Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Ground tissue is found in a plant’s
a. | stems only. | c. | roots and stems only. | b. | stems and leaves
only. | d. | roots, stems, and
leaves. |
|
|
|
2.
|
What type of tissue is the first tissue in a plant seedling?
a. | ground | c. | meristematic | b. | vascular | d. | dermal |
|
|
|
3.
|
In angiosperms, xylem consists of tracheids and
a. | sieve tube elements. | c. | vessel elements. | b. | companion cells. | d. | parenchyma
cells. |
|
|
|
4.
|
If some of the xylem of a young oak tree were destroyed, it would most likely
interfere with the tree’s ability to
a. | conduct sugars to the roots. | c. | absorb water from the
soil. | b. | absorb sunlight. | d. | conduct water to the leaves. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Unlike tracheids, vessel elements
a. | die before they conduct water. | c. | are found in
angiosperms. | b. | form a continuous tube. | d. | are found in phloem. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Vascular tissue in plants consists of
a. | meristem. | c. | parenchyma and collenchyma cells. | b. | xylem and
phloem. | d. | epidermal
cells. |
|
|
|
7.
|
A carrot is a(an)
a. | taproot. | c. | monocot. | b. | fibrous root. | d. | extensive root
system. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which of the following are found mainly in monocots?
a. | taproots | c. | extensive root systems | b. | long, thick primary
roots | d. | small secondary
roots |
|
|
|
9.
|
The vascular cylinder of a root consists of
a. | xylem only. | c. | phloem and xylem. | b. | phloem only. | d. | phloem, xylem, and ground
tissue. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Root pressure
a. | causes a plant’s roots to absorb water. | b. | forces water in
xylem downward. | c. | is produced within the cortex of the root. | d. | is produced in the
vascular cylinder by active transport. |
|
|
|
11.
|
One of the main functions of stems is to
a. | carry out photosynthesis. | b. | transport substances between roots and
leaves. | c. | store carbohydrates. | d. | store water. |
|
|
|
12.
|
The vascular tissue in a plant’s stem
a. | has buds. | b. | is continuous from the roots to the
leaves. | c. | carries nutrients up the stem but not down. | d. | consists of
nodes. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Unlike roots, stems
a. | transport water. | c. | are protected by epidermal cells. | b. | have ground
tissue. | d. | may carry out
photosynthesis. |
|
|
|
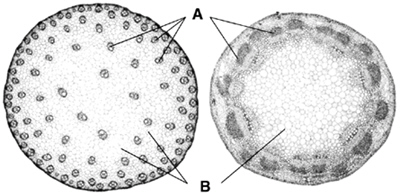
Figure
23–1
|
|
|
14.
|
Figure 23–1 shows cross sections of monocot and dicot
a. | roots. | c. | root hairs. | b. | leaf veins. | d. | stems. |
|
|
|
15.
|
One function of stems is to physically support leaves in a position to maximize
photosynthesis. In large trees, the support function of stems is primarily due to
a. | phloem. | c. | xylem. | b. | pith. | d. | cork cambium. |
|
|
|
16.
|
In dicot plants, secondary growth
a. | changes primary xylem and phloem to secondary xylem and phloem. | b. | makes the roots
longer. | c. | results from an increase in the primary xylem and phloem. | d. | produces bark and
wood. |
|
|
|
17.
|
What might a thin tree ring indicate?
a. | increased production of xylem | c. | decreased production of
phloem | b. | xylem production in winter | d. | a year of drought |
|
|
|
18.
|
Most of the photosynthetic activity in plants takes place in the
a. | mesophyll. | c. | stomata. | b. | guard cells. | d. | xylem. |
|
|
|
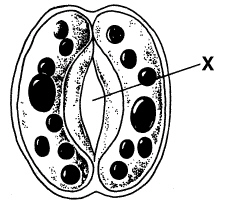
Figure
23–2
|
|
|
19.
|
In Figure 23–2, the X points to a
a. | guard cell. | c. | vein. | b. | mesophyll cell. | d. | stoma. |
|
|
|
20.
|
The stomata of leaves are usually open in
a. | light if a plant has enough water. | c. | darkness if a plant has enough
water. | b. | light if a plant has too little water. | d. | darkness if a plant has too little
water. |
|
|
|
21.
|
In many plants, stomata are found only on the lower surface of the leaf.
