Multiple Choice (Value 75)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Which of the following have been produced by selective breeding?
a. | horse breeds | c. | dog breeds | b. | cat breeds | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
2.
|
Scientists produced oil-eating bacteria by
a. | making bacteria polyploid. | c. | inducing mutations in
bacteria. | b. | inbreeding bacteria. | d. | hybridizing bacteria. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which of the following includes all the others?
a. | hybridization | c. | selective breeding | b. | inbreeding | d. | induced
mutations |
|
|
|
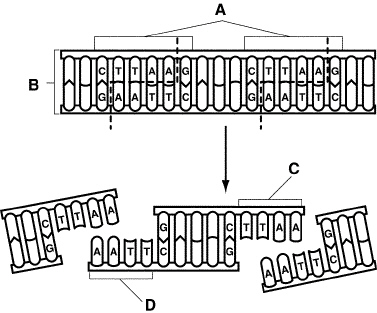
Figure
13–1
|
|
|
4.
|
What does Figure 13–1 show?
a. | gel electrophoresis | b. | DNA sequencing | c. | a restriction enzyme
producing a DNA fragment | d. | polymerase chain
reaction |
|
|
|
5.
|
In Figure 13–1, between which nucleotides is the DNA cut?
a. | adenine and thymine | c. | thymine and cytosine | b. | cytosine and guanine | d. | adenine and
guanine |
|
|
|
6.
|
Knowing the sequence of an organism’s DNA allows researchers to
a. | reproduce the organism. | c. | study specific
genes. | b. | mutate the DNA. | d. | cut the DNA. |
|
|
|
7.
|
If two DNA samples showed an identical pattern and thickness of bands produced
by gel electrophoresis, the samples contained
a. | the same amount of DNA. | c. | the same DNA
molecules. | b. | fragments of the same size. | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
8.
|
Scientists can transform plant cells by
a. | using the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens. | b. | removing the plant
cell walls and then mixing the cells with DNA. | c. | injecting DNA into the plant
cells. | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
9.
|
What kind of technique do scientists use to make transgenic organisms?
a. | hybridization | c. | inducing of mutations | b. | inbreeding | d. | genetic engineering |
|
|
|
10.
|
What has been an advantage of producing transgenic plants?
a. | increasing the food supply | c. | producing
clones | b. | using more pesticides | d. | studying human genes |
|
|
|
11.
|
The Scottish scientist Ian Wilmut cloned a
a. | bacterium. | c. | plant. | b. | sheep. | d. | cow. |
|
|
|
12.
|
On the Galápagos Islands, Charles Darwin observed
a. | completely unrelated species on each of the islands. | b. | species exactly like
those found in South America. | c. | somewhat similar species, with traits that
suited their particular environments. | d. | species completely unrelated to those found in
South America. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Darwin began to formulate his concept of evolution by natural selection
after
a. | experimentation with animals. | b. | observations of many species and their
geographical location. | c. | reading the writings of
Wallace. | d. | agreeing with Lamarck about the driving force behind
evolution. |
|
|
|
14.
|
James Hutton’s and Charles Lyell’s work was important to Darwin
because these scientists
a. | explained volcanoes and earthquakes. | b. | explained all geologic events on
Earth. | c. | suggested that Earth was old enough for evolution to have
occurred. | d. | refuted the work of Lamarck, which was based on
misunderstandings. |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which is a major concept included in Lamarck’s theory of evolution?
a. | Change is the result of survival of the fittest. | b. | Body structure can
change according to the actions of the organism. | c. | Population size decreases the rate of
evolution. | d. | Artificial selection is the basis for evolution. |
|
|
|
16.
|
In an experiment, suppose that the wings of fruit flies were clipped short for
fifty generations. The fifty-first generation emerged with normal-length wings. This observation
would tend to disprove the idea that evolution is based on
a. | inheritance of natural variations. | b. | inheritance of acquired
characteristics. | c. | natural selection. | d. | survival of the
fittest. |
|
|
|
17.
