Multiple Choice (Value 28) 1 Bonus Question
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
What happens to the energy produced by burning gasoline in a car engine?
a. | The energy is lost as heat in the exhaust. | b. | The energy is
transformed into work to move the car. | c. | The energy heats the parts of the
engine. | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
2.
|
A piece of metal is heated, then submerged in cool water. Which statement below
describes what happens?
a. | The temperature of the metal will increase. | b. | The temperature of
the water will increase. | c. | The temperature of the water will
decrease. | d. | The temperature of the water will increase and the temperature of the metal will
decrease. |
|
|
|
3.
|
How does a calorie compare to a joule?
a. | A calorie is smaller than a joule. | c. | A calorie is equal to a
joule. | b. | A calorie is larger than a joule. | d. | The relationship cannot be
determined. |
|
|
|
4.
|
What would likely happen if you were to touch the flask in which an endothermic
reaction were occurring?
a. | The flask would probably feel cooler than before the reaction
started. | b. | The flask would probably feel warmer than before the reaction
started. | c. | The flask would feel the same as before the reaction started. | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which of the following is NOT a form of energy?
a. | light | c. | heat | b. | pressure | d. | electricity |
|
|
|
6.
|
When energy is changed from one form to another, ____.
a. | some of the energy is lost entirely | b. | all of the energy can be accounted
for | c. | a physical change occurs | d. | all of the energy is changed to a useful
form |
|
|
|
7.
|
If heat is released by a chemical system, an equal amount of heat will be
____.
a. | absorbed by the surroundings | c. | released by the
surroundings | b. | absorbed by the universe | d. | released by the universe |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which of the following is transferred due to a temperature difference?
a. | chemical energy | c. | electrical energy | b. | mechanical energy | d. | heat |
|
|
|
9.
|
In an exothermic reaction, the energy stored in the chemical bonds of the
reactants is ____.
a. | equal to the energy stored in the bonds of the products | b. | greater than the
energy stored in the bonds of the products | c. | less than the energy stored in the bonds of the
products | d. | less than the heat released |
|
|
|
10.
|
A process that absorbs heat is a(n) ____.
a. | endothermic process | c. | exothermic process | b. | polythermic process | d. | ectothermic
process |
|
|
|
11.
|
When your body breaks down sugar completely, how much heat is released compared
to burning the same amount of sugar in a flame?
a. | The body releases more heat. | b. | The body releases less
heat. | c. | The body releases the same amount of heat. | d. | The body releases no
heat. |
|
|
|
12.
|
The quantity of heat required to change the temperature of 1 g of a substance by
1 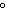 C is defined as ____. a. | a joule | c. | a calorie | b. | specific heat | d. | density |
|
|
|
13.
|
A piece of candy has 5 Calories (or 5000 calories). If it could be burned,
leaving nothing but carbon dioxide and water, how much heat would it give off?
a. | 500 calories | c. | 5000 joules | b. | 5 kilocalories | d. | Not enough information is
given. |
|
|
|
14.
|
How many joules are in 148 calories? (1 cal = 4.18 J)
a. | 6.61 J | c. | 148 J | b. | 35.4 J | d. | 619 J |
|
|
|
15.
|
What is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 200.0 g of
aluminum by 10 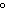 C? (specific heat of aluminum = 0.21 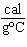 ) a. | 420 cal | c. | 42,000 cal | b. | 4200 cal | d. | 420,000 cal |
|
|
|
16.
|
What is the specific heat of a substance if 1560 cal are required to raise the
temperature of a 312-g sample by 15 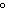 C? a. | 0.033 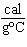 | c. | 0.99 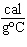 | b. | 0.33 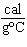 | d. | 1.33 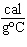 |
|
|
|
17.
|
How many kilocalories of heat are required to raise the temperature of 225 g of
aluminum from 20 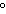 C to 100 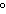 C? (specific heat of aluminum = 0.21
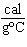 ) a. | 0.59 kcal | c. | 85 kcal | b. | 3.8 kcal | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
18.
|
The heat capacity of an object depends in part on its ____.
a. | mass | c. | shape | b. | enthalpy | d. | potential
energy |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following is a valid unit for specific heat?
|
|
|
20.
|
When 45 g of an alloy, at 25 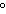 C, are dropped into 100.0 g of water,
the alloy absorbs 956 J of heat. If the final temperature of the alloy is 37 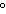 C, what is
its specific heat? a. | 0.423 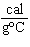 | c. | 9.88 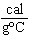 | b. | 1.77 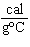 | d. | 48.8 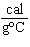 |
|
|
|
21.
|
How can you describe the specific heat of olive oil if it takes approximately
420 J of heat to raise the temperature of 7 g of olive oil by 30  C? a. | greater than the specific heat of water | c. | equal to the specific heat of
water | b. | less than the specific heat of water | d. | Not enough information is
given. |
|
|
|
22.
|
The specific heat of silver is 0.24 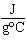 . How many joules of energy are needed
to warm 4.37 g of silver from 25.0  C to 27.5 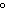 C? a. | 2.62 J | c. | 45.5 J | b. | 0.14 J | d. | 0.022 J |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the following has the greatest heat capacity?
a. | 1000 g of water | c. | 1 g of water | b. | 1000 g of steel | d. | 1 g of steel |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following substances has the highest specific heat?
a. | steel | c. | alcohol | b. | water | d. | chloroform |
|
|
|
25.
|
By what quantity must the heat capacity of an object be divided to obtain the
specific heat of that material?
a. | its mass | c. | its temperature | b. | its volume | d. | its energy |
|
|
|
26.
|
The heat content of a system is equal to the enthalpy only for a system that is
at constant ____.
a. | temperature | c. | pressure | b. | volume | d. | mass |
|
|
|
27.
|
On what principle does calorimetry depend?
a. | Hess's law | c. | law of enthalpy | b. | law of conservation of
energy | d. | law of multiple
proportions |
|
|
|
28.
|
How can the enthalpy change be determined for a reaction in an aqueous
solution?
a. | by knowing the specific heat of the reactants | b. | by mixing the
reactants in a calorimeter and measuring the temperature change | c. | by knowing the mass
of the reactants | d. | The enthalpy change for this type of reaction cannot be
determined. |
|
|
|
29.
|
A chunk of ice whose temperature is –20 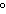 C is added to an
insulated cup filled with water at 0 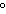 C. What happens in the cup? a. | The ice melts until it reaches the temperature of the water. | b. | The water cools
until it reaches the temperature of the ice. | c. | Some of the water freezes, so the chunk of ice
gets larger. | d. | none of the above |
|
Short Answer (Value 3)
|
|
|
30.
|
If 500 g of iron absorbs 22,000 cal of heat, what will be the change in
temperature? (specific heat of iron = 0.11 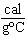 ) Formula q = mc Ät
|