True/False (Value 29)
Indicate
whether the statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
In a chosen coordinate system, the position of an object in motion can have
negative values.
|
|
|
2.
|
A time interval is a scalar quantity.
|
|
|
3.
|
The position-time graph of an object moving with a constant average velocity is
always a straight line.
|
|
|
4.
|
Vector measurements have both magnitude and direction.
|
|
|
5.
|
The reading on a speedometer represents the average velocity of the car.
|
|
|
6.
|
A collision between two moving objects can be represented on a position-time
graph.
|
|
|
7.
|
In a chosen coordinate system, the time interval of an object in motion can have
a negative value.
|
|
|
8.
|
The position-time graph of an object moving with a constant velocity is never a
straight line.
|
|
|
9.
|
Acceleration is the rate at which an object’s speed changes.
|
|
|
10.
|
Acceleration is a vector quantity.
|
|
|
11.
|
Acceleration can never be negative.
|
|
|
12.
|
The displacement of an object can be calculated by multiplying its velocity and
the time interval.
|
|
|
13.
|
It is not possible to derive an equation of motion for uniform acceleration
without a time variable.
|
|
|
14.
|
The acceleration of an object is the slope of its velocity-time graph.
|
|
|
15.
|
The sign associated with g, the acceleration due to gravity, depends upon the
choice of the coordinate system.
|
|
|
16.
|
Force is a scalar quantity.
|
|
|
17.
|
The object on which a force acts is called the system.
|
|
|
18.
|
The specific, identifiable cause of a force is called the system.
|
|
|
19.
|
A force cannot exist without an agent and a system.
|
|
|
20.
|
When a force is a push, the force arrows in a free body diagram point towards
the particle.
|
|
|
21.
|
The net force on an object is the resultant of the force vectors.
|
|
|
22.
|
Inertia is a force.
|
|
|
23.
|
The process of breaking a vector into its components is called vector
resolution.
|
|
|
24.
|
The direction of a vector is defined as the angle that the vector makes with the
x-axis, measured clockwise.
|
|
|
25.
|
Multiple vectors can be added together by adding their x-components into one
horizontal vector, then adding their y-components into one vertical vector, and finding the vector
sum of those 2 vectors.
|
|
|
26.
|
Static friction is exerted on one surface by another when the two surfaces are
moving relative to each other.
|
|
|
27.
|
Static friction is exerted on one surface by another when there is no motion
between the surfaces.
|
|
|
28.
|
Vectors can be summed by separately adding the x- and y-components.
|
|
|
29.
|
The equilibrant is equal in magnitude and direction to the net force on an
object.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
30.
|
The magnitude of a vector represents its _____.
a. | velocity | c. | size | b. | direction | d. | color |
|
|
|
31.
|
Which choice is NOT a valid way to construct a motion diagram?
a. | Add together the average speeds of the various objects in motion. | b. | Take a series of
photographs at equal time intervals of a moving object, perpendicular to the direction of motion;
overlay the images to see how the position changes with time. | c. | Draw vectors to
represent the velocities involved. | d. | Add vectors in a head-to-tail manner to
determine the resultant vector. |
|
|
|
32.
|
Duplain St. is 300 m long and runs from west to east between Baron and Burkey.
If Keith is strolling east from Baron at an average velocity of 3 km/hr, and Sue is power-walking
west from Burkey at an average velocity of 6 km/hr, how long will it take them to meet?
a. | 1 minute | c. | 3 minutes | b. | 2 minutes | d. | 6 minutes |
|
|
|
33.
|
A racehorse is running with a uniform speed of 69 km/hr along a
straightaway. What is the time it takes for the horse to cover 400 meters?
a. | 21 seconds | c. | 0.35 hours | b. | 2.1 minutes | d. | 27.6 hours |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which of the following is a pair of scalar quantities?
a. | velocity - distance | c. | time - speed | b. | velocity - displacement | d. | time -
displacement |
|
|
|
35.
