Matching (Value 5)
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | spontaneous reaction | d. | reaction mechanism | b. | entropy | e. | elementary reaction | c. | chemical
equilibrium |
|
|
|
1.
|
when the forward and reverse reactions take place at the same rate
|
|
|
2.
|
a reaction that releases free energy
|
|
|
3.
|
the measure of disorder
|
|
|
4.
|
Reactants are converted to products in a single step.
|
|
|
5.
|
includes all elementary reactions of a complex reaction
|
Multiple Choice (Value 25)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
6.
|
The energy that is available to do work in a reaction is called ____.
a. | heat | c. | entropy | b. | enthalpy | d. | free energy |
|
|
|
7.
|
Entropy measures ____.
a. | energy | c. | disorder | b. | heat transferred | d. | force |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which physical state of nitrogen has the highest entropy?
a. | solid | c. | gas | b. | liquid | d. | vapor |
|
|
|
9.
|
The amount of disorder in a system is measured by its ____.
a. | activation energy | c. | equilibrium position | b. | entropy | d. | K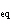 |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which one of the following systems has the highest entropy?
a. | 10 mL of water at 10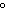 C C | b. | 10 mL of water at 50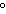 C C | c. | 10 mL of water at
100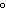 C C | d. | All have the same entropy because all are water. |
|
|
|
11.
|
If a system is left to change spontaneously, in what state will it end?
a. | the same state in which it began | b. | the state with lowest possible
energy | c. | the state with the maximum disorder | d. | the state with the lowest possible energy
consistent with the state of maximum disorder |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which reaction results in the greatest increase in entropy?
a. | A ® B | c. | 2A ® B | b. | A ®
2B | d. | 3A ® B |
|
|
|
13.
|
In which of these systems is the entropy decreasing?
a. | air escaping from a tire | c. | salt dissolving in
water | b. | snow melting | d. | a liquid cooling |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which of the following statements explains why the melting of ice is a
spontaneous reaction at room temperature and pressure?
a. | Melting is accompanied by a decrease of entropy. | b. | Melting is
accompanied by an increase of entropy. | c. | Melting is accompanied by a decrease of
energy. | d. | Melting is accompanied by an increase of energy. |
|
|
|
15.
|
The two factors that determine whether a reaction is spontaneous or
nonspontaneous are ____.
a. | entropy and disorder | b. | entropy and energy | c. | electron
configuration and ionic charge | d. | energy and heat of
reaction |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which of the following statements is true?
a. | All spontaneous processes are exothermic. | b. | All nonspontaneous
processes are endothermic. | c. | All spontaneous processes release free
energy. | d. | Entropy always increases in a spontaneous process. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Spontaneous reactions ____.
a. | are always exothermic | b. | always take place at a rapid
rate | c. | always result in increased disorder of the system | d. | always release free
energy |
|
|
|
18.
|
The melting of ice at temperatures above 0 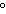 C ____. a. | liberates heat | c. | is not favorable | b. | is not spontaneous | d. | is endothermic |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following is true about the combustion of carbon?
a. | The reaction is spontaneous. | b. | Carbon is produced from oxygen and carbon
dioxide. | c. | Enthalpy remains constant. | d. | Entropy
decreases. |
|
|
|
20.
|
What determines whether or not a reaction is spontaneous?
a. | change in molar volume and heat change | b. | change in enthalpy only | c. | enthalpy change and
entropy change | d. | change in entropy only |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following is true about the numerical value of Gibbs free-energy
change for a spontaneous reaction?
a. | It is not related to enthalpy. | b. | It is negative. | c. | It indicates that
work must be expended. | d. | It is positive for temperatures above 850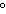 C. C. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which variable is NOT required to calculate the Gibbs free-energy change for a
chemical reaction?
a. | change in enthalpy | c. | temperature in kelvins | b. | temperature in 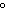 C C | d. | change in
entropy |
|
|
|
23.
|
What is the rate law for the following reaction?