|
The economist Thomas Malthus suggested that
a. | in the human population, people die faster than babies are born. | b. | there would soon be
insufficient food for the growing human population. | c. | in the 1700s, England needed more
housing. | d. | the majority of a species’ offspring die. |
|
|
|
18.
|
In 1859, Charles Darwin published his revolutionary scientific ideas in a work
titled
a. | Principles of Geology. | b. | Essay on the Principle of
Population. | c. | Evolution in Malaysia. | d. | On the Origin of
Species. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Why might Darwin have hesitated to publish his concept of evolution by natural
selection?
a. | He realized it was not supported by his data. | b. | He felt it was too
similar to Lamarck’s to be considered original. | c. | He was disturbed by his findings, which
challenged fundamental scientific beliefs. | d. | He realized that his idea was contradicted by
the work of Hutton and Lyell. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Charles Darwin’s observation that finches of different species on the
Galápagos Islands have many similar physical characteristics supports the hypothesis that these
finches
a. | have the ability to interbreed. | b. | acquired traits through use and
disuse. | c. | all eat the same type of food. | d. | descended from a common
ancestor. |
|
|
|
21.
|
According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection, individuals who survive
are the ones best adapted for their environment. Their survival is due to the
a. | possession of adaptations developed through use. | b. | possession of
inherited adaptations that maximize fitness. | c. | lack of competition within the
species. | d. | choices made by plant and animal breeders. |
|
|
|
22.
|
When a farmer breeds only his or her best livestock, the process involved
is
a. | natural selection. | c. | artificial variation. | b. | artificial
selection. | d. | survival of the
fittest. |
|
|
|
23.
|
According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection, the individuals that
tend to survive are those that have
a. | characteristics their parents acquired by use and disuse. | b. | characteristics that
plant and animal breeders value. | c. | the greatest number of
offspring. | d. | variations best suited to the environment. |
|
|
|
24.
|
An adaptation is an inherited characteristic that can be
a. | physical or behavioral. | b. | physical or geographical. | c. | acquired during the
organism’s lifetime. | d. | the result of artificial
selection. |
|
|
|
25.
|
The same kinds of cells that grow in similar patterns in different but related
organisms produce
a. | homologous structures such as wings and arms. | b. | the same kind of
embryos. | c. | natural variations in a population. | d. | descent with
modification. |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which concept is NOT included in the modern theory of evolution?
a. | descent with modification | b. | natural selection | c. | transmission of
acquired characteristics | d. | competition among the members of a
population |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which of the following statements describe what all members of a population
share?
a. | They are temporally isolated from each other. | b. | They are
geographically isolated from each other. | c. | They are members of the same
species. | d. | They have identical genes. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Interbreeding among members of a population results in
a. | different types of alleles in the gene pool. | b. | changes in the
relative frequencies of alleles in the gene pool. | c. | no changes in the relative frequencies of
alleles in the gene pool. | d. | an absence of genetic variation in the
population. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which of the following is NOT a way in which natural selection affects the
distribution of phenotypes?
a. | directional selection | c. | disruptive selection | b. | stabilizing selection | d. | chance events |
|
|
|
30.
|
When individuals at only one end of a bell curve of phenotype frequencies have
high fitness, the result is
a. | directional selection. | c. | disruptive selection. | b. | stabilizing
selection. | d. | genetic
drift. |
|
|
|
31.
|
When individuals with an average form of a trait have the highest fitness, the
result is
a. | not predictable. | c. | directional selection. | b. | disruptive
selection. | d. | stabilizing
selection. |
|
|
|
32.
|
If a mutation introduces a new skin color in a lizard population, which factor
might determine whether the frequency of the new allele will increase?
a. | how many other alleles are present | b. | whether the mutation makes some lizards more
fit for their environment than other lizards | c. | how many phenotypes the population
has | d. | whether the mutation was caused by nature or by human
intervention |
|
|
|
33.
