
|
10.
|
During DNA replication, a DNA strand that has the bases CTAGGT produces a strand
with the bases
a. | TCGAAC. | c. | AGCTTG. | b. | GATCCA. | d. | GAUCCA. |
|
|
|
11.
|
RNA contains the sugar
a. | ribose. | c. | glucose. | b. | deoxyribose. | d. | lactose. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which of the following are found in both DNA and RNA?
a. | ribose, phosphate groups, and adenine | b. | deoxyribose, phosphate groups, and
guanine | c. | phosphate groups, guanine, and cytosine | d. | phosphate groups,
guanine, and thymine |
|
|
|
13.
|
How many main types of RNA are there?
a. | 1 | c. | hundreds | b. | 3 | d. | thousands |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which type(s) of RNA is(are) involved in protein synthesis?
a. | transfer RNA only | b. | messenger RNA only | c. | ribosomal RNA and
transfer RNA only | d. | messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer
RNA |
|
|
|
15.
|
What is produced during transcription?
a. | RNA molecules | c. | RNA polymerase | b. | DNA molecules | d. | proteins |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which of the following statements is true?
a. | A promoter is part of an intron. | b. | A pre-mRNA molecule is longer than the gene
from which the molecule was transcribed. | c. | Introns are sequences of
DNA. | d. | Any mRNA molecules made from the same gene are always edited the same
way. |
|
|
|
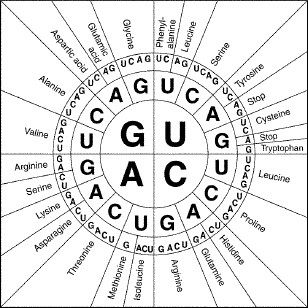
Figure
12–2
|
|
|
17.
|
What does Figure 12–2 show?
a. | anticodons | b. | the order in which amino acids are
linked | c. | the code for splicing mRNA | d. | the genetic
code |
|
|
|
18.
|
How many bases are needed to specify three amino acids?
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following terms is LEAST closely related to the others?
a. | spindle fiber | c. | polypeptide | b. | tRNA | d. | anticodon |
|
|
|
20.
|
During translation, the type of amino acid that is added to the growing
polypeptide depends on the
a. | codon on the mRNA only. | b. | anticodon on the mRNA only. | c. | anticodon on the
tRNA to which the amino acid is attached only. | d. | codon on the mRNA and the anticodon on the tRNA
to which the amino acid is attached. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Genes contain instructions for assembling
a. | purines. | c. | proteins. | b. | nucleosomes. | d. | pyrimidines. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which type of RNA functions as a blueprint of the genetic code?
a. | rRNA | c. | mRNA | b. | tRNA | d. | RNA polymerase |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the following statements is false?
a. | Some genes code for enzymes. | b. | The instructions for making some proteins are
not specified by genes. | c. | An organism’s inherited traits depend on
proteins. | d. | An organism’s genes determine its inherited
traits. |
|
|
|
24.
|
A mutation that involves one or a few nucleotides is called a(an)
a. | chromosomal mutation. | c. | point mutation. | b. | inversion. | d. | translocation. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following statements is true?
a. | A promoter determines whether a gene is expressed. | b. | An expressed gene is
turned off. | c. | Proteins that bind to regulatory sites on DNA determine whether a gene is
expressed. | d. | RNA polymerase regulates gene expression. |
|
|
|
26.
|
If a specific kind of protein is not continually used by a cell, the gene for
that protein is
a. | always transcribed. | c. | turned on and off at different times. | b. | never
expressed. | d. | not
regulated. |
|
|
|
27.
|
In E. coli, the lac operon controls the
a. | breakdown of lactose. | c. | breakdown of glucose. | b. | production of
lactose. | d. | production of
glucose. |
|
|
|
28.
|
A lac repressor turns off the lac genes by
a. | binding to the promoter. | c. | binding to the
operator. | b. | DNA polymerase. | d. | binding to the lac genes. |
|
|
|
29.
|
When E. coli is grown on glucose,
a. | lactose molecules bind to the lac repressor. | b. | the lac
repressor binds to the operator of the lac operon. | c. | RNA polymerase binds
to the promoter of the lac operon. | d. | the lac genes are
transcribed. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following is NOT generally part of a eukaryotic gene?
a. | operon | c. | promoter sequences | b. | TATA box | d. | enhancer
sequences |
|
|
|
31.
|
Gene regulation in eukaryotes
a. | usually involves operons. | b. | is simpler than in
prokaryotes. | c. | allows for cell specialization. | d. | includes the action of an operator
region. |
|
|
|
32.
|
Specialized cells regulate the expression of genes because they
a. | do not want the genes to become worn out. | b. | cannot control
translation. | c. | do not carry the complete genetic code in their nuclei. | d. | do not need the
proteins that are specified by certain genes. |
|
|
|
33.
|
Hox genes determine an animal’s
a. | basic body plan. | c. | skin color. | b. | size. | d. | eye color. |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which of the following statements is false?
a. | Mutations do not occur in hox genes. | b. | Hox genes that are found in different animals
are very different from each other. | c. | Hox genes control the normal development of an
animal. | d. | Hox genes occur in clusters. |
|
|
|
35.
|
Hox genes
a. | are regulated by operons. | c. | are not found in
humans. | b. | are found in bacteria. | d. | determine the location of a dog’s ears. |
|
Modified True/False (Value 10)
Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false,
change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true.
|
|
|
36.
|
The replication of a DNA molecule results in four copies of the same
gene. _________________________
|
|
|
37.
|
If a nucleic acid contains uracil, it is DNA.
_________________________
|
|
|
38.
|
The three types of RNA are messenger RNA, transfer RNA, and ribosomal
RNA. _________________________
|
|
|
39.
|
During DNA replication, only one strand of DNA serves as a template.
_________________________
|
|
|
40.
|
A codon consists of four nucleotides. _________________________
|
|
|
41.
|
The anticodon AGA is complementary to the mRNA codon TCT.
___________________
|
|
|
42.
|
In prokaryotes, an operon is a group of genes that are operated together.
_________________________
|
|
|
43.
|
Gene regulation in eukaryotes is less complex than in prokaryotes.
_________________________
|
|
|
44.
|
The TATA box in eukaryotes helps to ensure transcription.
_________________________
|
|
|
45.
|
In fruit flies, the hox gene that controls the development of the wings is
located before the hox gene that controls the development of the eye and before the hox gene
that controls the development of the abdomen. _________________________
|
Completion (Value 5)
Complete
each statement.
|
|
|
46.
|
Chromatin contains proteins called ____________________.
|
|
|
47.
|
In RNA, ____________________ and ____________________ are pyrimidines.
|
|
|
48.
|
During transcription, the _________________________ between base pairs are
broken.
|
|
|
49.
|
The order of nitrogenous bases in DNA determines the order of
____________________ in proteins.
|
|
|
50.
|
In eukaryotes, proteins that attract RNA polymerase bind to ____________________
sequences in DNA.
|