Matching (Value 15)
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | substituent | e. | asymmetric carbon | b. | structural isomers | f. | trans configuration | c. | geometric
isomers | g. | cis
configuration | d. | stereoisomers |
|
|
|
1.
|
atom or group of atoms that can take the place of a hydrogen in a parent
hydrocarbon molecule
|
|
|
2.
|
compounds that have the same molecular formula, but the atoms are joined in a
different order
|
|
|
3.
|
molecules in which atoms are joined in the same order but differ in the
arrangements of their atoms in space
|
|
|
4.
|
arrangement in which substituted groups are on opposite sides of a double
bond
|
|
|
5.
|
compounds that differ in the orientation of groups around a double bond
|
|
|
6.
|
carbon atom to which four different atoms or groups are attached
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | condensed structural formula | d. | saturated
compound | b. | homologous series | e. | complete structural formula | c. | unsaturated
compound |
|
|
|
7.
|
group of compounds in which there is a constant increment of change in
molecular structure from one compound in the series to the next
|
|
|
8.
|
formula showing all the atoms and bonds in a molecule
|
|
|
9.
|
organic compound that contains the maximum number of hydrogens per carbon
atom
|
|
|
10.
|
organic compound that contains at least one double or triple carbon-carbon
bond
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | aromatic compound | d. | lignite | b. | aliphatic hydrocarbon | e. | bituminous coal | c. | anthracite
coal |
|
|
|
11.
|
any straight-chain or branched-chain alkane, alkene, or alkyne
|
|
|
12.
|
any hydrocarbon compound in which a ring has bonding similar to benzene
|
|
|
13.
|
hard coal, having a carbon content of over 80%
|
|
|
14.
|
brown coal, having a carbon content of approximately 50%
|
|
|
15.
|
soft coal, having a carbon content of 70–80%
|
Multiple Choice (Value 30)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
16.
|
How many valence electrons does a carbon atom have?
|
|
|
17.
|
How many covalent bonds can each carbon atom form?
|
|
|
18.
|
Alkanes are hydrocarbons that contain what type of bonds?
a. | single covalent bonds only | c. | at least one triple
bond | b. | at least one double bond | d. | ionic bonds |
|
|
|
19.
|
How many carbons are in a molecule of hexane?
|
|
|
20.
|
What is the simplest straight-chain alkane?
a. | graphite | c. | methane | b. | ammonia | d. | ethane |
|
|
|
21.
|
The name for an alkyl group that contains two carbon atoms is ____.
a. | diphenyl | c. | dimethyl | b. | ethyl | d. | propyl |
|
|
|
22.
|
What is the physical state of the smallest alkanes at room temperature?
a. | gas | c. | solid | b. | liquid | d. | gas or liquid |
|
|
|
23.
|
What is the general formula for a straight-chain alkane?
|
|
|
24.
|
What is the increment of change in a series of straight-chain alkanes?
|
|
|
25.
|
What is the condensed structural formula for 2,2-dimethylbutane?
|
|
|
26.
|
The condensed structural formula for 2,2,3-trimethylbutane is ____.
|
|
|
27.
|
In which of the following liquids is hexane most likely to dissolve?
a. | aqueous ammonium hydroxide | c. | rubbing alcohol | b. | vinegar | d. | octane |
|
|
|
28.
|
Why are the molecules of hydrocarbons nonpolar?
a. | The intermolecular attractions are strong. | b. | All the bonds are
single covalent bonds. | c. | The electron pair is shared almost equally in
all the bonds. | d. | Van der Waals forces overcome polarity. |
|
|
|
29.
|
In which of the following compounds does rotation occur around all covalent
bonds between carbons?
a. | octene | c. | octane | b. | octyne | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
30.
|
A saturated straight-chain hydrocarbon with two carbons is ____.
a. | ethene | c. | propane | b. | decane | d. | ethane |
|
|
|
31.
|
What is the name of the smallest alkyne?
a. | butyne | c. | methyne | b. | ethyne | d. | propyne |
|
|
|
32.
|
An organic compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen and at least one
carbon-carbon triple bond is classified as an ____.
a. | alkane | c. | alkyne | b. | alkene | d. | arene |
|
|
|
33.
|
How are hydrogen atoms arranged in ethene?
a. | in the same plane, separated by angles of 120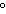 | b. | in different planes,
separated by angles of 120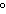 | c. | in the same plane, separated by angles of
180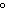 | d. | in different planes, separated by angles of 180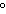 |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which of the following compounds is a structural isomer of butane?
a. | 2-methylbutane | c. | 2-methylpropane | b. | 2,2-dimethylbutane | d. | 2,2-diethylpropane |
|
|
|
35.
|
Which of the following is true about structural isomers?
a. | Structural isomers have the same molecular formula. | b. | Structural isomers
have different physical and chemical properties. | c. | Structural isomers have the same elemental
composition. | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
36.
|
A structural isomer of hexane is ____.
a. | 2,2-dimethylbutane | c. | benzene | b. | cyclohexane | d. | 2-methylpentene |
|
|
|
37.
|
How many different atoms or groups are attached to an asymmetric carbon?
|
|
|
38.
|
Which hydrocarbon rings are most common in nature?
a. | rings with 3 or 4 carbon atoms | c. | rings with 5 or 6 carbon
atoms | b. | rings with 4 or 5 carbon atoms | d. | rings with 6 or 7 carbon
atoms |
|
|
|
39.
|
In a cyclic hydrocarbon with only carbon-carbon single bonds and n number
of carbon atoms, how many hydrogen atoms are there in terms of n?
a. | 2 – n | c. | 2 + n | b. | 2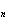 | d. | 2n |
|
|
|
40.
|
What compound is the simplest aromatic compound?
a. | methane | c. | ethyne | b. | ethene | d. | benzene |
|
|
|
41.
|
Which of the following is NOT an important fossil fuel?
a. | petroleum | c. | natural gas | b. | hydrogen | d. | coal |
|
|
|
42.
|
What is the main hydrocarbon component of natural gas?
a. | benzene | c. | ethene | b. | ethane | d. | methane |
|
|
|
43.
|
Which type of coal has the highest carbon content?
a. | anthracite | c. | lignite | b. | bituminous | d. | peat |
|
|
|
44.
|
Which of the following is NOT a fraction obtained from crude oil?
a. | ammonia | c. | gasoline | b. | natural gas | d. | kerosene |
|
|
|
45.
|
Which of the following is NOT a product obtained from the distillation of coal
tar?
a. | benzene | c. | coke | b. | phenol | d. | toluene |
|
Numeric Response (Value 3)
|
|
|
46.
|
How many arrangements are possible for two methyl groups with respect to a rigid
double bond?
|
|
|
47.
|
How many forms of coal are there?
|
|
|
48.
|
What percent of the composition of natural gas is methane?
|