Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Which of the following is an example of an organ?
a. | heart | c. | nerve cell | b. | epithelial tissue | d. | digestive
system |
|
|
|
2.
|
Which of the following is NOT an example of a heterotroph?
a. | leopard | c. | grass | b. | human | d. | mushroom |
|
|
|
3.
|
Eubacteria and archaebacteria differ in
a. | the presence of a nucleus. | c. | the presence of a cell
wall. | b. | size. | d. | the
makeup of their cell walls. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Unlike tracheids, vessel elements
a. | are found in angiosperms. | c. | form a continuous
tube. | b. | are found in phloem. | d. | die before they conduct water. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which of the following carries essential materials into the leaf to be used in
the process of photosynthesis?
a. | parenchyma | c. | phloem | b. | cambium | d. | xylem |
|
|
|
6.
|
The outer protein coat of a virus is called a
a. | DNA core. | c. | bacteriophage. | b. | tail sheath. | d. | capsid. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Members of the phylum Chrysophyta contain chloroplasts of what color?
a. | silver | c. | green | b. | red | d. | gold |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which of the following is a function of the nucleus?
a. | contains the information needed to make proteins | b. | stores
DNA | c. | controls most of the cell’s processes | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
9.
|
Food stored in a refrigerator will keep longer because the bacteria that spoil
food
a. | require light to live. | b. | take longer to multiply at low
temperatures. | c. | grow more slowly in the dark. | d. | die at low
temperatures. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Jan van Helmont concluded that plants gain most of their mass from
a. | water. | c. | carbon dioxide in the air. | b. | the
soil. | d. | oxygen in the
air. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Sometimes, organisms that are not closely related look similar because of
a. | convergent evolution. | c. | mutations. | b. | reclassification. | d. | molecular
clocks. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Diffusion occurs because
a. | molecules constantly move and collide with each other. | b. | molecules never move
or collide with each other. | c. | the concentration of a solution is never the
same throughout a solution. | d. | the concentration of a solution is always the
same throughout a solution. |
|
|
|
13.
|
The domain that corresponds to the kingdom Eubacteria is
a. | Fungi. | c. | Eukarya. | b. | Archaea. | d. | Bacteria. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which of the following is most likely to be used as a food source?
a. | root of a dicot | c. | fibrous root | b. | root with many root hairs | d. | root of a
monocot |
|
|
|
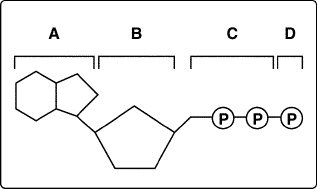
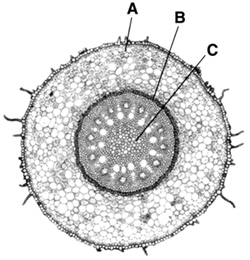
Figure
8–1
|
|
|
15.
|
In Figure 8–1, between which parts of the molecule must the bonds be
broken to form an ADP molecule?
a. | B and C | c. | A and B | b. | C and D | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which structures shown in Figure 8–1 make up an ATP molecule?
a. | A and B | c. | A, B, and C | b. | C and D | d. | A, B, C, and D |
|
|
|
17.
|
The cells of multicellular organisms are
a. | not dependent on one another. | b. | specialized to perform different
tasks. | c. | simpler than those of unicellular organisms. | d. | smaller than those
of unicellular organisms. |
|
|
|
18.
|
What do all organisms have in common?
a. | They are all prokaryotes. | b. | They are all eukaryotes. | c. | They use DNA and RNA
to pass on information. | d. | They are genetically
identical. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which organism is NOT likely to carry out cellular respiration?
a. | mushroom | c. | anaerobic bacterium | b. | tiger | d. | tree |
|
|
|
20.
|
What do the members of the phylum Pyrrophyta have in common with many of the
members of the phylum Chrysophyta?
a. | They have cell walls of cellulose. | b. | They have pellicles. | c. | They have cell walls
of silica. | d. | They can be both photosynthetic and heterotrophic. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which organelle converts the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that
are more convenient for the cell to use?
a. | chloroplast | c. | Golgi apparatus | b. | mitochondrion | d. | endoplasmic
reticulum |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which of these is a product of cellular respiration?
a. | water | c. | oxygen | b. | glucose | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
23.
