Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
As a cell grows, it
a. | places more demands on its DNA. | b. | uses up food and oxygen more
quickly. | c. | has more trouble moving enough materials across its cell
membrane. | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
2.
|
All of the following are problems that growth causes for cells EXCEPT
a. | DNA overload. | c. | obtaining enough food. | b. | excess
oxygen. | d. | expelling
wastes. |
|
|
|
3.
|
When during the cell cycle are chromosomes visible?
a. | only during interphase | c. | only during cell division | b. | only when they are
being replicated | d. | only
during the G1 phase |
|
|
|
4.
|
Which pair is correct?
a. | G1 phase, DNA replication | c. | S phase, cell
division | b. | G2 phase, preparation for mitosis | d. | M phase, cell
growth |
|
|
|
5.
|
When during the cell cycle is a cell’s DNA replicated?
a. | G1 phase | c. | S phase | b. | G2 phase | d. | M phase |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which event occurs during interphase?
a. | The cell grows. | c. | Spindle fibers begin to form. | b. | Centrioles
appear. | d. | Centromeres
divide. |
|
|
|
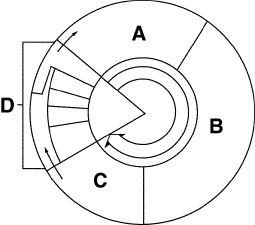
Figure
10–1
|
|
|
7.
|
Cell division is represented in Figure 10–1 by the letter
|
|
|
8.
|
Which of the following is a phase of mitosis?
a. | cytokinesis | c. | prophase | b. | interphase | d. | S phase |
|
|
|
9.
|
The first phase of mitosis is called
a. | prophase. | c. | metaphase. | b. | anaphase. | d. | interphase. |
|
|
|
10.
|
What is the role of the spindle during mitosis?
a. | It helps separate the chromosomes. | b. | It breaks down the nuclear
membrane. | c. | It duplicates the DNA. | d. | It makes the chromosomes visible.
|
|
|
|
11.
|
The two main stages of cell division are called
a. | mitosis and interphase. | c. | the M phase and the S
phase. | b. | synthesis and cytokinesis. | d. | mitosis and cytokinesis. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Right after a bone breaks, cells at the edge of the injury
a. | stop dividing. | b. | begin to divide rapidly. | c. | form a thin layer
over the edge of the injury. | d. | develop a defect in a gene called p53.
|
|
|
|
13.
|
Which of the following is a factor that can stop normal cells from
growing?
a. | contact with other cells | b. | growth factors | c. | a cut in the
skin | d. | cyclin that has been taken from a cell in mitosis |
|
|
|
14.
|
Cyclins are a family of closely related proteins that
a. | regulate the cell cycle. | c. | cause cancer. | b. | produce
p53. | d. | work to heal
wounds. |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following regulate(s) the cell cycle?
a. | growth factors | c. | p53 | b. | cyclins | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
16.
|
What is a tumor?
a. | an accumulation of cyclins | b. | a mass of cancer cells | c. | the rapidly dividing
cells found at the site of a wound | d. | a defective p53
gene |
|
|
|
17.
|
Offspring that result from crosses between parents with different traits
a. | are true-breeding. | c. | make up the parental generation. | b. | make up the
F2 generation. | d. | are called hybrids. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Gregor Mendel removed the male parts from the flowers of some plants in order
to
a. | prevent hybrids from forming. | b. | prevent cross-pollination. | c. | stimulate
self-pollination. | d. | make controlled crosses between
plants. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Gregor Mendel concluded that traits are
a. | not inherited by offspring. | b. | inherited through the passing of factors from
parents to offspring. | c. | determined by dominant factors
only. | d. | determined by recessive factors only. |
|
|
|
20.
|
The principle of dominance states that
a. | all alleles are dominant. | b. | all alleles are recessive. | c. | some alleles are
dominant and others are recessive. | d. | alleles are neither dominant nor
recessive. |
|
|
|
21.
|
When Gregor Mendel crossed true-breeding tall plants with true-breeding short
plants, all the offspring were tall because
a. | the allele for tall plants is recessive. | b. | the allele for short
plants is dominant. | c. | the allele for tall plants is
dominant. | d. | they were true-breeding like their parents. |
|
|
|
22.
|
If a pea plant has a recessive allele for green peas, it will produce
a. | green peas if it also has a dominant allele for yellow peas. | b. | both green peas and
yellow peas if it also has a dominant allele for yellow peas. | c. | green peas if it
does not also have a dominant allele for yellow peas. | d. | yellow peas if it does not also have a dominant
allele for green peas. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.
