Matching (Value 30)
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | oxidation number | c. | oxidizing agent | b. | half-reaction | d. | reducing agent |
|
|
|
1.
|
substance that accepts electrons
|
|
|
2.
|
substance that donates electrons
|
|
|
3.
|
integer related to the number of electrons under an atom's control
|
|
|
4.
|
reaction showing either the reduction or the oxidation reaction
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below.
a. | anode | d. | half-cell | b. | battery | e. | cathode | c. | fuel
cell |
|
|
|
5.
|
the electrode at which oxidation occurs
|
|
|
6.
|
one part of a voltaic cell in which either oxidation or reduction
occurs
|
|
|
7.
|
the electrode at which reduction occurs
|
|
|
8.
|
a group of cells that are connected together
|
|
|
9.
|
a voltaic cell in which a fuel substance undergoes oxidation and from which
electrical energy is obtained continuously
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | peptide | e. | disaccharide | b. | monosaccharide | f. | polysaccharide | c. | protein | g. | amino acid | d. | nucleotides | h. | nucleic acid |
|
|
|
10.
|
a simple carbohydrate molecule
|
|
|
11.
|
polymers produced by the linkage of monosaccharide monomers
|
|
|
12.
|
a sugar that forms from two monosaccharides
|
|
|
13.
|
any compound that contains an amino group and a carboxyl group in the same
molecule
|
|
|
14.
|
a peptide with more than 100 amino acids
|
|
|
15.
|
any combination of amino acids in which the amino group of one acid is united
with the carboxyl group of another through an amide bond
|
|
|
16.
|
nitrogen-containing polymers found primarily in cell nuclei
|
|
|
17.
|
monomers that make up DNA and RNA
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | positron | d. | transuranium element | b. | alpha particle | e. | gamma radiation | c. | beta
particle | f. | transmutation |
|
|
|
18.
|
element with atomic number greater than 92
|
|
|
19.
|
emitted helium nucleus
|
|
|
20.
|
energetic electron from decomposed neutron
|
|
|
21.
|
high-energy photons emitted by a radioisotope
|
|
|
22.
|
particle of charge +1 and mass equal to that of an electron
|
|
|
23.
|
conversion of an atom of one element to an atom of another element
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | fission | e. | scintillation counter | b. | fusion | f. | neutron absorption | c. | Geiger counter | g. | neutron moderation | d. | radioisotope |
|
|
|
24.
|
element with unstable nucleus
|
|
|
25.
|
combination of two nuclei to form a nucleus of greater mass
|
|
|
26.
|
process that decreases the number of slow-moving neutrons
|
|
|
27.
|
splitting of nucleus into smaller fragments
|
|
|
28.
|
process that slows down neutrons so a reactor fuel can capture them to continue
a chain reaction
|
|
|
29.
|
radiation detector that makes use of a phosphor-coated surface
|
|
|
30.
|
radiation detector that makes use of a gas-filled metal tube
|
Multiple Choice (Value 76)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
31.
|
Oxidation is ____.
a. | a loss of oxygen | c. | a loss of electrons | b. | a gain of electrons | d. | a gain of
hydrogen |
|
|
|
32.
|
What are transferred in an oxidation-reduction reaction?
a. | protons | c. | electrons | b. | ions | d. | atoms |
|
|
|
33.
|
In the reaction of sodium with oxygen, which atom is reduced?
a. | sodium | c. | both a and b | b. | oxygen | d. | neither a nor b |
|
|
|
34.
|
In the reaction of calcium with chlorine, which atom is oxidized?
a. | calcium | c. | both a and b | b. | chlorine | d. | neither a nor b |
|
|
|
35.
|
In the reaction of hydrogen with iodine, which atom is oxidized?
a. | hydrogen | c. | both a and b | b. | iodine | d. | neither a nor b |
|
|
|
36.
|
What is the reducing agent in the following reaction? 2Na + 2H 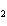 O ® 2NaOH + H 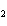 a. | Na | c. | NaOH | b. | H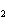 O O | d. | H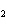 |
|
|
|
37.
|
What is the oxidizing agent in the following reaction? I 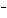 +
MnO 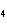 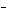 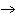 I 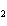 + MnO 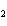
|
|
|
38.
|
The oxidation number of sulfur in each of the following is +6 EXCEPT for
____.
|
|
|
39.
|
In which of the following compounds is the oxidation number of nitrogen
different from the other three?
|
|
|
40.
