Multiple Choice (1 pt. each)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
When during the cell cycle are chromosomes visible?
a. | only during interphase | c. | only during the M phase | b. | only when they are
being replicated | d. | only
during the G1 phase |
|
|
|
2.
|
During which phase of mitosis do the chromosomes line up along the middle of the
dividing cell?
a. | prophase | c. | metaphase | b. | telophase | d. | anaphase |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which of the following represents the phases of mitosis in their proper
sequence?
a. | prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase | b. | interphase,
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase | c. | interphase, prophase, metaphase,
telophase | d. | prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis |
|
|
|
4.
|
What is the role of the spindle during mitosis?
a. | It helps separate the chromosomes. | c. | It duplicates the
DNA. | b. | It breaks down the nuclear membrane. | d. | It divides the cell in
half. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which of the following explains why normal cells grown in a petri dish tend to
stop growing once they have covered the bottom of the dish?
a. | The cells lack cyclin. | b. | The petri dish inhibits cell
growth. | c. | Contact with other cells stops cell growth. | d. | Most cells grown in
petri dishes have a defective p53. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Cancer is a disorder in which some cells have lost the ability to control
their
a. | size. | c. | growth rate. | b. | spindle fibers. | d. | surface area. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which of the following happens when a cell divides?
a. | The cell’s volume increases. | b. | It becomes more difficult for the cell to get
enough oxygen and nutrients. | c. | The cell has DNA overload. | d. | Each daughter cell
receives its own copy of the parent cell’s DNA. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which of the following is a phase in the cell cycle?
a. | G1 phase | c. | M phase | b. | G2 phase | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
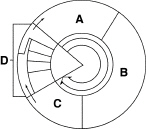
Figure 10–2
|
|
|
9.
|
Cell division is represented in Figure 10-2 by the letter?
|
|
|
10.
|
The cell cycle is the
a. | series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. | b. | period of time
between the birth and the death of a cell. | c. | time from prophase until
cytokinesis. | d. | time it takes for one cell to undergo mitosis. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following is a phase of mitosis?
a. | cytokinesis | c. | anaphase | b. | interphase | d. | S phase |
|
|
|
12.
|
What is a tumor?
a. | an accumulation of cyclins | b. | a mass of cancer cells | c. | the rapidly dividing
cells found at the site of a wound | d. | a defective p53
gene |
|
|
|
13.
|
Mendel concluded that traits are
a. | not inherited by offspring. | b. | inherited through the passing of factors from
parents to offspring. | c. | determined by dominant factors
only. | d. | determined by recessive factors only. |
|
|
|
14.
|
In the P generation, a tall plant was crossed with a short plant. Short plants
reappeared in the F2 generation because
a. | some of the F2 plants produced gametes that carried the allele for
shortness. | b. | the allele for shortness is dominant. | c. | the allele for shortness and the allele for
tallness segregated when the F1 plants produced gametes. | d. | they inherited an
allele for shortness from one parent and an allele for tallness from the other
parent. |
|
|
|
15.
|
A Punnett square shows all of the following EXCEPT
a. | all possible results of a genetic cross. | b. | the genotypes of the
offspring. | c. | the alleles in the gametes of each parent. | d. | the actual, or real,
results of a genetic cross. |
|
|
|
16.
|
How many different allele combinations would be found in the gametes produced by
a pea plant whose genotype was RrYY?
|
|
|
17.
|
A cross of a white hen with a black rooster produces erminette-colored (black
& white) offspring. This type of inheritance is known as
a. | incomplete dominance. | c. | codominance. | b. | polygenic inheritance. | d. | multiple
alleles. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Gregor Mendel used pea plants to study
a. | flowering. | c. | the inheritance of traits. | b. | gamete
formation. | d. | cross-pollination. |
|
|
|
19.
|
What are Mendel’s factors called today?
a. | alleles | c. | genes | b. | traits | d. | characters |
|
|
|
20.
|
Organisms that have two identical alleles for a particular trait are said to
be
a. | hybrid. | c. | heterozygous. | b. | homozygous. | d. | dominant. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Situations in which one allele for a gene is not completely dominant over
another allele for that gene are called
a. | multiple alleles. | c. | codominant alleles. | b. | incomplete dominance. | d. | multiple genes. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Mendel’s principles of genetics apply to
a. | plants only. | c. | pea plants only. | b. | animals only. | d. | all organisms. |
|
|
|
23.
