Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Plants are
a. | consumers. | c. | producers. | b. | herbivores. | d. | omnivores. |
|
|
|
2.
|
What is the original source of almost all the energy in most ecosystems?
a. | carbohydrates | c. | sunlight | b. | carbon | d. | water |
|
|
|
3.
|
The repeated movement of water between Earth’s surface and the atmosphere
is called
a. | the water cycle. | c. | the condensation cycle. | b. | precipitation. | d. | evaporation. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Which of the following is NOT a basic method used by ecologists to study the
living world?
a. | observing | c. | classifying | b. | experimenting | d. | modeling |
|
|
|
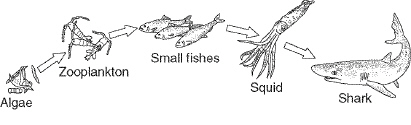
Figure
3–1
|
|
|
5.
|
The algae at the beginning of the food chain in Figure 3–1 are
a. | consumers. | c. | heterotrophs. | b. | decomposers. | d. | producers. |
|
|
|
6.
|
All the interconnected feeding relationships in an ecosystem make up a
food
a. | interaction. | c. | network. | b. | chain. | d. | web. |
|
|
|
7.
|
A mathematical formula designed to predict population fluctuations in a
community could be called a(an)
a. | biological system. | c. | ecological model. | b. | biological experiment. | d. | ecological
observation. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Nitrogen fixation is carried out primarily by
a. | plants. | c. | consumers. | b. | bacteria. | d. | humans. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Matter can recycle through the biosphere because
a. | matter is passed out of the body as waste. | b. | biological systems
use only carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen. | c. | matter is assembled into chemical
compounds. | d. | biological systems do not use up matter, they transform
it. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which of the following organisms does NOT
require sunlight to live?
a. | trees | c. | chemosynthetic bacteria | b. | photosynthetic
bacteria | d. | algae |
|
|
|
11.
|
What animals eat both producers and consumers?
a. | omnivores | c. | chemotrophs | b. | herbivores | d. | autotrophs |
|
|
|
12.
|
The total amount of living tissue within a given trophic level is called
the
a. | energy mass. | c. | trophic mass. | b. | biomass. | d. | organic mass. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Organisms need nutrients in order to
a. | recycle chemical compounds. | c. | carry out nitrogen
fixation. | b. | utilize hydrogen and oxygen. | d. | carry out essential life functions. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which of the following has a direct role in the nitrogen cycle?
a. | bacteria | c. | legumes | b. | decomposers | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
15.
|
The branch of biology dealing with interactions among organisms and between
organisms and their environment is called
a. | ecology. | c. | economy. | b. | recycling. | d. | modeling. |
|
|
|
16.
|
Only 10 percent of the energy stored in an organism can be passed on to the next
trophic level. Of the remaining energy, some is used for the organism’s life processes, and the
rest is
a. | eliminated as heat. | c. | stored as body tissue. | b. | used in
reproduction. | d. | stored as
fat. |
|
|
|
17.
|
What can happen after a lake receives a large input of a limiting
nutrient?
a. | The concentration of oxygen drops below the necessary level. | b. | Algae begin to die
and decomposers take over. | c. | An algal bloom occurs. | d. | Nitrogen compounds
are recycled. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following descriptions about the organization of an ecosystem is
correct?
a. | Species make up populations, which make up communities. | b. | Species make up
communities, which make up populations. | c. | Communities make up species, which make up
populations. | d. | Populations make up species, which make up
communities. |
|
|
|
19.
|
What is the process by which bacteria
convert nitrogen gas in the air to ammonia?
a. | decomposition | c. | denitrification | b. | nitrogen fixation | d. | excretion |
|
|
|
20.
|
An organism that uses energy to produce its own food supply from inorganic
compounds is called a(an)
a. | autotroph. | c. | detritivore. | b. | consumer. | d. | heterotroph. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following is NOT recycled in the biosphere?
a. | water | c. | energy | b. | nitrogen | d. | carbon |
|
|
|
22.
|
The lowest level of environmental complexity that includes living and nonliving
factors is the
a. | biome. | c. | community. | b. | biosphere. | d. | ecosystem. |
|
|
|
23.
|
All of the members of a particular species that live in one area are called
a(an)
a. | biome. | c. | ecosystem. | b. | community. | d. | population. |
|
|
|
24.
|
The simplest grouping of more than one kind of organism in the biosphere
is
a. | a population. | c. | an ecosystem. | b. | a species. | d. | a community. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Corn planted in a field that has been previously planted with legumes and then
plowed under is likely to be
a. | less productive because the legumes have already taken all the nitrogen, carbon, and
phosphorus from the soil. | b. | more productive because nitrogen-fixing
bacteria help to keep away pests. | c. | less productive because legumes remove
phosphorus from the soil. | d. | more productive because bacteria living on the
roots of legumes fix nitrogen in the soil. |
|
|
|
26.
|
Carbon cycles through the biosphere in all of the following processes
EXCEPT
a. | burning of fossil fuels. | c. | transpiration. | b. | photosynthesis. | d. | decomposition of plants and animals. |
|
|
|
27.
|
Most of the energy available to a consumer trophic level is used by organisms
for
a. | performing photosynthesis. | b. | transfer to the next trophic
level. | c. | producing inorganic chemical compounds. | d. | respiration,
movement, and reproduction. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which type of pyramid shows the amount of living tissue at each trophic level in
an ecosystem?
a. | a numbers pyramid | c. | an energy pyramid | b. | a biomass pyramid | d. | a food pyramid |
|
|
|
29.
|
In which way are plants in a sunny mountain meadow and sulfur bacteria in a
deep-sea volcanic vent alike?
a. | They both use chemosynthesis to produce their own food. | b. | They both produce
carbon and hydrogen. | c. | They both produce carbohydrates and
oxygen. | d. | They both use photosynthesis to make their own food. |
|
|
|
30.
|
A bird stalks, kills, and then eats an insect. Based on its behavior, which
ecological terms describe the bird?
a. | carnivore, consumer | c. | producer, heterotroph | b. | herbivore,
decomposer | d. | autotroph,
herbivore |
|
|
|
31.
|
A snake that eats a frog that has eaten an insect that fed on a plant is
a
a. | first-level consumer. | c. | second-level producer. | b. | third-level
consumer. | d. | first-level
producer. |
|
|
|
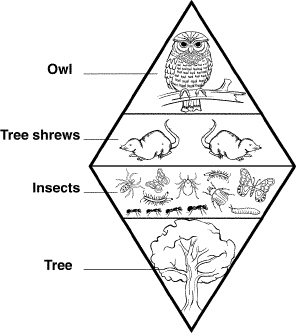
Figure
3–2
|
|
|
32.
|
The trophic levels in Figure 3–2 illustrate
a. | the amount of living organic matter at each level. | b. | the relative number
of individual organisms at each level. | c. | that the producers outnumber first-level
consumers. | d. | the relative amount of energy at each level. |
|
|
|
33.
|
How is carbon stored in the biosphere?
a. | in the atmosphere as carbon dioxide | b. | underground
as fossil fuels and calcium carbonate rock | c. | in the oceans as dissolved carbon
dioxide | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which is most likely to be a limiting nutrient in a freshwater pond?
a. | potassium | c. | nitrogen | b. | phosphorus | d. | carbon |
|
|
|
35.
|
The combined portions of Earth in which all living things exist is called
the
a. | biosphere. | c. | community. | b. | biome. | d. | ecosystem. |
|