Multiple Choice (Value 20)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
If some of the xylem of a young oak tree were destroyed, it would most likely
interfere with the tree’s ability to
a. | conduct water to the leaves. | c. | conduct sugars to the
roots. | b. | absorb water from the soil. | d. | absorb sunlight. |
|
|
|
2.
|
The closing of a plant’s stomata will
a. | cause less water to be pulled up from the plant’s roots. | b. | increase
transpiration pull. | c. | increase capillary action in the plant’s
stem. | d. | cause wilting. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which of the following describes the heartwood of a tree?
a. | produces protective layers of cork | b. | old, nonfunctioning xylem | c. | active xylem that
transports water and minerals | d. | old, nonfunctioning
phloem |
|
|
|
4.
|
A seed plant is anchored in the ground by its
a. | leaves. | c. | roots. | b. | stems. | d. | trichomes. |
|
|
|
5.
|
The stomata of leaves are usually open in
a. | darkness if a plant has enough water. | c. | light if a plant has enough
water. | b. | light if a plant has too little water. | d. | darkness if a plant has too little
water. |
|
|
|
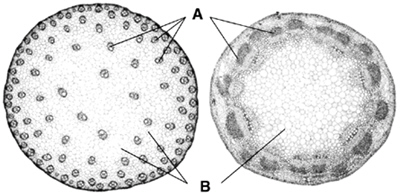
Figure
23–1
|
|
|
6.
|
Figure 23–1 shows cross sections of monocot and dicot
a. | stems. | c. | root hairs. | b. | roots. | d. | leaf veins. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which of the following is most likely to be used as a food source?
a. | root with many root hairs | c. | root of a
monocot | b. | fibrous root | d. | root of a dicot |
|
|
|
8.
|
A carrot is a(an)
a. | monocot. | c. | extensive root system. | b. | taproot. | d. | fibrous root. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Unlike tracheids, vessel elements
a. | are found in phloem. | c. | die before they conduct water. | b. | form a continuous
tube. | d. | are found in
angiosperms. |
|
|
|
10.
|
The outer covering of a plant consists of
a. | dermal tissue. | c. | meristematic tissue. | b. | vascular tissue. | d. | ground tissue. |
|
|
|
11.
|
What type of tissue is the first tissue in a plant seedling?
a. | vascular | c. | meristematic | b. | dermal | d. | ground |
|
|
|
12.
|
The attraction of water molecules to other molecules is called
a. | capillary action. | c. | cohesion. | b. | transpiration pull. | d. | adhesion. |
|
|
|

Figure
23–2
|
|
|
13.
|
In Figure 23–2, the water pressure in the
a. | guard cells is high. | c. | stoma is high. | b. | guard cells is low. | d. | stoma is low. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Root pressure
a. | is produced within the cortex of the root. | b. | forces water in
xylem downward. | c. | is produced in the vascular cylinder by active transport. | d. | causes a
plant’s roots to absorb water. |
|
|
|
15.
|
Water will move higher in a narrow glass tube than in a wide glass tube because
of
a. | pressure. | c. | capillary action. | b. | cohesion only. | d. | adhesion only. |
|
|
|
16.
|
Vascular tissue in plants consists of
a. | parenchyma and collenchyma cells. | c. | meristem. | b. | xylem and
phloem. | d. | epidermal
cells. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Most of the photosynthetic activity in plants takes place in the
a. | guard cells. | c. | xylem. | b. | stomata. | d. | mesophyll. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which one of the following statements is true?
a. | The vascular bundles of monocot and dicot stems are continuous from the root’s
vascular cylinder. | b. | The tissues in a monocot stem are different
from those in a dicot stem. | c. | Xylem and phloem cells of monocots are arranged
in a cylinder. | d. | The pith and cortex of dicot stems consist of meristematic
cells. |
|
|
|
19.
|
In many plants, stomata are found only on the lower surface of the leaf.
The most likely explanation for this observation is that
a. | water loss would be less on the shady lower surface than in direct
sun. | b. | gas exchange is more efficient from the lower surface. | c. | photosynthesis only
occurs in the spongy mesophyll near the bottom of the leaf. | d. | stomata are closer
to vascular bundles that bring water into the leaf. |
|
|
|
20.
|
The movement of sugars in a plant can be explained by
a. | root pressure. | c. | capillary action. | b. | transpiration pull. | d. | the pressure-flow
hypothesis. |
|
Modified True/False (Value 10)
Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false,
change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true.
|
|
|
21.
|
When plants pump nutrients from their roots to their branches, the roots
are the sink. _________________________
|
|
|
22.
|
Meristematic tissue produces new cells by mitosis.
_________________________
|
|
|
23.
|
The thin, flat part of a leaf is called the petiole.
_________________________
|
|
|
24.
|
When the guard cells of a leaf lose water, the stomata open.
_________________________
|
|
|
25.
|
A decrease in the active transport of minerals into a root would not
cause the root to release water into the soil. _________________________
|
|
|
26.
|
The secondary growth of a dicot stem results from cell divisions in the
stem’s vascular cambium and xylem. _________________________
|
|
|
27.
|
In plants, the opening and closing of stomata balance water loss with the need
for carbon dioxide. _________________________
|
|
|
28.
|
The principal organs in which plants carry out photosynthesis are leaves.
_________________________
|
|
|
29.
|
In a tree, the heartwood increases in width over time.
_________________________
|
|
|
30.
|
The vascular bundles in a dicot stem are arranged randomly.
_________________________
|
Completion (Value 5)
Complete
each statement.
|
|
|
31.
|
As the relative concentration of mineral ions in a root’s epidermal cells
increases, the relative concentration of water molecules ____________________.
|
|
|
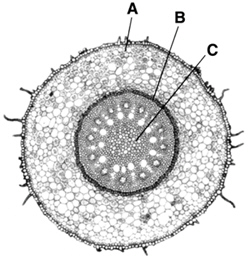
Figure
23–3
|
|
|
32.
|
Figure 23–3 shows a cross section of a(an) ____________________.
|
|
|
33.
|
Stomata open into the _________________________ layer of a leaf.
|
|
|

Figure
23–1
|
|
|
34.
|
In Figure 23–1, B is pointing to _________________________.
|
|
|
35.
|
The phloem cells called ___________________ are arranged end to end to form a
long pipeline.
|
Short Answer (Value 10)
|
|
|
36.
|
How is the function of a stem similar to that of a root?
|
|
|
37.
|
Contrast the growth of fibrous roots and taproots in soil.
|
|
|
38.
|
Contrast the flow of materials in xylem and phloem.
|
|
|
39.
|
Contrast the arrangement of vascular bundles in monocot stems and dicot
stems.
|
|
|
40.
|
What do roots absorb from the soil?
|