|
Identify the atom that increases in oxidation number in the following redox
reaction. 2MnO 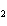 + 2K 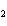 CO 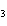 + O 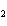  2KMnO 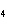 + 2CO 
|
|
|
41.
|
Which atom has a change in oxidation number of –3 in the following redox
reaction? K 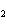 Cr 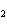 O 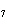 + H 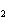 O + S
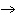 KOH + Cr 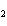 O 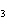 +
SO 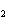
|
|
|
42.
|
In the following unbalanced reaction, which atom is reduced? H 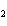 O +
Cl 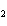 + SO 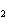  HCl + H 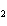 SO 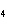 a. | hydrogen | c. | chlorine | b. | oxygen | d. | sulfur |
|
|
|
43.
|
In the following unbalanced reaction, which atom is oxidized? HNO 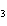 + HBr  NO + Br 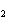 + H 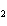 O a. | hydrogen | c. | oxygen | b. | nitrogen | d. | bromine |
|
|
|
44.
|
Which element decreases its oxidation number in the following
reaction? BiCl 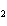 + Na 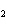 SO 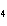 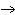 2NaCl + BiSO 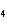 a. | bismuth | b. | chlorine | c. | oxygen | d. | No element decreases its oxidation
number. |
|
|
|
45.
|
Which element decreases its oxidation number in the following reaction? I 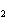 + 2KCl 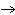 2KI + Cl 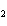 a. | iodine | b. | potassium | c. | chlorine | d. | No element decreases its oxidation
number. |
|
|
|
46.
|
Which element increases its oxidation number in the following reaction? 2Na +
2H 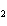 O 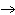 2NaOH + H 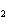 a. | sodium | b. | hydrogen | c. | oxygen | d. | No element increases its oxidation
number. |
|
|
|
47.
|
Which of the following reactions is a redox reaction?
a. | acid-base | c. | combustion | b. | double-replacement | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
48.
|
Which metal is the most easily oxidized?
a. | highly active metal | c. | slightly active metal | b. | moderately active
metal | d. | an inactive
metal |
|
|
|
49.
|
Of the following metals, which ions are most easily reduced?
a. | iron | c. | aluminum | b. | mercury | d. | potassium |
|
|
|
50.
|
Which of the following metals is oxidized by calcium ions?
a. | potassium | c. | iron | b. | zinc | d. | lead |
|
|
|
51.
|
Which metal ion is reduced by lead?
a. | potassium | c. | mercury | b. | calcium | d. | cadmium |
|
|
|
52.
|
Identify the pair of metals that lists the more easily oxidized metal on the
left.
a. | Ag, Na | c. | Ca, Al | b. | Fe, K | d. | K, Li |
|
|
|
53.
|
How can a redox reaction be used as a source of electrical energy?
a. | Two half-reactions must be physically separated. | b. | One half-reaction
must involve two metals. | c. | Two half-reactions must involve more than one
electron. | d. | One half-reaction must use a metal wire electrode. |
|
|
|
54.
|
What happens in a voltaic cell?
a. | Chemical energy is changed to electrical energy. | b. | Electrical energy is
changed to chemical energy. | c. | Electrical energy is changed to magnetic
energy. | d. | Magnetic energy is changed to electrical energy. |
|
|
|
55.
|
At which electrode does oxidation occur in a voltaic cell?
a. | anode only | b. | cathode only | c. | both anode and
cathode | d. | either anode or cathode, depending on the metal |
|
|
|
56.
|
Which electrode is labeled as positive in a voltaic cell?
a. | anode only | c. | both anode and cathode | b. | cathode
only | d. | neither anode nor
cathode |
|
|
|
57.
|
In a voltaic cell, from which electrode do the free electrons originate?
a. | anode only | c. | both anode and cathode | b. | cathode
only | d. | neither anode nor
cathode |
|
|
|
58.
|
Which of the following factors does NOT affect the voltage produced in a voltaic
cell?
a. | metal of the electrodes | c. | temperature | b. | concentrations of
ions | d. | pressure |
|
|
|
59.
|
What is the electrode in the center of the most common dry cell made of?
a. | copper | c. | iron | b. | zinc | d. | graphite |
|
|
|
60.
|
What metal is oxidized in the most common dry cell?
a. | copper | c. | iron | b. | zinc | d. | carbon |
|
|
|
61.
|
What is reduced in the most common dry cell?
a. | copper | c. | manganese dioxide | b. | zinc | d. | carbon |
|
|
|
62.