|
In the Punnett square shown in Figure 11–1, which of the following is true
about the offspring resulting from the cross?
a. | About half are expected to be short. | c. | About half are expected to be
tall. | b. | All are expected to be short. | d. | All are expected to be
tall. |
|
|
|
24.
|
How many different allele combinations would be found in the gametes produced by
a pea plant whose genotype was RrYY?
|
|
|
25.
|
A cross of a black chicken (BB) with a white chicken (WW) produces
all speckled offspring (BBWW). This type of inheritance is known as
a. | incomplete dominance. | c. | codominance. | b. | polygenic inheritance. | d. | multiple
alleles. |
|
|
|
26.
|
The farther apart two genes are located on a chromosome, the
a. | less likely they are to be inherited together. | b. | more likely they are
to be linked. | c. | less likely they are to assort independently. | d. | less likely they are
to be separated by a crossover during meiosis. |
|
|
|
27.
|
During mitosis, the
a. | DNA molecules unwind. | b. | histones and DNA molecules
separate. | c. | DNA polymerase makes copies of DNA strands. | d. | nucleosomes become
more tightly packed. |
|
|
|
28.
|
DNA replication results in two DNA molecules,
a. | each with two new strands. | b. | one with two new strands and the other with two
original strands. | c. | each with one new strand and one original
strand. | d. | each with two original strands. |
|
|
|
29.
|
During DNA replication, a DNA strand that has the bases CTAGGT produces a strand
with the bases
a. | TCGAAC. | c. | AGCTTG. | b. | GATCCA. | d. | GAUCCA. |
|
|
|
30.
|
How many main types of RNA are there?
a. | 1 | c. | hundreds | b. | 3 | d. | thousands |
|
|
|
31.
|
During translation, the type of amino acid that is added to the growing
polypeptide depends on the
a. | codon on the mRNA only. | b. | anticodon on the mRNA only. | c. | anticodon on the
tRNA to which the amino acid is attached only. | d. | codon on the mRNA and the anticodon on the tRNA
to which the amino acid is attached. |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which of the following statements is false?
a. | Some genes code for enzymes. | b. | The instructions for making some proteins are
not specified by genes. | c. | An organism’s inherited traits depend on
proteins. | d. | An organism’s genes determine its inherited
traits. |
|
|
|
33.
|
James Hutton’s and Charles Lyell’s work suggests that
a. | Earth is many millions of years old. | b. | Earth is several thousand years
old. | c. | all fossils were formed in the last 1000 years. | d. | all rocks on Earth
contain fossils. |
|
|
|
34.
|
James Hutton’s and Charles Lyell’s work was important to Darwin
because these scientists
a. | explained volcanoes and earthquakes. | b. | explained all geologic events on
Earth. | c. | suggested that Earth was old enough for evolution to have
occurred. | d. | refuted the work of Lamarck, which was based on
misunderstandings. |
|
|
|
35.
|
What did Charles Darwin learn from reading the work of James Hutton and Charles
Lyell?
a. | Earth is relatively young. | b. | Earth is very old. | c. | All geological
change is caused by living organisms. | d. | The processes that formed old rocks on Earth do
not operate today. |
|
|
|
36.
|
In an experiment, suppose that the wings of fruit flies were clipped short for
fifty generations. The fifty-first generation emerged with normal-length wings. This observation
would tend to disprove the idea that evolution is based on
a. | inheritance of natural variations. | b. | inheritance of acquired
characteristics. | c. | natural selection. | d. | survival of the
fittest. |
|
|
|
37.
|
The idea that only famine, disease, and war could prevent the endless growth of
human populations was presented by
a. | Charles Darwin. | c. | Thomas Malthus. | b. | Jean-Baptiste Lamarck. | d. | Charles Lyell. |
|
|
|
38.
|
When Charles Darwin returned from the voyage of the Beagle, he
a. | immediately published his ideas about evolution. | b. | realized his ideas
about evolution were wrong. | c. | wrote about his ideas but waited many years to
publish them. | d. | copied the evolutionary theory of Wallace. |
|
|
|
39.
|
Charles Darwin’s observation that finches of different species on the
Galápagos Islands have many similar physical characteristics supports the hypothesis that these
finches
a. | have the ability to interbreed. | b. | acquired traits through use and
disuse. | c. | all eat the same type of food. | d. | descended from a common
ancestor. |
|
|
|
40.
