Multiple Choice (Value 20)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Which of the following is NOT a way in which archaebacteria and eubacteria
differ?
a. | Archaebacteria lack an important carbohydrate found in the cell walls of
eubacteria. | b. | The two groups have very different membrane lipids. | c. | Archaebacteria have
gene sequences that are similar to those of eukaryotes. | d. | Archaebacteria
follow the lytic cycle, while eubacteria follow the lysogenic cycle. |
|
|
|
Figure
19–1
|
|
|
2.
|
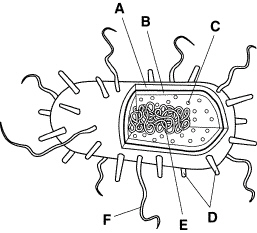
The structure in Figure 19–1 represents a(an)
a. | virus. | c. | methanogen. | b. | archaebacterium. | d. | eubacterium. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which structure or structures shown in Figure 19–1 have key differences in
eubacteria and archaebacteria?
a. | A, B, C | c. | D only | b. | A, B, E | d. | A only |
|
|
|
Figure
19–2
|
|
|
4.
|
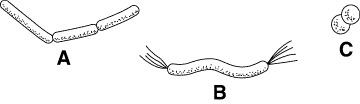
Which cell shape in Figure 19–2 is called a coccus?
a. | A | c. | C | b. | B | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which of the following can survive either with oxygen or without it?
a. | obligate aerobes | c. | facultative anaerobes | b. | obligate
anaerobes | d. | bacteriophages |
|
|
|
6.
|
Some bacteria are able to survive unfavorable conditions by forming
a. | photoautotrophs. | c. | coccus. | b. | capsids. | d. | endospores. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which of the following is(are) used to identify prokaryotes?
a. | cell shape | c. | the way prokaryotes obtain energy | b. | the way prokaryotes
move | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
8.
|
Humans use bacteria to
a. | clean up small oil spills. | c. | synthesize
drugs. | b. | mine minerals from the ground. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
9.
|
The outer protein coat of a virus is called a
a. | DNA core. | c. | bacteriophage. | b. | capsid. | d. | tail sheath. |
|
|
|
10.
|
The instructions for making new copies of a virus are
a. | a part of a virus’s capsid. | b. | coded in surface proteins attached to the
protein coat. | c. | coded in either RNA or DNA. | d. | found only in
bacteriophages. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Viruses
a. | are all about the same size. | b. | vary greatly in size and
structure. | c. | rarely contain DNA or RNA. | d. | can be seen with a basic compound light
microscope. |
|
|
|
12.
|
A prophage is made of
a. | bacteriophages. | c. | capsid proteins. | b. | carbohydrates. | d. | viral DNA. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Bacteriophages infect
a. | other viruses. | c. | any available host cell. | b. | bacteria
only. | d. | cells undergoing the
lytic cycle. |
|
|
|
14.
|
During a lytic infection, the host cell is
a. | destroyed. | c. | copied many times over. | b. | prepared for the
lysogenic cycle. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following is a way that bacteria cause disease?
a. | by capsids | c. | by conjugation | b. | by nitrogen fixation | d. | by releasing
toxins |
|
|
|
16.
|
A vaccine would be useful if given to
a. | a potato farmer whose entire crop is infected with a potato virus. | c. | a teenager who has
strep throat. | b. | a nurse who works around people infected with tuberculosis. | d. | a cow that probably has mad cow
disease. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following is NOT a viral disease?
a. | botulism | c. | measles | b. | AIDS | d. | polio |
|
|
|
18.
|
Viral diseases can be
a. | treated with antibiotics and prevented with vaccines. | b. | treated with
vaccines and prevented with antibiotics. | c. | prevented with antibiotics but not treated with
vaccines. | d. | prevented with vaccines but not treated with
antibiotics. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Plant viruses have a difficult time entering the cells they infect partly
because
a. | plant viruses are weaker than animal viruses. | b. | plant cells have
tough cell walls. | c. | many plant viruses are spread by
insects. | d. | plant viruses do not have a protein coat. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Prions differ from viruses because
a. | prions do not cause disease. | c. | prions only infect plant
cells. | b. | prions contain no DNA or RNA. | d. | prions do not contain any
protein. |
|
Modified True/False (Value 10)
Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false,
change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true.
|
|
|
21.
|
Scientists reason that archaebacteria may be the ancestors of eukaryotes.
If this is true, then archaebacteria and eukaryotes share a common ancestor that is more
recent than the common ancestor of archaebacteria and eubacteria. _________________________
|
|
|
22.
|
Many archaebacteria live in extreme environments, such as in Utah’s
Great Salt Lake. _________________________
|
|
|
23.
|
A major difference between archaebacteria and eubacteria is the presence of
peptidoglycan in the cell membrane of eubacteria._________________________
|
|
|

Figure
19–2
|
|
|
24.
|
Figure 19–2 shows the three shapes of viruses.
_________________________
|
|
|
25.
|
The spiral-shaped organism labeled B in Figure 19–2 is an example of a
spirillum. _________________________
|
|
|
26.
|
The bacterium Rhizobium, which grows on the roots of legumes, helps
“fix” the carbon in the air by forming ammonium.
_________________________
|
|
|
27.
|
T4 is the name of a bacteriophage. _________________________
|
|
|
Figure
19–3
|
|
|
28.
|
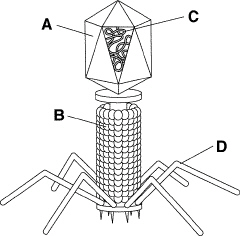
The structure labeled D in Figure 19–3 is called a tail fiber.
_________________________
|
|
|
29.
|
Bacteria can cause disease by releasing toxins into the body.
_________________________
|
|
|
30.
|
Insects often help spread viruses from one plant to another.
_________________________
|
Completion (Value 5)
Complete
each statement.
|
|
|
31.
|
Based on DNA sequences of key archaebacterial genes, archaebacteria and
____________________ seem to share a more recent common ancestor than do archaebacteria and
____________________.
|
|
|

Figure
19–2
|
|
|
32.
|
The organism labeled A in Figure 19–2 is an example of a(an)
____________________.
|
|
|

Figure
19–3
|
|
|
33.
|
In Figure 19–3, the structure labeled D is a(an)
____________________.
|
|
|
34.
|
Destroying bacteria by subjecting them to great heat or to chemical action is
called ____________________.
|
|
|
35.
|
A chemical solution that is used in hospitals to kill bacteria is called a(an)
____________________.
|
Short Answer (Value 4)
|
|
|
36.
|
Name the two kingdoms of bacteria. List one way that these two groups differ
from each other.
|
|
|
37.
|
Describe two methods of killing bacteria.
|