Multiple Choice (Value 16)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Gene maps are based on
a. | independent assortment. | b. | the frequencies of crossing-over between
genes. | c. | the number of genes in a cell. | d. | genetic
diversity. |
|
|
|
2.
|
Gregor Mendel’s principles of genetics apply to
a. | animals only. | c. | pea plants only. | b. | all organisms. | d. | plants only. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Why did Thomas Hunt Morgan use fruit flies in his studies?
a. | Fruit flies share certain characteristics with pea plants. | b. | Fruit flies have a
long lifespan. | c. | Fruit flies take a long time to produce offspring. | d. | Fruit flies produce
a large number of offspring. |
|
|
|
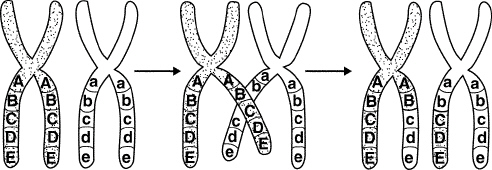
Figure
11–3
|
|
|
4.
|
What is shown in Figure 11–3?
a. | independent assortment | c. | crossing-over | b. | replication | d. | anaphase I of
meiosis |
|
|
|
5.
|
Gametes are produced by the process of
a. | replication. | c. | meiosis. | b. | mitosis. | d. | crossing-over. |
|
|
|
6.
|
The number of chromosomes in a gamete is represented by the symbol
|
|
|
7.
|
Gametes have
a. | twice the number of chromosomes found in body cells. | b. | one allele for each
gene. | c. | two sets of chromosomes. | d. | homologous
chromosomes. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Crossing-over rarely occurs in mitosis, unlike meiosis. Which of the following
is the likely reason?
a. | Chromatids are not involved in mitosis. | b. | A cell undergoing
mitosis does not have homologous chromosomes. | c. | There is no prophase during
mitosis. | d. | Tetrads rarely form during mitosis. |
|
|
|
9.
|
How many different allele combinations would be found in the gametes produced by
a pea plant whose genotype was RrYY?
|
|
|
RrYy | | | |
RY
|
Ry
|
rY
|
ry
| | | |
RY
|
RRYY
|
RRYy
|
RrYY
|
RrYy
| Seed Shape
R
= Round
r = Wrinkled |
RrYy |
Ry
|
RRYy
|
RRyy
|
RrYy
|
Rryy
|
Seed Color
Y = Yellow
y =
Green |
rY
|
RrYY
|
RrYy
|
rrYY
|
rrYy
| | |
ry
|
RrYy
|
Rryy
|
rrYy
|
rryy
| | | | | | | | |
Figure
11–2
|
|
|
10.
|
The Punnett square in Figure 11–2 shows that the gene for pea shape and
the gene for pea color
a. | are linked. | c. | have the same alleles. | b. | are always
homozygous. | d. | assort
independently. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following assort independently?
a. | codominant alleles | c. | chromosomes | b. | multiple alleles | d. | genes on the same
chromosome |
|
|
|
12.
|
What principle states that during gamete formation genes for different traits
separate without influencing each other’s inheritance?
a. | principle of probabilities | c. | principle of independent
assortment | b. | principle of dominance | d. | principle of segregation |
|
|
|
13.
|
Unlike mitosis, meiosis results in the formation of
a. | diploid cells. | c. | haploid cells. | b. | 2N daughter cells. | d. | body cells. |
|
|
|
14.
|
A cross of a black chicken (BB) with a white chicken (WW) produces
all speckled offspring (BBWW). This type of inheritance is known as
a. | codominance. | c. | incomplete dominance. | b. | polygenic
inheritance. | d. | multiple
alleles. |
|
|
|
15.
|
If an organism’s diploid number is 12, its haploid number is
|
|
|
16.
|
Chromosomes form tetrads during
a. | prophase I of meiosis. | c. | metaphase I of meiosis. | b. | anaphase II of
meiosis. | d. | interphase. |
|
Modified True/False (Value 7)
Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false,
change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true.
|
|
|
17.
|
If an organism is heterozygous for a particular gene, the two different alleles
will be separated during anaphase II of meiosis, assuming that no crossing-over has occurred.
_________________________
|
|
|
18.
|
Coat color in rabbits is determined by a single gene that has multiple
alleles. _________________________
|
|
|
19.
|
Genes in the same linkage group are usually inherited separately.
_________________________
|
|
|
20.
|
If an organism has four linkage groups, it has eight chromosomes.
_________________________
|
|
|
21.
|
If two speckled chickens are mated, according to the principle of codominance,
25% of the offspring are expected to be speckled. _________________________
|
|
|
22.
|
Mitosis results in two cells, whereas meiosis results in one cell.
_________________________
|
|
|
23.
|
If an organism has 16 chromosomes in each of its egg cells, the organism’s
diploid number is 32. _________________________
|
Completion (Value 5)
Complete
each statement.
|
|
|
24.
|
Crossing a pink-flowered four o’clock with a white-flowered four
o’clock will produce pink-flowered offspring and ____________________-flowered
offspring.
|
|
|
25.
|
The relative locations of each known gene can be shown on a ____________________
map.
|
|
|
26.
|
If pea plants that are homozygous for round, yellow seeds (RRYY) were
crossed with pea plants that are heterozygous for round, yellow seeds (RrYy), the expected
phenotype(s) of the offspring would be _________________________.
|
|
|
27.
|
An organism’s gametes have ____________________ the number of chromosomes
found in the organism’s body cells.
|
|
|
28.
|
Crossing-over occurs during the stage of meiosis called
____________________.
|
Short Answer (Value 10)
|
|
|
29.
|
The gene map of a fruit fly’s chromosome 2 shows the relative locations of
the star eye, dumpy wing, and black body genes to be 1.3, 13.0, and 48.5, respectively. Between which
two genes does crossing-over occur most frequently?
|
|
|
RrYy | | | |
RY
|
Ry
|
rY
|
ry
| | | |
RY
|
RRYY
|
RRYy
|
RrYY
|
RrYy
| Seed Shape
R
= Round
r = Wrinkled |
RrYy |
Ry
|
RRYy
|
RRyy
|
RrYy
|
Rryy
|
Seed Color
Y = Yellow
y =
Green |
rY
|
RrYY
|
RrYy
|
rrYY
|
rrYy
| | |
ry
|
RrYy
|
Rryy
|
rrYy
|
rryy
| | | | | | | | |
Figure
11–2
|
|
|
30.
|
What is the phenotype ratio of the offspring in the Punnett square shown in
Figure 11–2?
|
|
|
31.
|
What does a gene map show?
|
|
|
32.
|
What happens to the number of chromosomes per cell during meiosis?
|
|
|
33.
|
What is a linkage group?
|