|
In genetic drift, allele frequencies change because of
a. | mutations. | c. | natural selection. | b. | chance. | d. | genetic
equilibrium. |
|
|
|
34.
|
The genetic equilibrium of a population can be disturbed by each of the
following EXCEPT
a. | nonrandom mating. | b. | movement into and out of the
population. | c. | a large population size. | d. | mutations. |
|
|
|
35.
|
According to the Hardy-Weinberg principle, genetic equilibrium would be more
likely in a population of mice if
a. | the population size rapidly decreases. | b. | mutation rates within the population
rise. | c. | no natural selection takes place. | d. | there is frequent movement into and out of the
population. |
|
|
|
36.
|
The separation of populations by barriers such as rivers, mountains, or bodies
of water is called
a. | temporal isolation. | c. | behavioral isolation. | b. | geographic
isolation. | d. | genetic
equilibrium. |
|
|
|
37.
|
A factor that is necessary for the formation of a new species is
a. | reproduction at different times. | c. | different mating
behaviors. | b. | geographic barriers. | d. | reproductive isolation. |
|
|
|
38.
|
The geographic isolation of two populations of a species tends to increase
differences between their gene pools because it
a. | prevents interbreeding between the populations. | b. | prevents
interbreeding within each population. | c. | causes temporal isolation of the two
populations. | d. | increases differences in courtship behavior. |
|
|
|
39.
|
Although they often live in the same habitat, the American toad breeds earlier
in the spring than the Fowler’s toad does. What can be inferred from this information?
a. | The two species do not interbreed because of geographic
isolation. | b. | The two species do not interbreed because of temporal isolation. | c. | The two species
interbreed throughout the spring season. | d. | The American toad will cause the extinction of
the Fowler’s toad. |
|
|
|
40.
|
What did Peter and Rosemary Grant learn about mate choice from the
Galápagos finches?
a. | Phenotype plays no role in mate choice. | b. | Finches prefer mates
with beaks similar in size to their own. | c. | Finches prefer mates with smaller beaks than
their own. | d. | Finches prefer mates with larger beaks than their
own. |
|
|
|
41.
|
In Rosemary and Peter Grant’s study of the Galápagos finches, what
process was encouraged by ecological competition during the dry season?
a. | stabilizing selection | c. | directional selection | b. | reproductive
isolation | d. | genetic
drift |
|
|
|
42.
|
Which system regulates and controls growth, development, and metabolism?
a. | endocrine system | c. | integumentary system | b. | lymphatic system | d. | skeletal system |
|
|
|
43.
|
Which type of tissue lines your internal organs?
a. | epithelial | c. | nerve | b. | connective | d. | muscle |
|
|
|
44.
|
Which type of tissue enables a person’s fingers to move as he or she plays
the piano?
a. | epithelial | c. | nerve | b. | connective | d. | muscle |
|
|
|
45.
|
Which type of tissue provides support for the body?
a. | epithelial | c. | nerve | b. | connective | d. | muscle |
|
|
|
46.
|
Which system coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal
and external environment?
a. | lymphatic system | c. | excretory system | b. | nervous system | d. | reproductive
system |
|
|
|
47.
|
What begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the
environment?
a. | a threshold | c. | an impulse | b. | an action potential | d. | a dendrite |
|
|
|
48.
|
What is the function of neurotransmitters?
a. | to transmit nerve impulses through dendrites | b. | to stimulate the
production of epinephrine | c. | to transmit nerve impulses across
synapses | d. | none of the above |
|
|
|
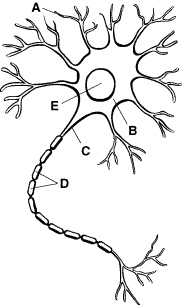
Figure
35–1
|
|
|
49.
|
Refer to Figure 35–1. The cell body of a neuron collects information from
which structure?
|
|
|
50.