|
Gametes are produced by the process of
a. | mitosis. | c. | crossing-over. | b. | meiosis. | d. | replication. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Unlike mitosis, meiosis results in the formation of
a. | diploid cells. | c. | 2N daughter cells. | b. | haploid cells. | d. | body cells. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Traits that are produced by the interaction of several genes are said to
be
a. | polygenic. | c. | haploid. | b. | codominant. | d. | diploid. |
|
|
|
26.
|
DNA replication results in two DNA molecules,
a. | each with two new strands. | b. | one with two new strands and the other with two
original strands. | c. | each with one new strand and one original
strand. | d. | each with two original strands. |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which type(s) of RNA is(are) involved in protein synthesis?
a. | transfer RNA only | b. | messenger RNA only | c. | ribosomal RNA and
transfer RNA only | d. | messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer
RNA |
|
|
|
28.
|
During transcription, an RNA molecule is formed
a. | that is complementary to both strands of DNA. | b. | that is
complementary to neither strand of DNA. | c. | that is double-stranded. | d. | inside the
nucleus. |
|
|
|
29.
|
How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids?
|
|
|
30.
|
Which type of RNA functions as a blueprint of the genetic code?
a. | rRNA | c. | mRNA | b. | tRNA | d. | RNA polymerase |
|
|
|
31.
|
Figure 12-5 shows the structure of a(an) 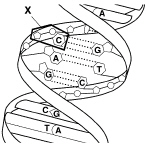
Figure 12–5
a. | DNA molecule. | c. | RNA molecule. | b. | amino acid. | d. | protein. |
|
|
|
32.
|
In eukaryotes, DNA
a. | is located in the nucleus. | c. | is located in the
ribosomes. | b. | floats freely in the cytoplasm. | d. | is circular. |
|
|
|
33.
|
RNA contains the sugar
a. | ribose. | c. | glucose. | b. | deoxyribose. | d. | lactose. |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which RNA molecule carries amino acids?
a. | messenger RNA | c. | ribosomal RNA | b. | transfer RNA | d. | RNA polymerase |
|
|
|
35.
|
Genes contain instructions for assembling
a. | purines. | c. | proteins. | b. | structures | d. | pyrimidines. |
|
|
|
36.
|
Selective breeding produces
a. | more offspring. | c. | desired traits in offspring. | b. | fewer
offspring. | d. | transgenic
organisms. |
|
|
|
37.
|
Which of the following are purines?
a. | adenine & thymine | c. | adenine & guanine | b. | cytosine &
guanine | d. | cytosine &
thymine |
|
|
|
38.
|
What does Figure 13-1 show? 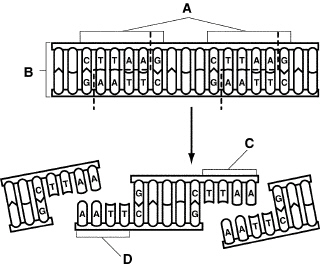
Figure 13–1
a. | gel electrophoresis | b. | DNA sequencing | c. | a restriction enzyme
cutting different sequences of DNA | d. | polymerase chain
reaction |
|
|
|
39.
|
Genetic engineering involves
a. | reading a DNA sequence. | b. | editing a DNA sequence. | c. | reinserting DNA into
living organisms. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
40.
|
If the DNA of a particular species of fly is found to contain 20% guanine, what
percentage of thymine would you expect to find in this fly’s DNA?
|
|
|
41.
|
A section of DNA contains the following bases in
this order: GATCCT. Which of the following mRNA sequences complements this section of DNA?
a. | CUAGGA | c. | CTAGGC
| b. | TCGAAG | d. | AGCUUC |
|
|
|
42.
|
On the Galápagos Islands, Charles Darwin observed
a. | completely unrelated species on each of the islands. | b. | species exactly like
those found in South America. | c. | somewhat similar species with traits that
suited their particular environment. | d. | species completely unrelated to those found in
South America. |
|
|
|
43.