|
A man starts his car from rest and accelerates at 1 m/s2 for 2
seconds. He then continues at a constant velocity for 10 seconds until he sees a tree blocking the
road and applies brakes. The car, decelerating at 1 m/s2, finally comes to rest. Which of
the following graphs represents the motion correctly?
|
|
|
36.
|
Given a graph of velocity v. time, what does a horizontal line represent?
a. | The object’s acceleration is positive. | c. | The object’s acceleration is
negative. | b. | The object is moving at constant velocity. | d. | The object is standing
still. |
|
|
|
37.
|
Which formula represents final velocity of an object with average
acceleration?
a. | vi = vf + aDt | c. | vf =
vi  aDt aDt | b. | vf = vi 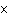 aDt aDt | d. | vf = vi + aDt |
|
|
|
38.
|
Line D represents movement that starts out toward the south, slows down, and
stops. Why is the slope of the line positive?
a. | The velocity is positive. | c. | The acceleration is
negative. | b. | The velocity is negative. | d. | The acceleration is positive. |
|
|
|
39.
|
Which line shows both positive velocity and positive acceleration?
a. | Line A | d. | Line D | b. | Line B | e. | Line E | c. | Line
C |
|
|
|
40.
|
The rate at which an object’s velocity changes is called its _____.
a. | acceleration | c. | displacement | b. | average velocity | d. | scalar
magnitude |
|
|
|
41.
|
Average acceleration vectors on a motion diagram indicate
a. | the size and direction of the average speed during a time
interval. | b. | the size and direction of the average displacement during a time
interval. | c. | the size and direction of the average velocity during a time
interval. | d. | the size and direction of the average acceleration during a time
interval. |
|
|
|
42.
|
The example of a book falling off of a table shows a(n) _____.
a. | contact force | c. | absence of acceleration | b. | scalar
quantity | d. | field
force |
|
|
|
43.
|
Which of the following is not true about a free body diagram?
a. | All forces point away from the particle. | b. | The arrows are
proportional to the size of the forces. | c. | The system is represented by a particle
model. | d. | You always know the magnitude of the forces ahead of
time. |
|
|
|
44.
|
Which of the following is NOT true?
a. | The force on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by the
acceleration. | b. | The force exerted on an object is related in a linear fashion to the acceleration
of the object. | c. | An object moving at constant velocity always
has a force acting on it. | d. | An object moving with constant acceleration
always has a force acting on it. |
|
|
|
45.
|
When an object is in equilibrium, the net force is _____.
a. | zero | c. | negative | b. | positive | d. | changing |
|
|
|
46.
|
“ FA on B = -FB on A” is an expression
of
a. | Newton’s first law | c. | Newton’s third
law | b. | Newton’s second law | d. | Fig Newton’s law |
|
|
|
47.
|
Tension refers to
a. | the force exerted by a string. | c. | dynamic
displacement. | b. | terminal velocity. | d. | free fall. |
|
|
|
48.
|
The normal force (FN) refers to
a. | the parallel contact force exerted by a surface on another
object. | b. | the perpendicular contact force exerted by a surface on another
object. | c. | the perpendicular tension exerted by a surface on a rope. | d. | the parallel
acceleration of a body at terminal velocity. |
|
|
|
49.
|
A weight is hung from the ceiling of an elevator by a massless string.
Under which circumstances will the tension in the cord be the smallest?
a. | The elevator is at rest. | b. | The elevator rises with increasing
speed. | c. | The elevator descends with decreasing speed. | d. | The elevator
descends with increasing speed. |
|
|
|
50.
|
The tangent of an angle is
a. | the length of the side opposite the angle divided by the length of the
hypotenuse. | b. | the length of the side adjacent the angle divided by the length of the
hypotenuse. | c. | the length of the side opposite the angle divided by the length of the adjacent
side. | d. | the length of the hypotenuse divided by the length of the side adjacent the
angle. |
|
|
|
51.