A + 2B ® C + D
a. | rate = k[A][B] | c. | rate =
k[A][B]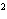 | b. | rate = k[A]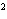 [B] [B] | d. | rate = k[A]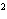 [B] [B]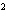 |
|
|
|
24.
|
What is the order of the following reaction? A + 2B ® C + D
a. | zero | c. | second | b. | first | d. | third |
|
|
|
25.
|
In a first-order reaction, how does the rate change if the concentration of the
reactant decreases to one-third its original value?
a. | The rate decreases by a factor of one-ninth. | b. | The rate decreases
by a factor of one-third. | c. | The rate decreases by a factor of
one-half. | d. | The rate stays the same. |
|
|
|
26.
|
If a reaction rate decreases by a factor of one-ninth when a reactant
concentration is decreased by one-third, what is the order of the reaction with respect to that
reactant?
a. | fourth | c. | second | b. | third | d. | first |
|
|
|
27.
|
When nitrous oxide is converted to nitrogen and oxygen, what is the term used to
describe the oxygen atoms formed?
a. | reactants | c. | activated complexes | b. | products | d. | intermediates |
|
|
|
28.
|
An elementary reaction ____.
a. | has only elements as reactants | b. | has only elements as
products | c. | never needs a catalyst | d. | converts reactants to products in a single
step |
|
|
|
29.
|
For a complex reaction, the reaction progress curve ____.
a. | is a flat line | c. | has several hills and valleys | b. | has only one
peak | d. | shows energy versus
pressure |
|
|
|
30.
|
What information is NOT given by an overall equation for a chemical
reaction?
a. | the relative numbers of molecules used | b. | the probable order of the
reaction | c. | the number of atoms participating in the reaction | d. | the reaction
mechanism |
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
31.
|
Calculate the concentration of a silver ion when the solubility product constant
of AgI is 10 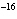 .
|
|
|
32.
|
What is the approximate concentration of aluminum ions if the solubility product
constant of Al(OH) 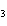 is 27 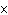 10 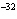 ?
|
|
|
33.
|
The solubility product constant of calcium hydroxide is 6.5 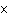 10 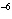 . If 0.10 mol of sodium hydroxide is added to 1 L of 0.0010 M Ca(OH) 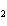 , what is
the final concentration of the calcium ion?
|
|
|
34.
|
In a first-order reaction, what is the rate constant if the rate is
0.050M/s and the reactant concentration is 0.030M?
|
|
|
35.
|
What is the rate of a first-order reaction that has a reactant concentration of
1.1M and a rate constant of 0.14/s?
|
|
|
36.
|
In a first-order reaction, what is the reactant concentration if the rate
constant is 0.2/s and the rate is 0.004M/s?
|
|
|
37.
|
What is the rate of a first-order reaction that has a reactant concentration of
0.1M and a rate constant of 0.1/s?
|
|
|
38.
|
In a first-order reaction, what is the reactant concentration if the rate
constant is 0.1/s and the rate is 0.001M/s?
|
|
|
39.
|
In a first-order reaction, what is the rate constant if the rate is
0.01M/s and the reactant concentration is 0.01M?
|
|
|
40.
|
The rate law for the following reaction is: Rate = k[A] 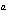 [B] 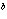 . aA + bB 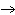 c cC + dD From the following
data, find the kinetic order of the reaction with respect to A and B, as well as the overall
order. Initial Concentration Initial
Concentration Initial Rate of A(mol/L)
of B(mol/L)
(mol/L  s) 0.05
0.05
2 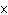 10  0.10
0.05
4 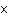 10 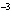 0.20
0.05
8 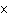 10 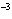 0.01
0.05
0.4  10 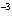 0.01
0.10
3.2 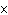 10 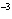 0.01
0.20
25.6 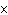 10 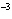
|
|
|
41.
|
In a two-step reaction mechanism, how many elementary reactions occur?
|