|
Lamarck’s theory of evolution includes the concept that new organs in a
species appear as a result of
a. | continual increases in population size. | b. | the actions of
organisms as they use or fail to use body structures. | c. | an unchanging local
environment. | d. | the natural variations already present within the population of
organisms. |
|
|
|
44.
|
When coyotes prey on rabbits,, some rabbits are killed and some escape. Which
part of Darwin’s concept of natural selection might be used to describe this situation?
a. | acquired characteristics | c. | survival of the
fittest | b. | reproductive isolation | d. | descent with modification |
|
|
|
45.
|
If a white-flowered parent was crossed with a
red-flowered parent in a species that displays incomplete dominance what type(s) of flowering
offspring would be expected in this species
a. | all red offspring | c. | all white offspring | b. | all pink offspring | d. | no offspring |
|
|
|
46.
|
Two parents are known
to be right-handed. Assuming that right-handed (R) is dominant to
left-handed (r), what
could be the genotypes of the parents if their son is left-handed? a. | rr x RR | c. | Rr x Rr | b. | Rr x RR | d. | RR x RR |
|
|
|
47.
|
Which concept is NOT included in the modern theory of evolution?
a. | descent with modification | b. | natural selection | c. | transmission of
acquired characteristics | d. | competition among the members of a
population |
|
|
|
48.
|
When a farmer breeds only his or her best livestock, the process involved
is
a. | natural selection. | c. | artificial variation. | b. | artificial
selection. | d. | survival of the
fittest. |
|
|
|
49.
|
Darwin called the ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its
environment
a. | diversity. | c. | adaptation. | b. | fitness. | d. | evolution. |
|
|
|
50.
|
The hypothesis that species change over time by natural selection was proposed
by
a. | Hutton. | c. | Malthus. | b. | Lamarck. | d. | Darwin. |
|
|
|
51.
|
Which of the following statements describes what all members of a population
share?
a. | They are temporally isolated from one another. | b. | They are
geographically isolated from one another. | c. | They are members of the same
species. | d. | They have identical genes. |
|
|
|
52.
|
In many kinds of organisms, most heritable differences are due to
a. | mutations during gamete formation. | b. | chemicals in the
environment. | c. | gene shuffling during gamete formation. | d. | the effects of
radiation. |
|
|
|
53.
|
Which of the following would effect the genetic equilibrium of a
population?
a. | nonrandom mating. | b. | movement into and out of the
population. | c. | mutations. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
54.
|
The division of the nervous system that regulates activities that are under
conscious control is the
a. | somatic nervous system. | c. | autonomic nervous
system. | b. | sensory nervous system. | d. | sympathetic nervous system. |
|
|
|
55.
|
Which general category of sensory receptors detects variations in
temperature?
a. | thermoreceptors | c. | photoreceptors | b. | mechanoreceptors | d. | pain receptors |
|
Completion: Complete each
statement.(1 pt. each)
|
|
|
1.
|
The process by which a cell divides into two daughter cells is called
____________________.
|
|
|
2.
|
Together, the G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase are called
____________________.
|
|
|
3.
|
Look at Figure 10-4. The process shown occurs directly following mitosis. This
process is called ____________________.
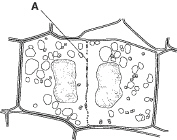
Figure 10–4
|
|
|
4.
|
A pea plant that has two different alleles for the same trait is said to be
____________________.
|
|
|
5.
|
An organism’s gametes have ____________________ the number of chromosomes
found in the organism’s body cells.
|
|
|
6.
|
The principle of independent assortment states that ____________________ for
different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes.
|
|
|
7.
|
The order of nitrogenous bases in DNA determines the order of
____________________ in proteins.
|
|
|
8.
|
According to the principle of base pairing, hydrogen bonds can form only between
________ and thymine, and between guanine and ____________.
|
|
|
9.
|
In Figure 12-7 below, A, B, and C are three types of
____________________. 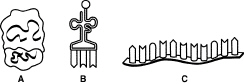
Figure 12–7
|
|
|
10.
|
In most animals, axons and dendrites are clustered into bundles of fibers called
____________________.
|
Short Answer: (2 pts each)
|
|
|
1.
|
Why are chromosomes not visible in most cells except during cell
division?
|
|
|
2.
|
How many recessive alleles for a trait must an organism inherit in order to show
that trait?
|
|
|
3.
|
Define genetics.
|
|
|
4.
|
How many sets of chromosomes are in a diploid cell?
|
|
|
5.
|
Define homologous chromosomes.
|
|
|
6.
|
In Figure 12-2, which molecule is tRNA, and what is its function? 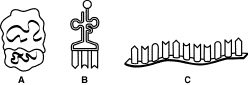
Figure 12–2
|
|
|
7.
|
According to Figure 12-3, what two codons specify the amino acid
arginine?