|
Which division(s) of the peripheral nervous system transmit(s) impulses from
sense organs to the central nervous system?
a. | sensory division | c. | sensory and motor divisions | b. | motor
division | d. | spinal cord
division |
|
|
|
51.
|
Which of the following general categories of sensory receptors are located
everywhere in the body except the brain?
a. | thermoreceptors | c. | photoreceptors | b. | mechanoreceptors | d. | pain receptors |
|
|
|
52.
|
Sensory receptors that are sensitive to chemicals are found in the
a. | skin, body core, and hypothalamus. | c. | eyes. | b. | skin, skeletal
muscles, and inner ears. | d. | nose and taste buds. |
|
|
|
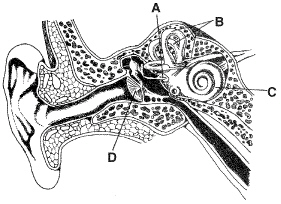
Figure
35–2
|
|
|
53.
|
Which labeled structure in Figure 35–2 creates pressure waves in the
cochlea?
a. | structure A | c. | structure C | b. | structure B | d. | structure D |
|
|
|
54.
|
Drugs that increase heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate are
called
a. | stimulants. | c. | opiates. | b. | depressants. | d. | alcohol. |
|
|
|
55.
|
What system does alcohol immediately affect?
a. | digestive | c. | nervous | b. | circulatory | d. | endocrine |
|
|
|
56.
|
The endocrine system is made up of
a. | hormones. | c. | gonads. | b. | glands. | d. | prostaglandins. |
|
|
|
57.
|
The nervous system is to a telephone as the endocrine system is to a
a. | chemical message. | c. | radio broadcast. | b. | television set. | d. | hormone. |
|
|
|
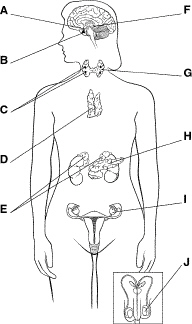
Figure
39–1
|
|
|
58.
|
Figure 39–1 shows the body’s
a. | hormones. | c. | endocrine glands. | b. | target cells. | d. | exocrine
glands. |
|
|
|
59.
|
What is the function of the structure labeled H in Figure 39–1?
a. | to produce sex hormones | c. | to produce insulin and
glucagon | b. | to produce thyroxine | d. | to produce thymosin |
|
|
|
60.
|
A thermostat is a good example of a(an)
a. | hormone-receptor complex. | c. | prostaglandin. | b. | feedback
system. | d. | exocrine
gland. |
|
|
|
61.
|
One way the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis is by having
a. | each gland secrete only one hormone. | b. | two hormones with opposite effects regulate
certain things. | c. | only steroid hormones regulate important functions. | d. | the pituitary gland
regulate all the other glands. |
|
|
|
62.
|
Which endocrine gland secretes sex hormones?
a. | adrenal medulla | c. | hypothalamus | b. | testis | d. | pituitary |
|
|
|
63.
|
Puberty usually begins between the ages of
a. | 5 and 8. | c. | 16 and 19. | b. | 9 and 15. | d. | 20 and 25. |
|
|
|
64.
|
Which hormones stimulate the gonads to mature?
a. | FSH and LH | c. | androgens | b. | estrogens | d. | testosterone and
progesterone |
|
|
|
65.
|
Testosterone is needed for the development of
a. | eggs. | c. | the uterus. | b. | sperm. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
66.
|
Specialized sex cells are known as
a. | gametes. | c. | gonads. | b. | hormones. | d. | organs. |
|
|
|
67.
|
Which of the following is NOT a function of the female reproductive
system?
a. | to produce eggs | b. | to prepare the body to carry an
embryo | c. | to deliver sperm | d. | to release eggs into the Fallopian
tubes |
|
|
|
68.
|
Which of the following is NOT a phase in the menstrual cycle?
a. | menstruation | c. | fertilization | b. | luteal | d. | ovulation |
|
|
|
69.