The most likely explanation for this observation is that
a. | photosynthesis only occurs in the spongy mesophyll near the bottom of the
leaf. | b. | stomata are closer to vascular bundles that bring water into the
leaf. | c. | gas exchange is more efficient from the lower surface. | d. | water loss would be
less on the shady lower surface than in direct sun. |
|
|
|
22.
|
If a plant’s gametophyte is conspicuous, the plant is NOT a
a. | bryophyte. | c. | spore-bearing vascular plant. | b. | seed
plant. | d. | nonvascular
plant. |
|
|
|
23.
|
In angiosperms, reproduction takes place in
a. | leaves. | c. | cones. | b. | flowers. | d. | pollen. |
|
|
|
24.
|
In some flowers, the female gametophytes are produced by multiple fused
a. | carpels. | c. | anthers. | b. | petals. | d. | sepals. |
|
|
|
25.
|
A sticky secretion on the scales of seed cones traps
a. | sporophytes. | c. | pollen grains. | b. | pollen cones. | d. | egg cells. |
|
|
|
26.
|
The tough outer layer of a seed is called the
a. | seed coat. | c. | nut. | b. | fruit. | d. | embryo wall. |
|
|
|
27.
|
A ripened ovary that contains angiosperm seeds is called a(an)
a. | embryo. | c. | fruit. | b. | seed. | d. | vegetable. |
|
|
|
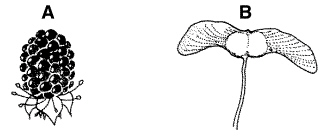
Figure
24–1
|
|
|
28.
|
The seed type shown in Figure 24–1 that is generally dispersed by animals
is(are)
a. | only A. | c. | both A and B. | b. | only B. | d. | neither A nor
B. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Seeds dispersed by animals typically are contained in
a. | fleshy, nutritious fruits. | c. | thin coatings that are easily
digested. | b. | unripened ovaries. | d. | lightweight structures. |
|
|
|
30.
|
A period during which the embryo of a seed is alive but not growing is
a. | fruit production. | c. | germination. | b. | seed production. | d. | dormancy. |
|
|
|
31.
|
The early growth stage of a plant embryo is called
a. | fertilization. | c. | germination. | b. | dormancy. | d. | pollination. |
|
|
|
32.
|
In the meristem regions of plants, you would expect to find
a. | inactive cells. | c. | companion cells. | b. | dividing cells. | d. | reproductive
cells. |
|
|
|
33.
|
Auxins are produced in
a. | xylem. | c. | pith. | b. | phloem. | d. | apical
meristem. |
|
|
|
34.
|
Hormones that stimulate cell elongation and are produced in the rapidly growing
region near the tip of the plant’s root or stem are called
a. | auxins. | c. | cytokinins. | b. | ethylenes. | d. | gibberellins. |
|
|
|
35.
|
If the apical meristem of a mature plant is removed, the plant will most
likely
a. | lose its ability to move phototropically. | b. | show a dramatic and
rapid increase in height. | c. | develop apical dominance and begin to
flower. | d. | lose apical dominance and grow lateral branches. |
|
|
|
36.
|
The growth patterns of ivy tendrils that wrap around objects is an example
of
a. | gravitropism. | c. | thigmotropism. | b. | phototropism. | d. | photoperiodism. |
|
|
|
37.
|
Roots growing with gravity and stems growing against gravity are examples
of
a. | gravitropism. | c. | thigmotropism. | b. | phototropism. | d. | photoperiodism. |
|
|
|
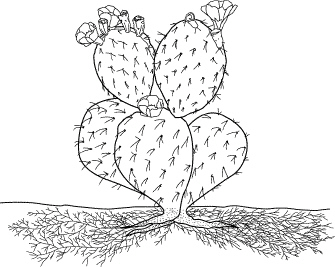
Figure
25–2
|
|
|
38.
|
How is the cactus in Figure 25–2 adapted to soak up rare rainfall
quickly?
a. | It has thin, sharp spines. | b. | It has stems that shrivel when it
rains. | c. | It has wide stems that catch rainwater. | d. | It has an extensive
shallow root system. |
|
Modified True/False
Indicate
whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
statement true.
|
|
|
39.
|
Phloem consists of vessel elements and companion cells.