|
When a farmer breeds only his or her best livestock, the process involved
is
a. | natural selection. | c. | artificial variation. | b. | artificial
selection. | d. | survival of the
fittest. |
|
|
|
41.
|
Which statement about the members of a population that live long enough to
reproduce is consistent with the theory of natural selection?
a. | They transmit characteristics acquired by use and disuse to their
offspring. | b. | They tend to produce fewer offspring than others in the
population. | c. | They are the ones that are best adapted to survive in their
environment. | d. | They will perpetuate unfavorable changes in the
species. |
|
|
|
42.
|
Charles Darwin called the ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its
specific environment
a. | diversity. | c. | adaptation. | b. | fitness. | d. | evolution. |
|
|
|
43.
|
According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection, the individuals that
tend to survive are those that have
a. | characteristics their parents acquired by use and disuse. | b. | characteristics that
plant and animal breeders value. | c. | the greatest number of
offspring. | d. | variations best suited to the environment. |
|
|
|
44.
|
Modern sea star larvae resemble some primitive vertebrate larvae. This
similarity may suggest that primitive vertebrates
a. | share a common ancestor with sea stars. | b. | evolved from sea
stars. | c. | evolved before sea stars. | d. | belong to the same species as sea
stars. |
|
|
|
45.
|
The same kinds of cells that grow in similar patterns in different but related
organisms produce
a. | homologous structures such as wings and arms. | b. | the same kind of
embryos. | c. | natural variations in a population. | d. | descent with
modification. |
|
|
|
46.
|
Gene shuffling includes the independent movement of chromosomes during meoisis
as well as
a. | mutations from radiation. | c. | crossing-over. | b. | changes in the
frequencies of alleles. | d. | mutations from chemicals. |
|
|
|
47.
|
In a particular population, sexual reproduction can produce
a. | mutations. | c. | new allele frequencies. | b. | many different
phenotypes. | d. | meiosis. |
|
|
|
48.
|
The gene shuffling that occurs as part of sexual reproduction
a. | changes the gene pool’s allele frequencies. | b. | does not change the
gene pool’s allele frequencies. | c. | keeps the phenotypes
consistent. | d. | is caused by radiation or chemicals. |
|
|
|
49.
|
Which of the following is NOT a way in which natural selection affects the
distribution of phenotypes?
a. | directional selection | c. | disruptive selection | b. | stabilizing selection | d. | chance events |
|
|
|
50.
|
The situation in which allele frequencies of a population remain constant is
called
a. | evolution. | c. | genetic equilibrium. | b. | genetic drift. | d. | natural
selection. |
|
|
|
51.
|
One of the conditions required to maintain genetic equilibrium is
a. | natural selection. | b. | mutations. | c. | nonrandom
mating. | d. | no movement into or out of the population. |
|
|
|
52.
|
A factor that is necessary for the formation of a new species is
a. | reproduction at different times. | c. | different mating
behaviors. | b. | geographic barriers. | d. | reproductive isolation. |
|
|
|
53.
|
The geographic isolation of two populations of a species tends to increase
differences between their gene pools because it
a. | prevents interbreeding between the populations. | b. | prevents
interbreeding within each population. | c. | causes temporal isolation of the two
populations. | d. | increases differences in courtship behavior. |
|
Modified True/False
Indicate
whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
statement true.
|
|
|
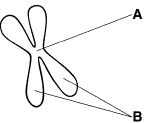
Figure
10–2
|
|
|
54.
|
The structure shown in Figure 10–2 is a replicated chromosome.
_________________________
|
|
|
55.
|
Proteins called cyclins help regulate the cell cycle.
_________________________
|
|
|
56.
|
A trait is a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to
another. _________________________
|
|
|
57.
|
Gregor Mendel concluded that the tall plants in the P generation passed the
factor for tallness to the F1 generation. _________________________
|
|
|
58.
|
During the formation of gametes in a hybrid tall plant, the tall allele and the
short allele stay together. _________________________
|
|
|
59.
|
Mitosis results in two cells, whereas meiosis results in one cell.
_________________________
|
|
|
60.
|
Genes in the same linkage group are usually inherited separately.