|
One menstrual cycle usually lasts about a
a. | day. | c. | month. | b. | week. | d. | year. |
|
|
|
70.
|
The chances of fertilization are very good if sperm are present and a(an)
a. | blastocyst is already present. | c. | woman is
menstruating. | b. | egg is in the Fallopian tubes. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
71.
|
During the process of fertilization, which step happens first?
a. | The sperm’s nucleus enters the egg cell. | b. | Enzymes break down
the protective layer of the egg cell membrane. | c. | A sperm attaches to a binding site on the egg
cell membrane. | d. | The cell membrane of the egg cell changes. |
|
|
|
72.
|
Where does fertilization usually occur?
a. | Fallopian tube | c. | uterus | b. | ovary | d. | vagina |
|
|
|
73.
|
The placenta connects the
a. | fetus to the mother’s uterus. | c. | umbilical cord to the
mother’s vagina. | b. | ectoderm to the endoderm. | d. | uterus to the
cervix. |
|
|
|
74.
|
Which of the following usually develop(s) during childhood?
a. | personality | b. | social skills | c. | long bones, to 80
percent of adult height | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
75.
|
All of the following usually occur during adolescence EXCEPT
a. | a growth spurt. | b. | secondary sex
characteristics. | c. | puberty. | d. | the appearance of first permanent
teeth. |
|
Modified True/False (Value 25)
Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false,
change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true.
|
|
|
76.
|
Animal breeders maintain cat and dog breeds by the process of
hybridization. _________________________
|
|
|
77.
|
Exposing a population of plants to radiation or certain chemicals can increase
the frequency of mutations that occur within the population. _________________________
|
|
|
78.
|
A polyploid plant has more than two copies of each gene.
_________________________
|
|
|
79.
|
To produce a recombinant plasmid, the plasmid and the foreign DNA are cut with
a different restriction enzyme. _________________________
|
|
|
80.
|
Scientists use genetic markers to determine which cells have been
successfully transformed. _________________________
|
|
|
81.
|
Bacterial cells that have been transformed with a plasmid that carries a genetic
marker for resistance to the antibiotic tetracycline will not survive in a culture treated
with tetracycline. _________________________
|
|
|
82.
|
Some transgenic animals grow faster because they have extra copies of
growth hormone genes. _________________________
|
|
|
83.
|
Because all members of a population can interbreed, biologists often
study their genes as a single group. _________________________
|
|
|
84.
|
Most inheritable differences are due to gene shuffling that occurs during the
production of gametes. _________________________
|
|
|
85.
|
Natural selection on single-gene traits can lead to changes in allele
frequencies. _________________________
|
|
|
86.
|
In small populations, an allele can become more or less common simply by
chance. _________________________
|
|
|
87.
|
Genetic drift may occur when a small group of individuals colonize a new
habitat. _________________________
|
|
|
88.
|
In a population of birds, if females prefer males with long tails, the
population violates the condition of directional selection described by the Hardy-Weinberg
principle. _________________________
|
|
|
89.
|
In the type of reproductive isolation called behavioral isolation, two
populations are separated by barriers such as rivers or mountains. _________________________
|
|
|
90.
|
The first step of the speciation of the Galápagos finches likely was
the arrival of founders from South America. _________________________
|
|
|
91.
|
The hypothalamus is to your body as the thermostat is to the internal
environment of a house. _________________________
|
|
|
92.
|
The brain and spinal cord can withstand considerable trauma due to the
meninges acting as a shock absorber. ______________________________
|
|
|
93.
|
If you accidentally hit your toe on a desk and then quickly move your leg in
response, the pathway that the nerve impulse takes from your toe to your leg is called a reflex
arc._________________________
|
|
|
94.
|
Chemoreceptors are associated with the sense of smell and touch.