_________________________
|
|
|
40.
|
Meristematic tissue produces new cells by mitosis.
_________________________
|
|
|
41.
|
A decrease in the active transport of minerals into a root would not
cause the root to release water into the soil. _________________________
|
|
|
42.
|
In a tree, the heartwood increases in width over time.
_________________________
|
|
|
43.
|
Transpiration from leaves occurs because of the osmosis of water from the
leaf to the environment. _________________________
|
|
|
44.
|
In plants, the opening and closing of stomata balance water loss with the need
for carbon dioxide. _________________________
|
|
|
45.
|
Water rises to the top of a giant redwood tree by transpiration pull.
_________________________
|
|
|
46.
|
In gymnosperms, gametophytes are hidden in cones.
_________________________
|
|
|
47.
|
Pollen cones are also called female cones.
_________________________
|
|
|
48.
|
When you look at a mature gymnosperm or angiosperm, you see the more conspicuous
gametophyte. _________________________
|
|
|
49.
|
A fruit always contains one or more seeds.
_________________________
|
|
|
50.
|
In seed plants, parts of the ovule toughen to form a fruit, which
protects the delicate embryo and its food supply. _________________________
|
|
|
51.
|
Fruit is an adaptation that helps ensure pollination.
_________________________
|
|
|
52.
|
Some seeds go through a period of dormancy, during which they do not
germinate. _________________________
|
|
|
53.
|
Cells on the shaded side of a stem elongate more than cells on the side
receiving light because of the hormone ethylene. _________________________
|
|
|
54.
|
Seedlings finding their way out of the soil and into the sunlight is an example
of photoperiodism. _________________________
|
|
|
55.
|
The growing tip of a climbing vine exhibits phototropism when it grows in
a circling motion. _________________________
|
Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
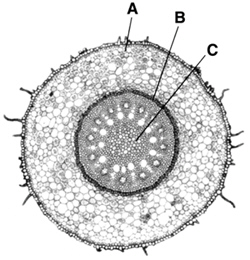
Figure
23–3
|
|
|
56.
|
Figure 23–3 shows a cross section of a(an) ____________________.
|
|
|
57.
|
Root hairs take in water from the soil through the process of
____________________.
|
|
|
58.
|
As the relative concentration of mineral ions in a root’s epidermal cells
increases, the relative concentration of water molecules ____________________.
|
|
|
59.
|
____________________ consists of the outer layers of secondary xylem in dicot
stems.
|
|
|
60.
|
____________________ cells control the opening and closing of stomata.
|
|
|
61.
|
A sperm nucleus moves toward a flower’s ovary through a long passageway
called a pollen ____________________.
|
|
|
62.
|
Any seed enclosed within its ovary wall is properly referred to as a
____________________.
|
|
|
63.
|
A coconut is a very large ____________________ that contains a milky endosperm
layer.
|
|
|
64.
|
Plant responses to external stimuli are called ____________________, from a
Greek word meaning “turning.”
|
|
|
65.
|
As cold weather approaches, ____________________ plants turn off photosynthetic
pathways.
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
66.
|
How is the function of a tree trunk related to photosynthesis?
|
|
|
67.
|
Contrast the flow of materials in xylem and phloem.
|
|
|
68.
|
Contrast the growth of fibrous roots and taproots in soil.
|
|
|
69.
|
Which roots are more effective in reducing erosion, fibrous roots or taproots?
Explain your answer.
|
|
|
70.
|
What do roots absorb from the soil?
|
|
|
71.
|
By what three processes does water rise from the roots to the top of a
tree?
|
|
|
72.
|
What is the typical method of pollen dispersal for gymnosperms? For
angiosperms?
|
|
|
73.
|
How can you tell by looking at a fruit how the seeds it contains are
dispersed?
|
|
|
74.
|
Name two environmental factors that can end a seed’s dormancy.
|