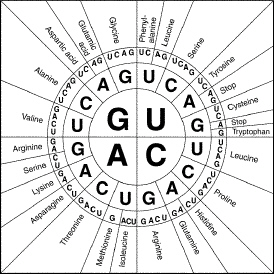
Figure 12–3
|
|
|
8.
|
Were Darwin’s hypotheses about natural selection and evolution similar to
the ideas of most other scientists of his time? Explain.
|
Scientific Reasoning Questions--2 pts each
|
|
|
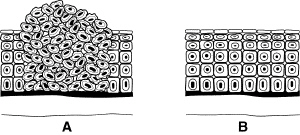
Figure 10-1
|
|
|
1.
|
Predicting Look at the cancer cells shown in Figure 10-1. What can happen
if these cells are left untreated?
|
|
|
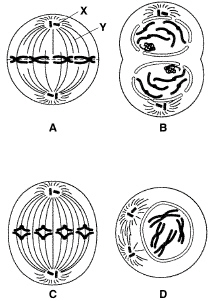
Figure 10–5
|
|
|
2.
|
Applying Concepts List the correct order for the diagrams in Figure 10-5
above.
|
|
|
Heterozygous male guinea pigs with black, rough hair (BbRr) are crossed with
heterozygous female guinea pigs with black, rough hair (BbRr). The incomplete Punnett square in
Figure 11-4 shows the expected results from the cross. | | BR | Br | bR | br | | BR | BBRR | BBRr | BbRR | BbRr | Hair Color: B = Black b =
White
| Br
| BBRr | BBrr | BbRr | Bbrr | Hair Texture: R = Rough
r = Smooth | bR
| BbRR | BbRr | ? | bbRr | br | BbRr | Bbrr | bbRr | bbrr
| | | | | | | |
Figure
11–4
|
|
|
3.
|
Using Tables and Graphs Identify the genotype of the offspring that would
be represented in the square labeled with a question mark in Figure 11-4 above.
|
|
|
4.
|
What is the phenotypic ratio of the offspring in the Figure 11-4 above?
|
|
|
5.
|
What would the phenotypic ratio of the offpring have been if the parents above
were BBRR x bbrr?
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.
|
Interpreting Graphics Identify the
genotypes for individuals II-4, II-5, III-11, & III-12
|
|
|
7.
|
Interpreting Graphics Explain why
more females than males inherit CH in generation III
|
|
|
This diagram a synapse between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of
another.
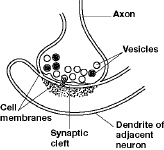
Figure 35–3
|
|
|
8.
|
Applying Concepts In Figure 35-3, what would cause the release of
neurotransmitters from the vesicles?
|
Essay: Choose 4 of following on which to write a brief
essay. Use the looseleaf provided. (5 pts each).
|
|
|
1.
|
Describe what happens during the four phases of mitosis.
|
|
|
2.
|
Describe how cancer cells are different from other cells. Based on these
differences, explain why cancer has been such a difficult condition to cure.
|
|
|
3.
|
Describe the structure of a DNA molecule.
|
|
|
4.
|
Explain the advantage and disadvantage of inbreeding. Give an example of
each.
|
|
|
5.
|
Choose one of the following genetic birth defects and write a short explanatory
paragraph about it: Turner’s Syndrome, Patau’s Syndrome, or Down’s
Syndrome.
|
|
|
6.
|
Suppose that selective breeding has produced a population of very similar
pheasants. Would that population survive if it were released into the world? Explain.
|
|
|
7.
|
Compare resting potential and action potential in a neuron.
|