Matching (Value 8)
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | acid dissociation constant | d. | Lewis acid | b. | diprotic
acid | e. | pH | c. | hydrogen-ion
donor |
|
|
|
1.
|
can accept an electron pair
|
|
|
2.
|
acid with two ionizable protons
|
|
|
3.
|
Brønsted-Lowry acid
|
|
|
4.
|
negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration
|
|
|
5.
|
ratio of the concentration of the dissociated to the undissociated form
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | salt hydrolysis | d. | equivalence point | b. | end point | e. | buffer capacity | c. | titration |
|
|
|
6.
|
process of adding a known amount of solution of known concentration to
determine the concentration of another solution
|
|
|
7.
|
The number of moles of hydrogen ions equals the number of moles of hydroxide
ions.
|
|
|
8.
|
Indicator changes color.
|
Multiple Choice (Value 15)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
9.
|
What characterizes a strong acid or base?
a. | polar covalent bonding | b. | complete ionization in
water | c. | ionic bonding | d. | presence of a hydroxide or hydrogen
ion |
|
|
|
10.
|
What is another name for the acid dissociation constant?
a. | equilibrium constant | c. | rate constant | b. | ionization constant | d. | mole fraction |
|
|
|
11.
|
How many ionization constants are associated with oxalic acid?
|
|
|
12.
|
A 0.12M solution of an acid that ionizes only slightly in solution would
be termed ____.
a. | concentrated and weak | c. | dilute and weak | b. | strong and dilute | d. | concentrated and
strong |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which of the following pairs consists of a weak acid and a strong base?
a. | sulfuric acid, sodium hydroxide | c. | acetic acid, sodium
hydroxide | b. | acetic acid, ammonia | d. | nitric acid, calcium hydroxide |
|
|
|
14.
|
The ionization constant ( K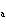 ) of HF is 6.7 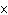 10 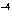 . Which of the following is true in a 0.1 M solution of this acid?
|
|
|
15.
|
If an acid has a K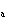 = 1.6 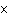 10 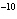 , what
is the acidity of the solution? a. | acidic | c. | neutral | b. | basic | d. | The answer cannot be
determined. |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which acid has the greatest acid dissociation constant?
a. | nitric acid | c. | carbonic acid | b. | acetic acid | d. | boric acid |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which base is strong, but never concentrated?
a. | magnesium hydroxide | c. | ammonia | b. | sodium hydroxide | d. | water |
|
|
|
18.
|
A base has a K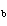 of 2.5 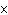 10 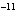 . Which of the
following statements is true? a. | This is a concentrated base. | b. | This base ionizes slightly in aqueous
solution. | c. | This is a strong base. | d. | An aqueous solution of this base would be
acidic. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which base has the smallest base dissociation constant?
a. | potassium hydroxide | c. | calcium hydroxide | b. | sodium hydroxide | d. | ammonia |
|
|
|
20.
|
The process of adding a known amount of solution of known concentration to
determine the concentration of another solution is called ____.
a. | neutralization | c. | titration | b. | hydrolysis | d. | buffer capacity |
|
|
|
21.
|
In a titration, when the number of moles of hydrogen ions equals the number of
moles of hydroxide ions, what is said to have happened?
a. | The equivalence point has been reached. | b. | The end point has
been reached. | c. | The point of neutralization has been reached. | d. | The titration has
failed. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Acetic acid ionizes in water as follows: 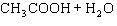  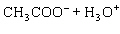 Fewer than 1% of ethanoic acid molecules are ionized at any instant. The acetate ion
(CH 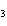 COO  ) is therefore ____. a. | a poor hydrogen-ion acceptor | c. | a poor hydrogen-ion
donor | b. | a good hydrogen-ion acceptor | d. | a good hydrogen-ion
donor |
|
|
|
23.
|
What kind of ion is contained in salts that produce an acidic solution?
a. | a positive ion that releases a proton to water | b. | a negative ion that
releases a proton to water | c. | a positive ion that attracts a proton from
water | d. | a negative ion that attracts a proton from water |
|
Short Answer (Value 15)
|
|
|
24.
|
What is the acid dissociation constant of a weak acid if a concentration of
0.3M gives a hydrogen-ion concentration of 0.001M? (Value 3)
|
|
|
25.
|
How many moles of sulfuric acid are required to neutralize 0.50 mol of sodium
hydroxide? (Value 3)
|
|
|
26.
|
A 25 ml solution of H2SO4 is completely neutralized by 18
ml of 1.0M NaOH. What is the concentration of the H2SO4 solution? (Value
3)
|
|
|
27.
|
What is the hydrogen-ion concentration if the pH is 3.7? (Value 3)
|
|
|
28.
|
Calculate the acid dissociation constant of a weak monoprotic acid if a
0.5M solution of this acid gives a hydrogen-ion concentration of 0.000 1M? (Value
3)
|
Essay
|
|
|
29.
|
M = moles/L
pH =
-log[H+]
pH + pOH = 14.00
[H+] =
10-pH
pOH = -log[OH-]
Kw = [H+][OH-] =
1.0 x 10-14
[OH-] = 10-pOH
|