Matching (Value 21)
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | calorimeter | d. | enthalpy | b. | calorie | e. | specific heat | c. | joule | f. | heat
capacity |
|
|
|
1.
|
quantity of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1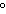 C C
|
|
|
2.
|
quantity of heat needed to change the temperature of 1 g of a substance by
1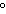 C C
|
|
|
3.
|
device used to measure the heat absorbed or released during a chemical or
physical process
|
|
|
4.
|
heat content of a system at constant pressure
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | activated complex | d. | activation energy | b. | reaction rate | e. | free energy | c. | inhibitor |
|
|
|
5.
|
the minimum energy colliding particles must have in order to react
|
|
|
6.
|
arrangement of atoms at the peak of an energy barrier
|
|
|
7.
|
the number of atoms, ions, or molecules that react in a given time to form
products
|
|
|
8.
|
a substance that interferes with a catalyst
|
|
|
9.
|
energy available to do work
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | exothermic reaction | d. | nuclear reaction | b. | endothermic Reaction | e. | elementary reaction | c. | chemical
equilibrium |
|
|
|
10.
|
CH4(s) + 2O2(g) ® CO2(g) + 2H2O(l)
ÄH° = -890 kJ
|
|
|
11.
|
2HCl(g) ®
H2(g) + Cl2(g)
ÄH° = 185 kJ
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | acid dissociation constant | d. | Lewis acid | b. | diprotic
acid | e. | pH | c. | hydrogen-ion
donor |
|
|
|
12.
|
acid with two ionizable protons
|
|
|
13.
|
Brønsted-Lowry acid
|
|
|
14.
|
negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration
|
|
|
15.
|
ratio of the concentration of the dissociated to the undissociated form
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | condensed structural formula | d. | saturated
compound | b. | homologous series | e. | complete structural formula | c. | unsaturated
compound |
|
|
|
16.
|
formula showing all the atoms and bonds in a molecule
|
|
|
17.
|
structural formula in which some bonds and/or atoms are left out
|
|
|
18.
|
organic compound that contains the maximum number of hydrogens per carbon
atom
|
|
|
19.
|
organic compound that contains at least one double or triple carbon-carbon
bond
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | substitution reaction | d. | hydrogenation reaction | b. | addition
reaction | e. | dehydrogenation
reaction | c. | hydration reaction |
|
|
|
20.
|
a reaction involving the addition of halogen to a carbon—carbon double
bond to produce an halocarbon
|
|
|
21.
|
a reaction involving the subsitiution of a hydrogen with an halogen
|
Multiple Choice (Value 107)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.There are 117 questions.Two questions will be bonus marks.
|
|
|
22.
|
What happens to the energy produced by burning gasoline in a car engine?
a. | The energy is lost as heat in the exhaust. | b. | The energy is
transformed into work to move the car. | c. | The energy heats the parts of the
engine. | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
23.
|
A piece of metal is heated, then submerged in cool water. Which statement below
describes what happens?
a. | The temperature of the metal will increase. | b. | The temperature of
the water will increase. | c. | The temperature of the water will
decrease. | d. | The temperature of the water will increase and the temperature of the metal will
decrease. |
|
|
|
24.
|
How does a calorie compare to a joule? (1 J = 0.2390 cal or 4.184 J = 1
cal)
a. | A calorie is smaller than a joule. | c. | A calorie is equal to a
joule. | b. | A calorie is larger than a joule. | d. | The relationship cannot be
determined. |
|
|
|
25.
|
What would likely happen if you were to touch the flask in which an endothermic
reaction were occurring?
a. | The flask would probably feel cooler than before the reaction
started. | b. | The flask would probably feel warmer than before the reaction
started. | c. | The flask would feel the same as before the reaction started. | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
26.
|
If heat is released by a chemical system, an equal amount of heat will be
____.
a. | absorbed by the surroundings | c. | released by the
surroundings | b. | absorbed by the universe | d. | released by the universe |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which of the following is transferred due to a temperature difference?
a. | chemical energy | c. | electrical energy | b. | mechanical energy | d. | heat |
|
|
|
28.
|
A piece of candy has 5 Calories (or 5000 calories). If it could be burned,
leaving nothing but carbon dioxide and water, how much heat would it give off?
