Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | salt hydrolysis | d. | equivalence point | b. | end point | e. | buffer capacity | c. | titration |
|
|
|
1.
|
process of adding a known amount of solution of known concentration to
determine the concentration of another solution
|
|
|
2.
|
The number of moles of hydrogen ions equals the number of moles of hydroxide
ions.
|
|
|
3.
|
Indicator changes color.
|
|
|
4.
|
Cations or anions of a dissociated salt remove hydrogen ions from or donate
hydrogen ions to water.
|
|
|
5.
|
the amount of acid or base that can be added to a buffer solution before a
significant change in pH occurs
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
6.
|
When an acid reacts with a base, what compounds are formed?
a. | a salt only | c. | metal oxides only | b. | water only | d. | a salt and
water |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which of the following is a property of an acid?
a. | sour taste | c. | strong color | b. | nonelectrolyte | d. | unreactive |
|
|
|
8.
|
The formula of the hydrogen ion is often written as ____.
|
|
|
9.
|
What is an acid according to Arrhenius?
a. | a substance that ionizes to yield protons in aqueous solution | b. | a substance that is
a hydrogen ion donor | c. | a substance that accepts an electron
pair | d. | a substance that is a hydrogen ion acceptor |
|
|
|
10.
|
A Lewis acid is a substance that can ____.
a. | donate a pair of electrons | c. | donate a hydrogen
ion | b. | accept a pair of electrons | d. | accept a hydrogen ion |
|
|
|
11.
|
In the reaction of aluminum bromide with ionized sodium bromide, which compound
is the Lewis acid?
a. | aluminum bromide | c. | sodium ion | b. | bromide ion | d. | None are Lewis
acids. |
|
|
|
12.
|
What type of acid is sulfuric acid?
a. | monoprotic | c. | triprotic | b. | diprotic | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which compound can act as both a Brønsted-Lowry acid and a
Brønsted-Lowry base?
a. | water | c. | sodium hydroxide | b. | ammonia | d. | hydrochloric
acid |
|
|
|
14.
|
In the reaction CO 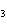 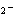 + H 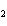 O  HCO 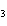 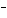 + OH 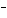 , the
carbonate ion is acting as a(n) ____. a. | Arrhenius base | c. | Brønsted-Lowry base | b. | Arrhenius
acid | d. | Brønsted-Lowry
acid |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following reactions illustrates amphoterism?
|
|
|
16.
|
What are the acids in the following equilibrium reaction? CN 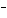 + H 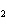 O  HCN
+ OH 
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following represents a Brønsted-Lowry conjugate acid-base
pair?
|
|
|
18.
|
If the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution is 10 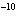 M M, is the solution
acidic, alkaline, or neutral? a. | acidic | c. | neutral | b. | alkaline | d. | The answer cannot be
determined. |
|
|
|
19.
|
What is pH?
a. | the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration | b. | the positive
logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration | c. | the negative logarithm of the hydroxide ion
concentration | d. | the positive logarithm of the hydroxide ion
concentration |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which type of solution is one with a pH of 8?
a. | acidic | b. | basic | c. | neutral | d. | The type varies, depending on the
solution. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of these solutions is the most basic?
|
|
|
22.
|
What characterizes a strong acid or base?
a. | polar covalent bonding | b. | complete ionization in
water | c. | ionic bonding | d. | presence of a hydroxide or hydrogen
ion |
|
|
|
23.
|
With solutions of strong acids and strong bases, the word strong refers
to ____.
a. | normality | c. | solubility | b. | molarity | d. | degree of
ionization |
|
|
|
24.
|
What is another name for the acid dissociation constant?
a. | equilibrium constant | c. | rate constant | b. | ionization constant | d. | mole fraction |
|
|
|
25.
|
A 0.12M solution of an acid that ionizes only slightly in solution would
be termed ____.
a. | concentrated and weak | c. | dilute and weak | b. | strong and dilute | d. | concentrated and
strong |
|
|
|
26.
|
A substance with a K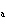 of 1 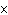 10 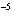 would be
classified as a ____. a. | strong acid | c. | strong base | b. | weak acid | d. | weak base |
|
|
|
27.
|
The ionization constant ( K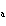 ) of HF is 6.7 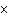 10 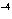 . Which of the
following is true in a 0.1 M solution of this acid?
|
|
|
28.
|
If an acid has a K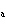 = 1.6 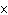 10 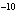 , what is the
acidity of the solution? a. | acidic | c. | neutral | b. | basic | d. | The answer cannot be
determined. |
|
|
|
29.
|
The K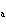 of carbonic acid is 4.3 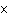 10 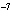 . H 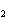 CO 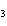 
H 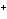
+ HCO 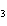 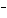 This means that H 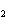 CO 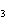 is a ____. a. | good hydrogen-ion acceptor | c. | good hydrogen-ion
donor | b. | poor hydrogen-ion acceptor | d. | poor hydrogen-ion donor |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which acid has the greatest acid dissociation constant?
a. | nitric acid | c. | carbonic acid | b. | acetic acid | d. | boric acid |
|
|
|
31.
|
Which base has the smallest base dissociation constant?
a. | potassium hydroxide | c. | calcium hydroxide | b. | sodium hydroxide | d. | ammonia |
|
|
|
32.
|
The process of adding a known amount of solution of known concentration to
determine the concentration of another solution is called ____.
a. | neutralization | c. | titration | b. | hydrolysis | d. | buffer capacity |
|
|
|
33.
|
What kind of ion is contained in salts that produce an acidic solution?
a. | a positive ion that releases a proton to water | b. | a negative ion that
releases a proton to water | c. | a positive ion that attracts a proton from
water | d. | a negative ion that attracts a proton from water |
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
34.
|
A 0.500 M solution of a weak acid, H X, is only partially ionized.
The [H 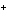 ] was found to be 4.02 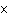 10 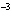 M M. Find the
dissociation constant for this acid.
|
|
|
35.
|
What is the pH if the hydrogen-ion concentration is 6.8 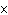 10 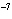 M M?
|
|
|
36.
|
What is the acid dissociation constant of a weak acid if a concentration of
0.3M gives a hydrogen-ion concentration of 0.001M?
|
|
|
37.
|
Calculate the acid dissociation constant of a weak monoprotic acid if a
0.5M solution of this acid gives a hydrogen-ion concentration of 0.000 1M?
|
Numeric Response
|
|
|
38.
|
If the hydroxide ion concentration is 10 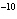 M M, what is the pH of
the solution?
|
|
|
39.
|
What is the pH of a solution with a concentration of 0.01M hydrochloric
acid?
|