_________________________
|
|
|
61.
|
The three types of RNA are messenger RNA, transfer RNA, and ribosomal
RNA. _________________________
|
|
|
62.
|
A codon consists of four nucleotides. _________________________
|
|
|
63.
|
DNA codes for the DNA polymerase enzyme. _________________________
|
|
|
64.
|
According to Lamarck, the sea floor can be pushed up to form mountains by
forces within Earth. _________________________
|
|
|
65.
|
In Charles Darwin’s time, many people thought that Earth and its living
things were formed about a few thousand years ago. _________________________
|
|
|
66.
|
Evidence that the surface of a mountain was once under the sea includes the
presence of marine fossils on the mountain. _________________________
|
|
|
67.
|
In the type of reproductive isolation called behavioral isolation, two
populations are separated by barriers such as rivers or mountains. _________________________
|
Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
68.
|
A cell that has 5 chromosomes in the G1 phase will have
____________________ chromatids in the G2 phase.
|
|
|
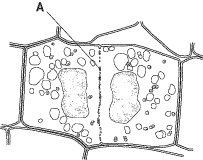
Figure
10–3
|
|
|
69.
|
The process shown in Figure 10–3 occurs only in ____________________ cells
that have just divided.
|
|
|
70.
|
During metaphase, the centromere on each chromosome is connected to a structure
called a _________________________.
|
|
|
71.
|
The plants that Gregor Mendel crossed to produce the F1 generation
made up the ____________________ generation.
|
|
|
|
|
|
72.
|
In the Punnett square shown in Figure 11–1, the genotypes of the offspring
are ____________________.
|
|
|
73.
|
When two heterozygous tall pea plants are crossed, the expected genotype ratio
of the offspring is _________________________.
|
|
|
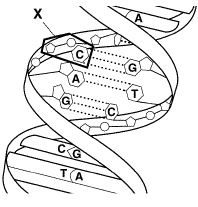
Figure
12–1
|
|
|
74.
|
The structure labeled X in Figure 12–1 is a(an)
____________________.
|
|
|
75.
|
The Watson and Crick model of DNA is a(an) _________________________, in which
two strands are wound around each other.
|
|
|
76.
|
During transcription, the _________________________ between base pairs are
broken.
|
|
|
77.
|
Crossing-over can occur during the meiotic divisions that produce cells called
____________________.
|
|
|
78.
|
Most inherited differences in the appearances of two brothers are due to the
_________________________ that occurred during the production of gametes in their parents.
|
|
|
79.
|
The number of possible phenotypes for a given trait depends on how many
____________________ control the trait.
|
|
|
80.
|
A polygenic trait can have many possible genotypes and
____________________.
|
|
|
81.
|
In the Galápagos finches that Rosemary and Peter Grant studied, a pattern
of natural selection called ____________________ selection favored individuals with larger, heavier
beaks during a drought.
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
82.
|
Identify a factor that can stop cells from dividing.
|
|
|
RrYy | | | |
RY
|
Ry
|
rY
|
ry
| | | |
RY
|
RRYY
|
RRYy
|
RrYY
|
RrYy
| Seed Shape
R
= Round
r = Wrinkled |
RrYy |
Ry
|
RRYy
|
RRyy
|
RrYy
|
Rryy
|
Seed Color
Y = Yellow
y =
Green |
rY
|
RrYY
|
RrYy
|
rrYY
|
rrYy
| | |
ry
|
RrYy
|
Rryy
|
rrYy
|
rryy
| | | | | | | | |
Figure
11–2
|
|
|
83.
|
What is the phenotype ratio of the offspring in the Punnett square shown in
Figure 11–2?
|
|
|
84.
|
Which genes do not code for proteins?
|
|
|
85.
|
What did observations of the tortoises of the Galápagos lead Charles Darwin
to hypothesize about these animals’ ancestry?
|
|
|
86.
|
Why might genetic drift occur if a small number of individuals colonize a new
habitat?
|
Essay
|
|
|
87.
|
Describe how the skin cells near a cut behave. What role does contact with other
cells have in the behavior of cells near a cut?
|
|
|
88.
|
Explain the difference between incomplete dominance and codominance.
|
|
|
89.
|
Why is it possible that Alfred Wallace independently developed the same ideas
about evolution that Darwin did?
|
|
|
90.
|
How are directional selection and disruptive selection similar? How are they
different?
|
|
|
91.
|
Assume that a geographic barrier that results in two very different ecosystems
splits a single population. What would likely happen to the two separate populations? Would this
process occur more quickly, less quickly, or at the same rate as it would if the two populations
lived in similar ecosystems?
|