|
Which of the following is true for a dry cell?
a. | It contains boric acid, which is a solid acid. | b. | The graphite rod
does not undergo reduction, even though it is the cathode. | c. | It can be recharged
many times. | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
63.
|
Why can’t a lead storage battery be recharged indefinitely?
a. | A direct current must pass through the cells. | b. | The electrodes lose
lead sulfate. | c. | It is difficult to reverse the direction of current flow. | d. | The electrolyte is
too expensive. |
|
|
|
64.
|
How is a lead storage battery recharged?
a. | A direct current is applied to it. | b. | A magnet is held close to
it. | c. | Alternating current is forced through it. | d. | The pressure on it
is increased. |
|
|
|
65.
|
Which of the following is true about fuel cells?
a. | They only produce energy in short bursts. | b. | They are
inexpensive. | c. | They have never been built or used. | d. | They can be designed so that they emit no
pollutants. |
|
|
|
66.
|
What is the cell potential?
a. | the difference in reduction potentials of the half-cells | b. | the difference in
oxidation potentials of the half-cells | c. | the sum of reduction potentials of the
half-cells | d. | the sum of oxidation potentials of the half-cells |
|
|
|
67.
|
What standard reduction electrode has a half-cell potential of 0.00 V?
a. | oxygen | c. | lithium | b. | hydrogen | d. | fluorine |
|
|
|
68.
|
What symbol is used to show the standard reduction potential of an oxidation
reaction in a half-cell?
|
|
|
69.
|
In which direction will the following reaction go if the standard reduction
potentials are 0.80 V for Ag/Ag 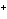 and –0.44 V for Fe/Fe 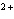 ?
Ag 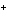 + Fe 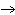 Ag + Fe 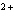 a. | forward | c. | No such reaction can occur. | b. | reverse | d. | Not
enough information is given. |
|
|
|
70.
|
The two products of photosynthesis are ____.
a. | heat and oxygen | c. | glucose and oxygen | b. | heat and light | d. | carbon dioxide and
water |
|
|
|
71.
|
Which form of polysaccharide is found in animals?
a. | starch | c. | sucrose | b. | glycogen | d. | glucose |
|
|
|
72.
|
The repeating unit of cellulose is ____.
a. | glucose | c. | fructose | b. | lactose | d. | sucrose |
|
|
|
73.
|
Differences between amino acids are normally due to differences in which part of
the molecule?
a. | amino group | c. | central carbon | b. | carboxyl group | d. | side chain |
|
|
|
74.
|
A peptide bond is a bond between which functional groups?
a. | amino and alcohol | c. | carboxyl and alcohol | b. | amino and carboxyl | d. | carbonyl and
carbonyl |
|
|
|
75.
|
What is the role of an enzyme?
a. | speeds up biochemical reactions | b. | causes biochemical
reactions | c. | is a product in biochemical reactions | d. | provides extra heat for biochemical
reactions |
|
|
|
76.
|
In which of the following substances can a lipid NOT dissolve?
a. | water | c. | ketone | b. | alcohol | d. | carboxylic acid |
|
|
|
77.
|
Saponification is what type of reaction?
a. | hydrolysis | c. | hydrogenation | b. | dehydrogenation | d. | acid-base |
|
|
|
78.
|
An ester of a long-chain fatty acid and a long-chain alcohol is a(n)
____.
a. | fat | c. | triglyceride | b. | oil | d. | wax |
|
|
|
79.
|
A nucleotide contains which of the following functional groups?
a. | phosphate | c. | sulfur | b. | halogen | d. | carboxyl |
|
|
|
80.
|
How many termination code words are there?
a. | three | c. | twenty | b. | four | d. | thousands |
|
|
|
81.
|
Which of the following molecules is responsible for transmitting the energy
needed by cells?
|
|
|
82.
|
Which of the following terms represents the entire set of chemical reactions
carried out by an organism?
a. | anabolism | c. | metabolism | b. | catabolism | d. | omnibolism |
|
|
|
83.
|
An unstable nucleus ____.
a. | increases its nuclear mass by fission | c. | emits energy when it
decays | b. | increases its half-life | d. | expels all of its protons |
|
|
|
84.
|
What is the change in atomic mass when an atom emits gamma radiation?
a. | decreases by 2 | c. | remains the same | b. | decreases by 1 | d. | increases by 1 |
|
|
|
85.
|
Ionizing radiation that consists of helium nuclei is ____.