a. | 500 calories | c. | 5000 joules | b. | 5 kilocalories | d. | Not enough information is
given. |
|
|
|
29.
|
How many joules are in 148 calories? (1 cal = 4.18 J)
a. | 6.61 J | c. | 148 J | b. | 35.4 J | d. | 619 J |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following is a valid unit for specific heat?
|
|
|
31.
|
What does the symbol  HR HR stand for? a. | the specific heat of a substance | b. | the heat capacity of a
substance | c. | the heat of reaction for a chemical reaction | d. | one Calorie given
off by a reaction |
|
|
|
32.
|
Standard conditions of temperature and pressure (STP) for a thermochemical
equation are ____.
a. | 0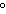 C and 101 kPa C and 101 kPa | c. | 0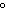 C and 0
kPa C and 0
kPa | b. | 25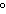 C and 101 kPa C and 101 kPa | d. | 25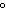 C and 22.4
kPa C and 22.4
kPa |
|
|
|
33.
|
A chunk of ice whose temperature is –20 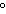 C is added to an
insulated cup filled with water at 0 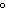 C. What happens in the cup? a. | The ice melts until it reaches the temperature of the water. | b. | The water cools
until it reaches the temperature of the ice. | c. | Some of the water freezes, so the chunk of ice
gets larger. | d. | none of the above |
|
|
|
34.
|
The amount of heat released by the complete burning of 1 mole of a substance is
the ____.
a. | specific heat | c. | heat capacity | b. | heat of combustion | d. | heat of fusion |
|
|
|
35.
|
To calculate the amount of heat absorbed as a substance melts, which of the
following information is NOT needed?
a. | the mass of the substance | c. | the change in
temperature | b. | the specific heat of the substance | d. | the density of the
sample |
|
|
|
36.
|
What is the heat of solution?
a. | the amount of heat required to change a solid into a liquid | b. | the amount of heat
absorbed or released when a solid dissolves | c. | the amount of heat required to change a vapor
into a liquid | d. | the amount of heat released when a vapor changes into a
liquid |
|
|
|
37.
|
When 10 g of diethyl ether is converted to vapor at its boiling point, about how
much heat is absorbed? (C 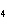 H 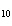 O,  H H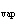 =
15.7 kJ/mol, boiling point: 34.6 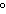 C) a. | 2 kJ | c. | 0.2 kJ | b. | 2 J | d. | Not enough information is
given. |
|
|
|
38.
|
The amount of heat involved in the synthesis/formation of 1 mole of a compound
from its elements, with all substances in their standard states at 25 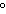 C, is called
____. a. | enthalpy | c. | standard heat of formation | b. | heat of
reaction | d. | heat of
solidification |
|
|
|
39.
|
Another name for the activated complex is ____.
a. | energy barrier | c. | rate limiter | b. | transition state | d. | collision group |
|
|
|
40.
|
At what stage of a reaction do atoms have the highest energy?
a. | reactant stage | b. | product stage | c. | transition state
stage | d. | The stage of highest energy depends on the atom. |
|
|
|
41.
|
Why does a catalyst cause a reaction to proceed faster?
a. | There are more collisions per second only. | b. | The collisions occur
with greater energy only. | c. | The activation energy is lowered
only. | d. | There are more collisions per second and the collisions are of greater
energy. |
|
|
|
42.
|
What happens to a catalyst in a reaction?
a. | It is unchanged. | c. | It is incorporated into the reactants. | b. | It is incorporated
into the products. | d. | It
evaporates away. |
|
|
|
43.
|
At equilibrium, what is the rate of production of reactants compared with the
rate of production of products?
a. | much higher | c. | the same | b. | higher | d. | lower |
|
|
|
44.
|
If sulfur dioxide and oxygen can be made into sulfur trioxide, what is the
reverse reaction?
|
|
|
45.
|
In an endothermic reaction at equilibrium, what is the effect of raising the
temperature?
a. | The reaction makes more products. | c. | The reaction is
unchanged. | b. | The reaction makes more reactants. | d. | The answer cannot be
determined. |
|
|
|
46.
|
Which of the changes listed below would shift the following reaction to the
right? 4HCl( g) + O 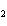 ( g)  2Cl 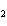 ( g) + 2H 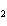 O( g) a. | addition of Cl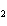 | c. | increase of
pressure | b. | removal of O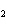 | d. | decrease of
pressure |
|
|
|
47.
