True/False (Value 5)
Indicate
whether the statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
Force is a scalar quantity.
|
|
|
2.
|
The object on which a force acts is called the system.
|
|
|
3.
|
A force cannot exist without an agent and a system.
|
|
|
4.
|
A free-body diagram represents forces acting on a system.
|
|
|
5.
|
When a force is a push, the force arrows in a free body diagram point towards
the particle.
|
|
|
6.
|
As the speed of an object moving through a fluid increases, the magnitude of the
drag force decreases.
|
Multiple Choice (Value 5)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
7.
|
Which of the following system of forces provides the block the highest net
force?
a. | 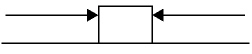 11
N
71 N 11
N
71 N | c. | 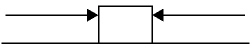 227 N
153 N
227 N
153 N
| b. | 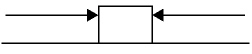 405
N 403
N 405
N 403
N | d. | 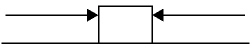 22.7
N
15.3 N 22.7
N
15.3 N |
|
|
|
8.
|
The example of a book falling off of a table shows a(n) _____.
a. | contact force | c. | absence of acceleration | b. | scalar
quantity | d. | field
force |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which of the following is not true about a free body diagram?
a. | All forces point away from the particle. | b. | The arrows are
proportional to the size of the forces. | c. | The system is represented by a particle
model. | d. | You always know the magnitude of the forces ahead of
time. |
|
|
|
10.
|
When the drag force on an object falling through the air equals the force of
gravity, the object has reached
a. | terminal force. | c. | terminal illness. | b. | terminal acceleration. | d. | terminal
velocity. |
|
|
|
11.
|
A weight is hung from the ceiling of an elevator by a massless string.
Under which circumstances will the tension in the cord be the greatest?
a. | The elevator rises with decreasing speed. | b. | The elevator rises
with increasing speed. | c. | The elevator is at rest. | d. | The elevator
descends with increasing speed. |
|
Completion (Value 1)
Complete
each statement.
|
|
|
12.
|
A force is ____________________.
|
Short Answer (Value 3)
|
|
|
Identify the system, forces, and agents in each situation.
|
|
|
13.
|
A bird egg falls freely from a nest.
|
|
|
14.
|
A tow truck uses a cable to pull a car onto the flat bed of the tow
truck.
|
|
|
15.
|
You are a skydiving physicist. During a dive, you observe that two unequal
masses hung over a pulley remain balanced, that is, there is no tendency for the pulley to
turn. What conclusions can you draw?
|
Problem
|
|
|
16.
|
A car of mass 1330 kg is traveling at 28.0 m/s. The driver applies the brakes to
bring the car to rest over a distance of 79.0 m. Calculate the retarding force acting on the
car.
|
|
|
17.
|
An elevator is moving down with an acceleration of 3.36 m/s2. What
would be the apparent weight of a 64.2-kg man in the elevator?
|
|
|
18.
|
The blocks shown below are placed on a smooth horizontal surface and connected
by a piece of string. If a 8.8-N force is applied to the 8.8-kg block, what is the tension in the
string?
8.8 N 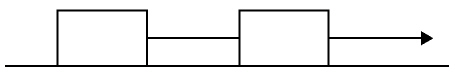
|
|
|
19.
|
Two horizontal forces, 145 N and 315 N are applied to a sled resting on a
frictionless skating rink. If they are applied in opposite directions, what is the net
horizontal force on the sled?
|
|
|
20.
|
Little Georgie Atwood was playing with his blocks and some massless
string. He connected the first block with mass M1 on one end of the string, put the
string over a frictionless pulley, and attached the other block with mass M2 on the other
end of the string.
Derive an expression describing the acceleration of each block.
|
|
|
21.
|
Little Georgie Atwood was playing with his blocks and some massless
string. He connected the first block with mass M1 on one end of the string, put the
string over a frictionless pulley, and attached the other block with mass M2 on the other
end of the string.
If M1 = 25.0 g and M2 = 55.0 g, what is the
acceleration of each block?
|
|
|
22.
|
A block with mass 4.4 kg ( 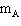 ) is free to slide along a horizontal
frictionless air hockey table. This sliding block is connected by a string and pulley to a
second block with mass 2.9 kg ( 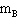 ) that is hanging over the edge of the table. The
hanging block will fall, pulling the sliding block to the right. Find the acceleration of the
hanging block ( 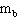 ).
|
|
|
23.
|
A block with mass 4.4 kg ( 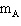 ) is free to slide along a horizontal
frictionless air hockey table. This sliding block is connected by a string and pulley to a
second block with mass 2.9 kg ( 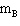 ) that is hanging over the edge of the table. The
hanging block will fall, pulling the sliding block to the right. Find the tension in the
cord.
|
|
|
24.
|
An Eskimo pushes a loaded sled with a mass of 300 kg for a distance of 25 m over
the frictionless surface of hard-packed snow. He exerts a constant 170 N force as he does
so. If the sled starts from rest, what is its final velocity?
|
|
|
25.
|
A crate with a mass of 450 kg rests on the bed of a truck that is moving at a
speed of 90.0 km/h. The driver brakes and slows to a speed of 50.0 km/h in 15 s. Assuming the
force is constant, what force acts on the crate during this time? Assume that the crate does
not slide on the bed of the truck.
|