a. | X radiation | c. | beta radiation | b. | gamma radiation | d. | alpha radiation |
|
|
|
86.
|
What is the change in the atomic number when an atom emits an alpha
particle?
a. | decreases by 2 | c. | increases by 1 | b. | decreases by 1 | d. | increases by 2 |
|
|
|
87.
|
What is the change in atomic number when an atom emits a beta particle?
a. | decreases by 2 | c. | increases by 2 | b. | decreases by 1 | d. | increases by 1 |
|
|
|
88.
|
What particle decomposes to produce the electron of beta radiation?
a. | proton | c. | electron | b. | neutron | d. | positron |
|
|
|
89.
|
Which of the following materials is necessary to stop a beta particle?
a. | three feet of concrete | c. | thin pieces of wood | b. | three inches of lead | d. | single sheet of
paper |
|
|
|
90.
|
Which of the following materials is most effective for stopping gamma
radiation?
a. | several cm of lead | c. | single sheet of aluminum foil | b. | one cm of
water | d. | single sheet of
paper |
|
|
|
91.
|
What does the band of stability for atomic nuclei refer to?
a. | the ratio of protons to neutrons | b. | the ratio of neutrons to
protons | c. | the ratio of beta particles to neutrinos | d. | the ratio of alpha
particles to beta particles |
|
|
|
92.
|
If an isotope decays by the process of beta emission, ____.
a. | the mass number changes | b. | the atomic number changes | c. | protons are given
off | d. | the number of neutrons remains the same |
|
|
|
93.
|
What particle is needed to complete the following equation? 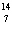 N + ____
 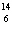 C + 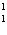 H
|
|
|
94.
|
To what element does polonium-208 (atomic number 84) decay when it emits an
alpha particle?
|
|
|
95.
|
A transmutation reaction must always involve a(n) ____.
a. | change in the number of electrons in the atom | b. | decrease in the
number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom | c. | increase in the number of neutrons in the
nucleus of an atom | d. | change in the number of protons in a nucleus of
an atom |
|
|
|
96.
|
The production of carbon-14 ____.
a. | takes place in the upper atmosphere | b. | is mostly due to fallout from nuclear
explosions | c. | occurs to a large extent in nuclear reactors | d. | is caused by
photosynthesis in plants |
|
|
|
97.
|
Controlled nuclear chain reactions ____.
a. | take place in nuclear reactors | b. | are always fusion reactions | c. | never produce
radioactive by-products | d. | are characteristic of atomic
bombs |
|
|
|
98.
|
Which type of coolant(s) usually is (are) used to remove heat from a nuclear
reactor core?
a. | water only | c. | liquid sodium or water | b. | liquid sodium
only | d. | CFCs |
|
|
|
99.
|
A reaction that results in the combining of smaller atomic nuclei is
____.
a. | chemical | c. | fusion | b. | fission | d. | ionization |
|
|
|
100.
|
What does neutron absorption accomplish in a nuclear reactor?
a. | It slows down the reaction. | b. | It speeds up the reaction. | c. | It increases the
rate of heat absorption. | d. | It recycles the
fuel. |
|
|
|
101.
|
Control rods made of ____.
a. | carbon | c. | plutonium | b. | liquid sodium | d. | cadmium |
|
|
|
102.
|
Which of the following statements is correct?
a. | Water is used to moderate (slow down) neutrons in a nuclear
reactor. | b. | Carbon control rods are used to absorb neutrons in a nuclear fission
reaction. | c. | A very high temperature is required to initiate a nuclear fission
reaction. | d. | The energy released from the sun is the result of a nuclear fission
reaction. |
|
|
|
103.
|
What type of radiation is best detected by a scintillation counter?
a. | alpha radiation only | c. | alpha and beta radiation only | b. | gamma radiation
only | d. | all types of
radiation |
|
|
|
104.
|
What instrument is used routinely to check a person's exposure to
radiation?
a. | Geiger counter | c. | film badge | b. | scintillation counter | d. | moderating rod |
|
|
|
105.
|
What is the main detector of a Geiger counter?
a. | ionizable gas in a metal tube | c. | plates of ionizable
plastic | b. | phosphor-covered surface | d. | potassium metal surface |
|
|
|
106.
|
Radioisotopes taken internally for medical reasons ____.
a. | must be eliminated from the body slowly | b. | should be
fissionable isotopes | c. | are usually deposited in fat
tissue | d. | should have a short half-life |
|