|
What is the effect of adding more water to the following equilibrium
reaction? CO 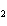 + H 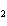 O  H 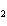 CO 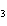 a. | More H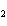 CO CO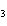 is produced. is produced. | b. | CO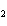 concentration increases.
concentration increases. | c. | The equilibrium is pushed in the direction of
reactants. | d. | There is no effect. |
|
|
|
48.
|
What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? C + O 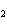  CO 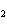
|
|
|
49.
|
If a reaction has an equilibrium constant just greater than 1, what type of
reaction is it?
a. | irreversible | c. | reversible, favoring products | b. | spontaneous | d. | reversible, favoring reactants |
|
|
|
50.
|
The melting of ice at temperatures above 0 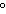 C ____. a. | liberates heat | c. | is not favorable | b. | is not spontaneous | d. | is endothermic |
|
|
|
51.
|
Which of the following is true about the combustion of carbon?
a. | The reaction is spontaneous. | b. | Carbon is produced from oxygen and carbon
dioxide. | c. | Enthalpy remains constant. | d. | Entropy
decreases. |
|
|
|
52.
|
When nitrous oxide is converted to nitrogen and oxygen, what is the term used to
describe the oxygen atoms formed?
a. | reactants | c. | activated complexes | b. | products | d. | intermediates |
|
|
|
53.
|
What information is NOT given by an overall equation for a chemical
reaction?
a. | the relative numbers of molecules used | b. | the probable order of the
reaction | c. | the number of atoms participating in the reaction | d. | the reaction
mechanism |
|
|
|
54.
|
When an acid reacts with a base, what compounds are formed?
a. | a salt only | c. | metal oxides only | b. | water only | d. | a salt and
water |
|
|
|
55.
|
What is the formula for phosphoric acid?
|
|
|
56.
|
Which of the following is a property of an acid?
a. | sour taste | c. | strong color | b. | nonelectrolyte | d. | unreactive |
|
|
|
57.
|
What is a property of a base?
a. | bitter taste | c. | strong color | b. | watery feel | d. | unreactive |
|
|
|
58.
|
The formula of the hydrogen ion is often written as ____.
|
|
|
59.
|
Which hydroxide compound yields the lowest concentration of hydroxide ions in
aqueous solution?
a. | sodium hydroxide | c. | calcium hydroxide | b. | potassium hydroxide | d. | magnesium
hydroxide |

|
|
|
60.
|
Which of these is an Arrhenius base?
|
|
|
61.
|
What is transferred between a conjugate acid-base pair?
a. | an electron | c. | a hydroxide ion | b. | a proton | d. | a hydronium ion |
|
|
|
62.
|
In the reaction of aluminum bromide with ionized sodium bromide, which compound
is the Lewis acid?
a. | aluminum bromide | c. | sodium ion | b. | bromide ion | d. | None are Lewis
acids. |
|
|
|
63.
|
What type of acid is sulfuric acid?
a. | monoprotic | c. | triprotic | b. | diprotic | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
64.
|
Which compound can act as both a Brønsted-Lowry acid and a
Brønsted-Lowry base?
a. | water | c. | sodium hydroxide | b. | ammonia | d. | hydrochloric
acid |
|
|
|
65.
|
In the reaction CO 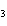 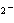 + H 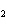 O  HCO 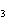 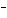 + OH 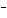 , the carbonate ion is acting as
a(n) ____. a. | Arrhenius base | c. | Brønsted-Lowry base | b. | Arrhenius
acid | d. | Brønsted-Lowry
acid |
|
|
|
66.
|
Which of the following reactions illustrates amphoterism?
|
|
|
67.
|
What are the acids in the following equilibrium reaction? CN 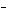 + H 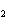 O  HCN + OH 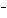
|
|
|
68.
|
If the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution is 1 x 10 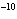 M M,
is the solution acidic, alkaline, or neutral? a. | acidic | c. | neutral | b. | alkaline | d. | The answer cannot be
determined. |
|
|
|
69.
|
The acid dissociation constant for an acid dissolved in water is equal to the
____.
a. | equilibrium constant | b. | equilibrium constant times the concentration of
water | c. | equilibrium constant divided by the concentration of water | d. | equilibrium constant
times the equilibrium constant of water |
|
|
|
70.
|
What is another name for the acid dissociation constant?
