True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
The period of a simple harmonic oscillator is the time it takes for one complete
cycle of oscillation to be completed.
|
|
|
2.
|
Waves that collide with a barrier will reflect at an angle equal to the angle of
incidence.
|
|
|
3.
|
Hooke’s Law states that the force exerted by a spring is inversely
proportional to the amount it is stretched.
|
|
|
4.
|
When work is done on a spring to stretch it, elastic potential energy is stored
in the spring.
|
|
|
5.
|
When a mass suspended from a spring is in its equilibrium position, the upward
force exerted by the spring is equal to the downward force exerted by gravity acting on the
mass.
|
|
|
6.
|
The period of a pendulum is directly proportional to the mass of the bob.
|
|
|
7.
|
When representing waves in two dimensions, a ray can be drawn parallel to the
crests of the waves.
|
|
|
8.
|
A standing wave results from the interference of two waves of equal wavelength
that travel in opposite directions.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
9.
|
Which shows the correct angle of reflection given the incident ray shown?
|
|
|
10.
|
What is the period of a pendulum near Earth’s surface that is 130 cm
long?
a. | 9.1 s | c. | 22.9 s | b. | 2.3 s | d. | 0.83 s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.
|
In the diagram, the wavelength is shown by:
|
|
|
12.
|
In the diagram, the amplitude of the wave is shown by:
|
|
|
13.
|
If 320 J of work is done on a spring with a spring constant of 730 N/m, how far
will it stretch?
a. | 0.87 m | c. | 0.61 m | b. | 0.94 m | d. | 0.58 m |
|
|
|
14.
|
How much work must be done on a spring (k = 730 N/m) to stretch is by 1.5
m?
a. | 548 J | c. | 1643 J | b. | 649 J | d. | 821 J |
|
|
|
15.
|
If the period of a certain wave (wavelength = 4.5 m) is 2 seconds, what is the
speed of the wave?
a. | 9.0 m/s | c. | 1.1 m/s | b. | 0.44 m/s | d. | 2.3 m/s |
|
|
|
16.
|
A spring (k = 790 N/m) has a length of 48 cm when zero net force is applied to
it. What will its length be when 230 N of force is applied to stretch it?
a. | 0.29 m | c. | 3.4 m | b. | 0.77 m | d. | 3.9 m |
|
Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
17.
|
On a graph of force versus displacement of a spring, the
____________________ is given by the slope of the line.
|
|
|
18.
|
The angle between an incident ray and the normal is called the
____________________.
|
|
|
19.
|
A wave that strikes a boundary is called a(n) ____________________
wave.
|
|
|
20.
|
____________________ interference occurs when a crest and a trough of
equal amplitudes coincide.
|
|
|
21.
|
Transverse waves vibrate ____________________ to the direction the wave
propagates.
|
|
|
22.
|
A ____________________ is due to the interference of two traveling waves
moving in opposite directions.
|
|
|
23.
|
A wave carrying a larger amount of energy will have a greater
____________________.
|
|
|
24.
|
The speed of a wave is determined solely by the wave’s
____________________.
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
25.
|
What conditions are necessary for resonance to occur?
|
|
|
26.
|
An incident wave is propagated down a spring. When it meets another
spring, some of the energy continues down the spring, while some is reflected back on the first
spring, but inverted. Predict how the second spring compares to the first in terms of stiffness
or heaviness.
|
Problem
|
|
|
27.
|
Spring A with a spring constant of 279 N/m is stretched by a distance of 18.0 cm
when a block is suspended from its end. An object is suspended from another spring B with a spring
constant of 145 N/m. If the elastic potential energy in both the springs is the same, how far does
spring B stretch?
|
|
|
28.
|
A spring is subjected to a stretching force. The following graph shows the
variation of the force with the extension produced in the spring. Calculate the increase in the
potential energy of the spring when the extension increases from 1.7 cm to 3.3 cm. 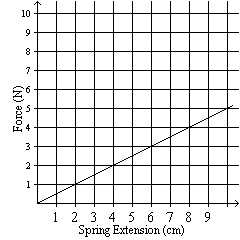
|
|
|
29.
|
A spring has 54,000 J of elastic potential energy stored when it is stretched
out. If its spring constant is 285 N/m, how much has the spring been stretched?
|
|
|
Displacement of a
Spring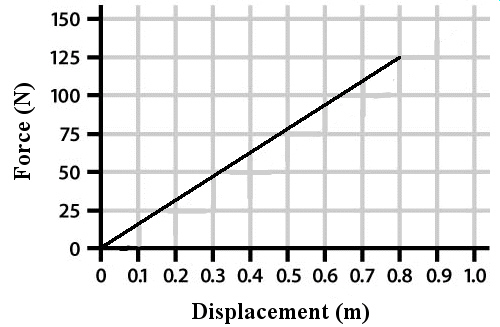
|
|
|
30.
|
How much potential energy is stored in the spring if it is displaced 0.6
m?
|
|
|
31.
|
The displacement of a spring when different amounts of force are applied is
shown in this graph. What is the spring constant of this spring?
|
|
|
32.
|
A lifeguard on a beach observes that waves have a speed of 2.60 m/s and a
distance of 2.50 m between wave crests. What is the period of the wave motion?
|