Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | heat of reaction | d. | heat of fusion | b. | heat of formation | e. | heat of solution | c. | Hess's law of
heat summation |
|
|
|
1.
|
the enthalpy change caused by dissolving a substance
|
|
|
2.
|
the energy required to melt a solid at its melting point
|
|
|
3.
|
the change in enthalpy that accompanies the formation of a compound from its
elements
|
|
|
4.
|
states that if you add two or more thermochemical equations to give a final
equation, you can also add the heats of reaction to give the final heat of reaction
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | activated complex | d. | activation energy | b. | reaction rate | e. | free energy | c. | inhibitor |
|
|
|
5.
|
the minimum energy colliding particles must have in order to react
|
|
|
6.
|
arrangement of atoms at the peak of an energy barrier
|
|
|
7.
|
the number of atoms, ions, or molecules that react in a given time to form
products
|
|
|
8.
|
a substance that interferes with a catalyst
|
|
|
9.
|
energy available to do work
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
10.
|
Which of the following is NOT a form of energy?
a. | light | c. | heat | b. | pressure | d. | electricity |
|
|
|
11.
|
If heat is released by a chemical system, an equal amount of heat will be
____.
a. | absorbed by the surroundings | c. | released by the
surroundings | b. | absorbed by the universe | d. | released by the universe |
|
|
|
12.
|
When your body breaks down sugar completely, how much heat is released compared
to burning the same amount of sugar in a flame?
a. | The body releases more heat. | b. | The body releases less
heat. | c. | The body releases the same amount of heat. | d. | The body releases no
heat. |
|
|
|
13.
|
A piece of candy has 5 Calories (or 5000 calories). If it could be burned,
leaving nothing but carbon dioxide and water, how much heat would it give off?
a. | 500 calories | c. | 5000 joules | b. | 5 kilocalories | d. | Not enough information is
given. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which of the following has the greatest heat capacity?
a. | 1000 g of water | c. | 1 g of water | b. | 1000 g of steel | d. | 1 g of steel |
|
|
|
15.
|
What does the symbol 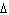 H H stand for? a. | the specific heat of a substance | b. | the heat capacity of a
substance | c. | the heat of reaction for a chemical reaction | d. | one Calorie given
off by a reaction |
|
|
|
16.
|
Standard conditions of temperature and pressure for a thermochemical equation
are ____.
a. | 0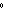 C and 101 kPa C and 101 kPa | c. | 0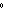 C and 0
kPa C and 0
kPa | b. | 25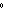 C and 101 kPa C and 101 kPa | d. | 25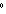 C and 22.4
kPa C and 22.4
kPa |
|
|
|
17.
|
Calculate the energy required to produce 7.00 mol Cl 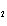 O 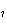 on
the basis of the following balanced equation. 2Cl 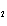 ( g) + 7O 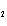 ( g) + 130 kcal 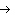 2Cl 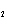 O 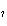 ( g) a. | 7.00 kcal | c. | 130 kcal | b. | 65 kcal | d. | 455 kcal |
|
|
|
18.
|
What is the standard heat of reaction for the following
reaction? Zn( s) + Cu 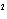 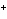 ( aq) 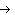 Zn 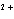 ( aq) +
Cu( s) ( 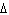 H H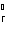 for Cu 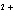 =
+64.4 kJ/mol; 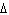 H H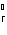 for Zn 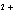 =
–152.4 kJ/mol) a. | 216.8 kJ released per mole | c. | 88.0 kJ absorbed per
mole | b. | 88.0 kJ released per mole | d. | 216.8 kJ absorbed per mole |
|
|
|
19.
|
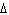 H H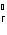 for the formation of rust
(Fe 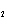 O 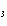 ) is –826 kJ/mol. How much
energy is involved in the formation of 5 grams of rust? a. | 25.9 kJ | c. | 66 kJ | b. | 25.9 J | d. | 66 J |
|
|
|
20.
|
Calculate 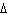 H H for the reaction of sulfur dioxide with
oxygen. 2SO 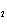 ( g) + O 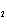 ( g) 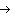 2SO 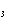 ( g) ( 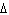 H H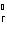 SO 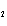 ( g) =
–296.8 kJ/mol; 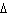 H H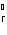 SO 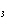 ( g) = –395.7 kJ/mol) a. | –98.9 kJ | c. | 197.8 kJ | b. | –197.8 kJ | d. | Not enough information is
given. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Why does a higher temperature cause a reaction to go faster?
a. | There are more collisions per second only. | b. | Collisions occur
with greater energy only. | c. | There are more collisions per second and the
collisions are of greater energy. | d. | There are more collisions per second or the
collisions are of greater energy. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Why does a catalyst cause a reaction to proceed faster?
a. | There are more collisions per second only. | b. | The collisions occur
with greater energy only. | c. | The activation energy is lowered
only. | d. | There are more collisions per second and the collisions are of greater
energy. |
|
|
|
23.
|
What happens to a catalyst in a reaction?
a. | It is unchanged. | c. | It is incorporated into the reactants. | b. | It is incorporated
into the products. | d. | It
evaporates away. |
|
|
|
24.
|
The rate of a chemical reaction normally ____.
a. | decreases as temperature increases | b. | is slowed down by a
catalyst | c. | increases as reactant concentration increases | d. | decreases as
reactant concentration increases |
|
|
|
25.