a. | equilibrium constant | c. | rate constant | b. | ionization constant | d. | mole fraction |
|
|
|
71.
|
Acetic acid ionizes in water as follows: 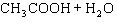  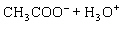 Fewer than 1% of ethanoic acid molecules are ionized at any instant. The acetate ion
(CH 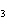 COO  ) is therefore ____. a. | a poor hydrogen-ion acceptor | c. | a poor hydrogen-ion
donor | b. | a good hydrogen-ion acceptor | d. | a good hydrogen-ion
donor |
|
|
|
72.
|
A 0.12M solution of an acid that ionizes only slightly in solution would
be termed ____.
a. | concentrated and weak | c. | dilute and weak | b. | strong and dilute | d. | concentrated and
strong |
|
|
|
73.
|
Which of the following pairs consists of a weak acid and a strong base?
a. | sulfuric acid, sodium hydroxide | c. | acetic acid, sodium
hydroxide | b. | acetic acid, ammonia | d. | nitric acid, calcium hydroxide |
|
|
|
74.
|
A substance with a K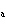 of 1 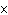 10 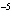 would be
classified as a ____. a. | strong acid | c. | strong base | b. | weak acid | d. | weak base |
|
|
|
75.
|
If an acid has a K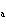 = 1.6 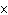 10 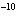 , what is
the acidity of the solution? a. | acidic | c. | neutral | b. | basic | d. | The answer cannot be
determined. |
|
|
|
76.
|
A base has a K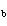 of 2.5 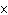 10 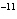 . Which of the
following statements is true? a. | This is a concentrated base. | b. | This base ionizes slightly in aqueous
solution. | c. | This is a strong base. | d. | An aqueous solution of this base would be
acidic. |
|
|
|
77.
|
Which base has the smallest base dissociation constant?
a. | potassium hydroxide | c. | calcium hydroxide | b. | sodium hydroxide | d. | ammonia |
|
|
|
78.
|
The process of adding a known amount of solution (using aburette)of known
concentration to determine the concentration of another solution is called ____.
a. | neutralization | c. | titration | b. | hydrolysis | d. | buffer capacity |
|
|
|
79.
|
What kind of ion is contained in salts that produce an acidic solution?
a. | a positive ion that releases a proton to water | b. | a negative ion that
releases a proton to water | c. | a positive ion that attracts a proton from
water | d. | a negative ion that attracts a proton from water |
|
|
|
80.
|
How many valence electrons does a carbon atom have?
|
|
|
81.
|
Alkanes are hydrocarbons that contain what type of bonds?
a. | single covalent bonds only | c. | at least one triple
bond | b. | at least one double bond | d. | ionic bonds |
|
|
|
82.
|
What is the name of the alkane having five carbons?
a. | propane | c. | octane | b. | methane | d. | pentane |
|
|
|
83.
|
What is the simplest straight-chain alkane?
a. | graphite | c. | methane | b. | ammonia | d. | ethane |
|
|
|
84.
|
Which of the following is a condensed structural formula for propane?
|
|
|
85.
|
The names of the straight-chain alkanes all end with the suffix ____.
|
|
|
86.
|
The name for an alkyl group that contains two carbon atoms is ____.
a. | diphenyl | c. | dimethyl | b. | ethyl | d. | propyl |
|
|
|
87.
|
What is the physical state of the smallest alkanes at room temperature?
a. | gas | c. | solid | b. | liquid | d. | gas or liquid |
|
|
|
88.
|
What is the general formula for a straight-chain alkane?
|
|
|
89.
|
What is the condensed structural formula for 2,2-dimethylbutane?
|
|
|
90.
|
What is the name of the compound CH 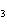 CH(CH 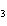 )C(CH 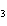 ) 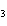 ? a. | 2,2,3-trimethylbutane | c. | 1,1,1,2-tetramethylpropane | b. | tetramethylpropane | d. | isoheptane |
|
|
|
91.
|
The condensed structural formula for 2,2,3-trimethylbutane is ____.
|
|
|
92.
|
In which of the following liquids is hexane most likely to dissolve?
a. | aqueous ammonium hydroxide | c. | rubbing alcohol | b. | vinegar | d. | octane |
|
|
|
93.
|
Why are the molecules of hydrocarbons nonpolar?
