Matching (Value 10)
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | substituent | e. | asymmetric carbon | b. | structural isomers | f. | trans configuration | c. | geometric
isomers | g. | cis
configuration | d. | stereoisomers |
|
|
|
1.
|
atom or group of atoms that can take the place of a hydrogen in a parent
hydrocarbon molecule
|
|
|
2.
|
arrangement in which substituted groups are on the same side of a double
bond
|
|
|
3.
|
compounds that differ in the orientation of groups around a double bond
|
|
|
4.
|
arrangement in which substituted groups are on opposite sides of a double
bond
|
|
|
5.
|
carbon atom to which four different atoms or groups are attached
|
|
|
6.
|
molecules in which atoms are joined in the same order but differ in the
arrangements of their atoms in space
|
|
|
7.
|
compounds that have the same molecular formula, but the atoms are joined in a
different order
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | aromatic compound | d. | lignite | b. | aliphatic hydrocarbon | e. | bituminous coal | c. | anthracite
coal |
|
|
|
8.
|
brown coal, having a carbon content of approximately 50%
|
|
|
9.
|
hard coal, having a carbon content of over 80%
|
|
|
10.
|
soft coal, having a carbon content of 70–80%
|
Multiple Choice (Value 15)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
11.
|
In a cyclic hydrocarbon with only carbon-carbon single bonds and n number
of carbon atoms, how many hydrogen atoms are there in terms of n?
a. | 2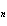 | c. | 2n | b. | 2 +
n | d. | 2 –
n |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which of the following molecules does NOT display resonance?
a. | benzene | c. | m-xylene | b. | phenylethane | d. | cyclohexane |
|
|
|
13.
|
In the cis configuration, the methyl groups are placed ____.
a. | on the same side of the double bond | c. | to the left of the double
bond | b. | in between the double bonds | d. | on opposite sides of the double bond |
|
|
|
14.
|
What is the main hydrocarbon component of natural gas?
a. | methane | c. | ethene | b. | ethane | d. | benzene |
|
|
|
15.
|
What compound is the simplest aromatic compound?
a. | methane | c. | benzene | b. | ethyne | d. | ethene |
|
|
|
16.
|
How many different atoms or groups are attached to an asymmetric carbon?
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following is NOT a product obtained from the distillation of coal
tar?
a. | coke | c. | toluene | b. | benzene | d. | phenol |
|
|
|
18.
|
Hydrocarbons containing a saturated carbon ring are called ____.
a. | cyclic hydrocarbons | c. | alkylated hydrocarbons | b. | aromatic
hydrocarbons | d. | aliphatic
hydrocarbons |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following is NOT a fraction obtained from crude oil?
a. | gasoline | c. | natural gas | b. | kerosene | d. | ammonia |
|
|
|
20.
|
A structural isomer of hexane is ____.
a. | cyclohexane | c. | 2,2-dimethylbutane | b. | benzene | d. | 2-methylpentene |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which type of coal has the highest carbon content?
a. | peat | c. | bituminous | b. | anthracite | d. | lignite |
|
|
|
22.
|
What is the first step in the refining of petroleum?
a. | cooling | c. | cracking | b. | drilling | d. | distillation |
|
|
|
23.
|
The controlled process by which hydrocarbons are broken down or rearranged into
smaller, more useful molecules is called ____.
a. | fractionating | c. | vaporizing | b. | distillation | d. | cracking |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following is NOT an important fossil fuel?
a. | natural gas | c. | coal | b. | hydrogen | d. | petroleum |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which hydrocarbon rings are most common in nature?
a. | rings with 5 or 6 carbon atoms | c. | rings with 3 or 4 carbon
atoms | b. | rings with 6 or 7 carbon atoms | d. | rings with 4 or 5 carbon
atoms |
|
Short Answer (Value 4)
|
|
|
26.
|
How many carbon and hydrogen atoms are in a methane molecule?
|
|
|
27.
|
How many more hydrogen atoms does a cyclohexane molecule have than a benzene
molecule?
|
Numeric Response (Value 4)
|
|
|
28.
|
How many arrangements are possible for two methyl groups with respect to a rigid
double bond?
|
|
|
29.
|
What percent of the composition of natural gas is methane?
|
Essay: Complete 2 of the following 4 questions. (Value 4)
|
|
|
30.
|
Describe the arrangement of atoms in ethyne. What is the significance of this
arrangement?
|
|
|
31.
|
Explain how geometric isomers differ from each other. Describe the difference
between the trans and cis configurations of geometric isomers. Provide an example of
each configuration for a molecule that has geometric isomers.
|
|
|
32.
|
What are optical isomers? Provide examples.
|
|
|
33.
|
Describe how fractional distillation is used to refine petroleum. Relate the
structure of hydrocarbons present in crude oil to their boiling points.
|