|
If sulfur dioxide and oxygen can be made into sulfur trioxide, what is the
reverse reaction?
|
|
|
26.
|
In a reaction (at equilibrium) that makes more moles of gas than it consumes,
what is the effect of increasing the pressure?
a. | The reaction makes more products. | c. | The reaction is
unchanged. | b. | The reaction makes more reactants. | d. | The answer cannot be
determined. |
|
|
|
27.
|
What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? C + O 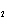  CO 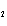
|
|
|
28.
|
In an equilibrium reaction with a K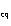 of 1 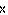 10 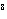 , the ____. a. | reactants are favored | c. | the products are favored | b. | reaction is
spontaneous | d. | reaction is
exothermic |
|
|
|
29.
|
What happens to the energy produced by burning gasoline in a car engine?
a. | The energy is lost as heat in the exhaust. | b. | The energy is
transformed into work to move the car. | c. | The energy heats the parts of the
engine. | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
30.
|
A piece of metal is heated, then submerged in cool water. Which statement below
describes what happens?
a. | The temperature of the metal will increase. | b. | The temperature of
the water will increase. | c. | The temperature of the water will
decrease. | d. | The temperature of the water will increase and the temperature of the metal will
decrease. |
|
|
|
31.
|
How does a calorie compare to a joule?
a. | A calorie is smaller than a joule. | c. | A calorie is equal to a
joule. | b. | A calorie is larger than a joule. | d. | The relationship cannot be
determined. |
|
|
|
32.
|
In an exothermic reaction, the energy stored in the chemical bonds of the
reactants is ____.
a. | equal to the energy stored in the bonds of the products | b. | greater than the
energy stored in the bonds of the products | c. | less than the energy stored in the bonds of the
products | d. | less than the heat released |
|
|
|
33.
|
How can you describe the specific heat of olive oil if it takes approximately
420 J of heat to raise the temperature of 7 g of olive oil by 30 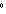 C? a. | greater than the specific heat of water | c. | equal to the specific heat of
water | b. | less than the specific heat of water | d. | Not enough information is
given. |
|
|
|
34.
|
The specific heat of silver is 0.24 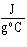 . How many joules of energy are
needed to warm 4.37 g of silver from 25.0 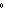 C to 27.5 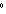 C? a. | 2.62 J | c. | 45.5 J | b. | 0.14 J | d. | 0.022 J |
|
|
|
35.
|
Which of the following substances has the highest specific heat?
a. | steel | c. | alcohol | b. | water | d. | chloroform |
|
|
|
36.
|
What is the heat of solution?
a. | the amount of heat required to change a solid into a liquid | b. | the amount of heat
absorbed or released when a solid dissolves | c. | the amount of heat required to change a vapor
into a liquid | d. | the amount of heat released when a vapor changes into a
liquid |
|
|
|
37.
|
Using a table that lists standard heats of formation, you can calculate the
change in enthalpy for a given chemical reaction. The change in enthalpy is equal to ____.
|
|
|
38.
|
Why does a higher concentration make a reaction faster?
a. | There are more collisions per second only. | b. | Collisions occur
with greater energy only. | c. | There are more collisions per second and the
collisions are of greater energy. | d. | There are more collisions per second or the
collisions are of greater energy. |
|
|
|
39.
|
If a reaction is reversible, what are the relative amounts of reactant and
product at the end of the reaction?
a. | no reactant; all product | b. | no product; all reactant | c. | some product; some
reactant | d. | The relationship between reactants and products cannot be
determined. |
|
|
|
40.
|
Consider the reaction N 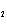 ( g) 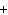
3H 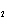 ( g)  2NH 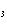 ( g). What is the effect
of decreasing the volume on the contained gases? a. | The reaction shifts toward the product gas. | b. | The system reacts by
increasing the number of gas molecules. | c. | The pressure on the gases decreases
momentarily. | d. | Ammonia is consumed in the reaction. |
|
|
|
41.
|
Which of the changes listed below would shift the following reaction to the
right? 4HCl( g) + O 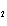 ( g)  2Cl 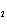 ( g) + 2H 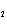 O( g) a. | addition of Cl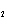 | c. | increase of
pressure | b. | removal of O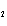 | d. | decrease of
pressure |
|
|
|
42.
|
The K of a reaction is 4  10  . At equilibrium, the ____. a. | reactants are favored | b. | products are favored | c. | reactants and
products are present in equal amounts | d. | rate of the forward reaction is much greater
than the rate of the reverse reaction |
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
43.
|
If 500 g of iron absorbs 22,000 cal of heat, what will be the change in
temperature? (specific heat of iron = 0.11  )
|
|
|
44.
|
Calculate the value of K for the following reaction at
equilibrium. 2NClO( g)  2NO( g) + Cl  ( g) An
analysis of the equilibrium mixture in a 1-L flask gives the following results: NClO, 1.6 mol; NO,
6.4 mol; Cl  , 0.49 mol
|
Essay
|
|
|
45.
|
Explain the difference between temperature and heat. Also, state what determines
the direction of heat transfer.
|
|
|
46.
|
Explain the distinction between heat capacity and specific heat. Provide an
example to illustrate this distinction.
|