a. | The intermolecular attractions are strong. | b. | All the bonds are
single covalent bonds. | c. | The electron pair is shared almost equally in
all the bonds. | d. | Van der Waals forces overcome polarity. |
|
|
|
94.
|
In which of the following compounds does rotation occur around all covalent
bonds between carbons?
a. | octene | c. | octane | b. | octyne | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
95.
|
The general name for hydrocarbons with at least one triple covalent bond is
____.
a. | alkenes | c. | alkanes | b. | alkyls | d. | alkynes |
|
|
|
96.
|
What is the name of the smallest alkyne?
a. | butyne | c. | methyne | b. | ethyne | d. | propyne |
|
|
|
97.
|
Hydrocarbons containing a saturated carbon ring are called ____.
a. | cyclic hydrocarbons | c. | aliphatic hydrocarbons | b. | aromatic
hydrocarbons | d. | alkylated
hydrocarbons |
|
|
|
98.
|
What compound is the simplest aromatic compound?
a. | methane | c. | ethyne | b. | ethene | d. | benzene |
|
|
|
99.
|
Which of the following is NOT an important fossil fuel?
a. | petroleum | c. | natural gas | b. | hydrogen | d. | coal |
|
|
|
100.
|
What is the main hydrocarbon component of natural gas?
a. | benzene | c. | ethene | b. | ethane | d. | methane |
|
|
|
101.
|
Which type of coal has the highest carbon content?
a. | anthracite | c. | lignite | b. | bituminous | d. | peat |
|
|
|
102.
|
The controlled process by which hydrocarbons are broken down or rearranged into
smaller, more useful molecules is called ____.
a. | vaporizing | c. | distillation | b. | cracking | d. | fractionating |
|
|
|
103.
|
What is the first step in the refining of petroleum?
a. | cracking | c. | cooling | b. | drilling | d. | distillation |
|
|
|
104.
|
The most important way to classify organic compounds is by ____.
a. | the number of carbon atoms in the longest chain | b. | functional
group | c. | the type of carbon—carbon bonds | d. | reactivity |
|
|
|
105.
|
What is the common name of the following compound? 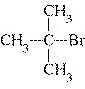 a. | isopropyl bromide | c. | isobutyl bromide | b. | tert-butyl bromide | d. | sec-butyl
bromide |
|
|
|
106.
|
What is the carbon skeleton of the product formed in the following reaction?
C 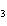 H 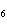 + HBr ® a. |
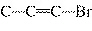 | c. |
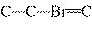 | b. |
C¾C¾C¾Br | d. |
C¾C¾Br¾C |
|
|
|
107.
|
Which of the following compounds is trichloromethane?
|
|
|
108.
|
Phenols are characterized by ____.
a. | their behavior as gases | c. | an ¾OH group on a benzene ring | b. | ether linkages | d. | their use as flavoring
agents |
|
|
|
109.
|
What is the common name of the following alcohol? 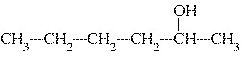 a. | sec-hexyl alcohol | c. | isohexyl
alcohol | b. | tert-hexyl alcohol | d. | hexyl alcohol |
|
|
|
110.
|
Which of the following compounds is a ether?
|
|
|
111.
|
Which pair of formulas represents the same compound?
|
|
|
112.
|
Which of the following is true about isopropyl alcohol?
a. | It has a relatively high boiling point. | c. | It is completely
odorless. | b. | It is insoluble in water. | d. | It is white. |
|
|
|
113.
|
Which of the following alcohols is used in antifreeze?
a. | ethanol | c. | ethylene glycol | b. | isopropyl alcohol | d. | glycerol |
|
|
|
114.
|
In an addition reaction, which bond of the reactant is broken?
a. | carbon—carbon single bond | c. | carbon—carbon double
bond | b. | carbon—hydrogen single bond | d. | carbon—hydrogen double
bond |
|
|
|
115.
|
What type of compound is CH 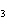 ¾ ¾O ¾CH 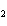 ¾ ¾CH 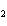 ¾ ¾CH 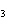 ? a. | alcohol | c. | ether | b. | aldehyde | d. | ketone |
|
|
|
116.
|
Which of the following compounds has the lowest boiling point?
a. | diethyl ether | c. | diphenyl ether | b. | 2-butanol | d. | 4-octanol |
|
|
|
117.