|
The coefficient of kinetic friction is NOT
a. | the slope of the line representing the change in the kinetic friction force and the
normal force. | b. | designated mk. | c. | more than the
coefficient of static friction. | d. | equal to the quotient of the kinetic friction
force and the normal force. |
|
|
|
52.
|
Equilibrium can occur
a. | only if there is constant acceleration. | b. | only if the sum of
the forces is zero. | c. | only if an object is
motionless. | d. | only if the sum of the forces is greater than zero. |
|
|
|
53.
|
A 50.0 kg wooden box is pushed across a floor with a constant speed of 2.5
m/s. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.20. If the force being applied to the box
is halved, what is the resulting acceleration on the box?
a. |  0.98 m/s2 0.98 m/s2 | c. |  5.0
m/s2 5.0
m/s2 | b. |  1.25 m/s2 1.25 m/s2 | d. |  12.5
m/s2 12.5
m/s2 |
|
|
|
54.
|
A 50.0 kg wooden box is pushed across a floor with a constant speed of 2.5
m/s. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.20. If the force being applied to the box
is tripled, what is the resulting acceleration on the box?
a. |  0.98 m/s2 0.98 m/s2 | c. | 3.92
m/s2 | b. | 0.784 m/s2 | d. | 196 m/s2 |
|
Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
55.
|
A(n) ____________________ model is a simplified version of a motion diagram that
represents the object in motion by a series of single points.
|
|
|
56.
|
The vector that represents the sum of the other two vectors is called the
____________________.
|
|
|
57.
|
The absolute value of the average velocity is the average
____________________.
|
|
|
58.
|
A force is ____________________.
|
|
|
59.
|
A force that puts an object in equilibrium is called the
____________________.
|
Matching
|
|
|
a. | position-time graph | c. | motion diagram | b. | particle model | d. | displacement |
|
|
|
60.
|
What represents the motion of an object?
|
|
|
61.
|
What is an example of a motion diagram where the object is replaced by a series
of single points?
|
|
|
62.
|
What diagram can be used to find where and when two objects meet?
|
|
|
63.
|
What is a change of position that has both magnitude and direction?
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
64.
|
What information is provided by the points on the line of a position-time graph
of an object?
|
|
|
65.
|
What is the distance traveled by a vehicle in 12 minutes, if its speed is 35
km/h?
|
|
|
66.
|
Given below is the position-time graph representing the motion of two friends, A
and B, jogging in a park. Use this graph to find their displacements after 4 s. 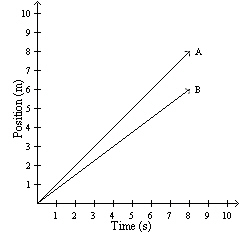
|
|
|
67.
|
What is the difference between average velocity and average speed?
|
|
|
68.
|
Give examples of the four types of motion.
|
|
|
69.
|
A car is traveling north at 88 km/hr (55 mph) on a two-lane road and enters the
south end of a two-way passing zone that is 500 m long. A southbound car enters the north end
of the passing zone and wishes to pass a car in front of it. How much time does the southbound
driver have to pass the car and return to its lane without hitting the northbound car, if it is going
129 km/hr (80 mph)?
|
|
|
70.
|
Mohinder leaves home and rides his bike north at 40 km/hr for 6 km. He stops at
the store and spends 5 minutes buying a magazine. He gets back on his bike and rides south for 2 km
at a speed of 45 km/hr. He stops at the bank and spends 10 minutes doing his
banking.
Construct a position-time graph that shows each leg of Mohinder’s progress from
home to the bank. What is his average velocity?
|
|
|
Below is a motion diagram for an inline skater going in a straight line. The
time interval between successive positions is 2 s. 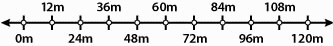
|
|
|
71.
|
What is the displacement of the skater after 8 s?
|
|
|
Identify the system, forces, and agents in each situation.
|
|
|
72.
|
A UNICEF care package falls through the air.
|
|
|
73.
|
A piano is hoisted up into an apartment via a cable winch.
|