_________________________
|
|
|
95.
|
A person with a relatively small number of cones in the retinas may have
trouble distinguishing colors. _________________________
|
|
|
96.
|
The cochlea and the two tiny sacs located behind it help the body
maintain its equilibrium. ______________________________
|
|
|
97.
|
About 40 percent of the fatal accidents that occur on Americans highways involve
the drug alcohol. _________________________
|
|
|
98.
|
Thyroxine inhibits the secretion of TSH by the anterior pituitary gland,
which maintains homeostasis. _________________________
|
|
|
99.
|
The parathyroid glands secrete hormones that help the body deal with
stress. ______________________________
|
|
|
100.
|
If the primary germ layers fail to form normally during gastrulation, the
embryo could develop misshapen organs. _________________________
|
Completion (Value 25)
Complete
each statement.
|
|
|
101.
|
Humans use selective breeding to pass desired _________________________ on to
the next generation of organisms.
|
|
|
102.
|
____________________ is the technique of selective breeding that has led to
deformities in certain dog breeds.
|
|
|
103.
|
Genetic defects caused by excessive inbreeding can be eliminated through the
process of _________________________.
|
|
|
104.
|
A DNA sample will form a single band on an electrophoresis gel if all the
fragments are the same ____________________.
|
|
|
105.
|
Some plasmids have genetic markers that make them resistant to
____________________.
|
|
|
106.
|
The insulin produced by __________ bacteria is identical to the insulin produced
by humans because both are coded by the same DNA sequence.
|
|
|
107.
|
The geologist ____________________ proposed that past changes in Earth must be
explained in terms of events and processes observable today.
|
|
|
108.
|
According to Darwin’s theory of evolution, ____________________ change
over time.
|
|
|
109.
|
According to Darwin’s theory of evolution, all species on Earth are united
by _________________________.
|
|
|
110.
|
When the phenotypes of polygenic traits are represented by a bell curve, the
____________________ of individuals close together on the curve is not very different.
|
|
|
111.
|
According to the _________________________ principle, allele frequencies in a
population will remain constant unless one or more of five specific factors cause those frequencies
to change.
|
|
|
112.
|
For new species to evolve, populations must be ____________________ isolated
from each other.
|
|
|
113.
|
If two populations have been reproductively isolated and can no longer breed and
produce fertile offspring, the process of _________________________ has occurred.
|
|
|
114.
|
Your skin, hair, nails, and sweat and oil glands make up your
_________________________ system.
|
|
|
115.
|
Neurons are classified into three types according to the ____________________
the impulse travels.
|
|
|
116.
|
The process by which a stimulus produces a response that opposes the original
stimulus is called ____________________ inhibition.
|
|
|
117.
|
The difference in electrical charge across the cell membrane of a resting neuron
is its resting ____________________.
|
|
|
118.
|
The two major divisions of the human nervous system are the central and the
____________________ nervous systems.
|
|
|
119.
|
Small muscles attached to the ____________________ of your eye change its shape
to help you focus on near or distant objects.
|
|
|
120.
|
Cirrhosis of the liver is a possible result of the long-term use of
____________________.
|
|
|
121.
|
The ____________________ system is made up of glands that release their products
into the ____________________.
|
|
|
122.
|
If a child’s diet lacks iodine, the ____________________ gland cannot
produce its hormone and the child is likely to develop a condition called
____________________.
|
|
|
123.
|
In the female body, each egg is surrounded by a ____________________, which
breaks open when the egg is mature.
|
|
|
124.
|
If the temperature of the scrotum increases by 5º Celsius,
____________________ may not develop properly.
|
|
|
125.
|
The placenta is the connection between the ____________________ and the
developing fetus.
|
Short Answer (Value 50)
|
|
|
126.
|
A mule is produced by mating a male donkey with a female horse. What can you
conclude, in general, about the characteristics of a mule?
|
|
|
127.
|
Why would breeders want to increase a population’s mutation rate?
|
|
|
128.
|
What is a plasmid?
|
|
|
129.
|
Why do transgenic bacteria that have the gene for human insulin produce insulin
in great abundance?
|
|
|
130.
|
Compare the genes in Dolly and the sheep from which she was cloned.
|
|
|
131.
|
Compare the sexes of an animal clone and the animal from which it was cloned.