|
Name the following compound. CH 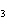 ¾ ¾CH 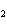 ¾ ¾CH 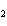 ¾ ¾CH 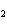 ¾ ¾O ¾C 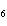 H 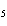 a. | cyclohexylbutyl ether | c. | phenylbutyl ether | b. | butylcyclohexyl ether | d. | butylphenyl
ether |
|
|
|
118.
|
Name the compound CH 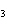 CH 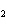 O CH 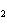 CH 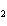 CH 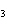 . a. | diethyl ether | c. | ethylpropyl ether | b. | dipropyl ether | d. | pentane oxide |
|
|
|
119.
|
Which of these compounds would you expect to be most soluble in water?
|
|
|
120.
|
Which carbon skeleton represents an ether?
a. |
C¾C¾C¾O¾C¾C¾C | c. |
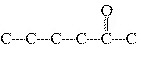 | b. |
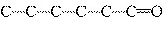 | d. |
none of the
above |
|
|
|
121.
|
What type of compound is the following? 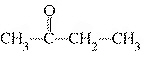 a. | alcohol | c. | ether | b. | aldehyde | d. | ketone |
|
|
|
122.
|
Which carbon skeleton represents a ketone?
|
|
|
123.
|
Which carbon skeleton contains a carboxyl group?
|
|
|
124.
|
Which of the following carbon skeletons represents a carboxylic acid?
|
|
|
125.
|
Which of the following compounds is known as acetic acid?
|
|
|
126.
|
The IUPAC name for a carboxylic acid with two carbons in a straight chain would
be ____.
a. | ethanalic acid | c. | methacarboxylic acid | b. | dimethylmethanoic acid | d. | ethanoic acid |
|
|
|
127.
|
Which carbon skeleton represents an ester?
|
|
|
128.
|
The monomer used as the building block in polyethylene is ____.
a. | ethane | c. | monoethane | b. | ethene | d. | amino acid |
|
|
|
129.
|
Which indicator turns pink at pH 8.0 (titration).
a. | Thymol Blue | c. | Phenyl Red | b. | Phenolphthalein | d. | Brothymol Blue |
|
Short Answer: Complete three of the below five short answer questions
(Value 9)
|
|
|
130.
|
Consider a 67-g chunk of ice (  H H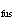 = 6.0 kJ/mol) in a
beaker immersed in a water bath. To produce just enough heat to melt the ice, how many moles of solid
NaOH (  H H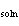 = –445.1 kJ/mol) must you dissolve in the water
bath?
|
|
|
131.
|
If the pH is 9, what is the concentration of hydroxide ion?
|
|
|
132.
|
What is the hydrogen-ion concentration if the pH is 3.7?
|
|
|
133.
|
How many carbon and hydrogen atoms are in a 1-octene molecule?
|
Numeric Response: Complete two of the below four numeric response
questions (Value 6)
|
|
|
134.
|
If the hydrogen ion concentration is 1 x 10 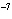 M M, what is the
pH of the solution?
|
|
|
135.
|
If the hydroxide ion concentration is 1 x 10 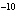 M M, what is the
pH of the solution?
|
|
|
136.
|
What is the pH of a solution with a concentration of 0.01M hydrochloric
acid?
|
Problem (Value 21)
|
|
|
137.
|
Exactly 0.500 Kg of solid sodium at 75 oC is changed into vapour and
heated to 900 oC. (Use your periodic table to find the melting and boiling point of
sodium)
a. Draw a heating curve for this change.
(value 4)
b. Find the total energy absorbed during this
change. (Value 6)
c. Draw a potential energy diagram for each of
the phase changes if 1.00 mol of sodium is involved. (Value 6)
|
|
|
138.
|
Use Hess’s Law to predict the enthalpy change ( DHc) for the combustion of C 2H 6(g). Results should be in
terms of mole of C 2H 6(g) (Value 5)
C2H6(g) à C2H4(g) + H2(g)
ÄHo = 136.2 kJ
C2H4 +
3O2(g) à 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(l)
ÄHo = -1410.8 kJ
H2(g) + ½O2 à H2O
ÄHo = -285.8 kJ
|
|
|
|
139.
|
Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1 x
10-14
pH = -log (H+)
pOH= -log
(OH+)
[H+] = 10-pH
[OH-] =
10-pOH
|