Explain your answer.
|
|
|
132.
|
In what way did the voyage of the Beagle provide Charles Darwin with an
ideal opportunity for collecting and analyzing data?
|
|
|
133.
|
State a general observation that Charles Darwin made about organisms and their
environments.
|
|
|
134.
|
In artificial selection, what factor substitutes for naturally occurring
selection pressures?
|
|
|
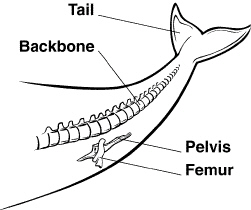
Figure
15–1
|
|
|
135.
|
What did Charles Darwin conclude about the existence of a common ancestor for
all life?
|
|
|
136.
|
Are the members of a population necessarily the same species? Explain.
|
|
|
137.
|
Explain how you could calculate the relative frequency of an allele in a gene
pool.
|
|
|
138.
|
What are the two main sources of genetic variation? Which of them is more
common?
|
|
|
139.
|
Would a trait that has only two distinct phenotypes more likely be a single-gene
trait or a polygenic trait? How do you know?
|
|
|
140.
|
Why might a geographic barrier such as a large river cause the formation of a
new species of small rodents but not a new species of birds?
|
|
|
141.
|
How does the work of Peter and Rosemary Grant in the Galápagos relate to
the work of Charles Darwin?
|
|
|
142.
|
How can the nervous system help a person run without falling? Explain.
|
|
|
143.
|
At what location does a neuron transfer an impulse to another cell?
|
|
|

Figure
35–1
|
|
|
144.
|
Identify the structure and its labeled parts illustrated in Figure
35–1.
|
|
|
145.
|
What is a motor neuron?
|
|
|
146.
|
Name two stimuli from the environment. For each, name the main sense involved
and the sense organ responsible for detecting the stimulus.
|
|
|
147.
|
How do opiates help people overcome sensations of pain?
|
|
|
148.
|
Explain why the body of an athlete who takes an artificial form of testosterone,
such as a steroid, might stop producing its own testosterone.
|
|
|

Figure
39–1
|
|
|
149.
|
Which glands are labeled C in Figure 39–1? What is the main function of
these glands?
|
|
|
150.
|
Many sperm will take the same path toward fertilizing an egg. What prevents more
than one sperm from fertilizing an egg?
|
Essay (Value 24)
|
|
|
151.
|
Explain an advantage and a disadvantage of inbreeding.
|
|
|
152.
|
Compare and contrast the techniques used in genetic engineering and in selective
breeding to produce organisms with desired traits.
|
|
|
153.
|
In the process of cloning a sheep, Ian Wilmut removed a nucleus from an egg cell
of one sheep and then substituted the nucleus from a body cell of a second sheep. Why did he
substitute the nucleus of a body cell rather than the nucleus of a second egg cell?
|
|
|
154.
|
Why is it possible that Alfred Wallace independently developed the same ideas
about evolution that Darwin did?
|
|
|
155.
|
If the relative frequency of a single allele for a particular trait declines
over time, what would happen to the relative frequencies of some or all other alleles for that trait?
Explain.
|
|
|
156.
|
How are directional selection and disruptive selection similar? How are they
different?
|
|
|
157.
|
If each of the Galápagos Islands had contained an identical assortment and
abundance of vegetation, would the impact of natural selection have been as pronounced as it was?
Explain.
|
|
|
158.
|
Identify functions of the hormones released by the pituitary gland. What
controls the release of these hormones?
|
|
|
159.
|
Starting with the follicular phase, identify the hormones that are produced
during the female’s menstrual cycle. Give the function of each hormone.
|
|
|
160.
|
What is puberty?
|