|
The main function of the cell wall is to
a. | store DNA. | c. | direct the activities of the cell. | b. | help the cell
move. | d. | support and protect
the cell. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Often, the second part of a scientific name is
a. | a Latinized description of a particular trait. | b. | capitalized if it
derives from a proper name. | c. | different in different
locations. | d. | the same as for other members of the same genus. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following structures is found in the cytoplasm?
a. | cell wall | c. | ribosome | b. | nucleolus | d. | chromatin |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which of the following is produced when bacteria break down complex compounds in
sewage?
a. | carbon dioxide gas | c. | purified water | b. | nitrogen | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
27.
|
A bloom is
a. | the clouding of water by sewage. | b. | a symbiotic relationship between algae and
coral. | c. | an enormous mass of algae. | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
28.
|
A well-tested explanation that unifies a broad range of observations is
a(an)
a. | hypothesis. | c. | theory. | b. | inference. | d. | controlled
experiment. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Organisms in the kingdoms Eubacteria and Archaebacteria were previously grouped
in a kingdom called
a. | Monera. | c. | Fungi. | b. | Animalia. | d. | Eukarya. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which statement about malaria is true?
a. | Malaria has been eradicated by control of the Anopheles
mosquito. | b. | All strains can be treated with modern drugs, and there is an effective
vaccine. | c. | Not all strains can be treated, and there is no completely effective
vaccine. | d. | Many strains can be treated with modern drugs; however, there is no completely
effective vaccine. |
|
|
|
31.
|
Ingenhousz showed that plants produce oxygen bubbles when exposed to
a. | a burning candle. | c. | ATP. | b. | light. | d. | carbon dioxide. |
|
|
|
32.
|
A carrot is a(an)
a. | extensive root system. | c. | fibrous root. | b. | taproot. | d. | monocot. |
|
|
|
33.
|
Which of the following is the best reason for using a scanning electron
microscope?
a. | ability to magnify objects that are larger than 0.2 micrometers | b. | ability to observe
live organisms | c. | ability to see three-dimensional images of the surfaces of
objects | d. | ability to see movement within living cells |
|
|
|
34.
|
What does a cladistic analysis show about organisms?
a. | the relative importance of each derived character | b. | the general fitness
of the organisms analyzed | c. | the order in which derived characters
evolved | d. | all traits of each organism analyzed |
|
|
|
35.
|
The function of conjugation in paramecia is to
a. | expel excess water, thereby maintaining homeostasis. | b. | exchange genetic
material, thus increasing diversity of the population. | c. | trigger the release of
trichocysts. | d. | create new individual paramecia. |
|
|
|
36.
|
Bacteria that break down the nutrients in dead matter into simpler substances
that are taken up by plant roots are called
a. | flagella. | c. | photoautotrophs. | b. | decomposers. | d. | endospores. |
|
|
|
37.
|
Based on their names, you know that the baboons Papio annubis and
Papio cynocephalus do NOT belong to the same
a. | class. | c. | species. | b. | genus. | d. | family. |
|
|
|
38.
|
Which type(s) of microscopes can produce three-dimensional images of
cells?
a. | scanning electron microscopes | c. | both A and B | b. | transmission
electron microscopes | d. | neither A nor B |
|
|
|
39.
|
What technique is used to separate different cell parts?
a. | cell fractionation | c. | microscopy | b. | cell culture | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
40.
|
A method called Gram staining is used to tell
a. | whether a prokaryote has flagella. | b. | how a prokaryote obtains
energy. | c. | what kind of cell wall a prokaryote has. | d. | what shape a
prokaryote has. |
|
|
|
41.
|
Science differs from other disciplines, such as history and the arts, because
science relies on
a. | testing explanations. | c. | observations. | b. | facts. | d. | theories. |
|
|
|
42.
|
Escherichia coli is classified as a(an)
a. | eukaryote. | b. | archaebacterium. | c. | eubacterium. | d. | virus. |
|
|
|
43.
|
Which of the following terms includes all the others?
a. | paleontologist | c. | botanist | b. | biologist | d. | zoologist |
|
|
|
44.
|
Phytoplankton are only found at the surface of ocean waters because
a. | they are an important food source to surface-dwelling marine
organisms. | b. | they cannot withstand the colder temperatures of deep water. | c. | they require
sunlight to carry out photosynthesis. | d. | they feed on tiny organisms living at the
surface. |
|
|
|
45.
|
What is true about dissimilar organisms such as a cow and a yeast?
a. | They are not related at all. | b. | Their degree of relatedness can be determined
from their genes. | c. | They can interbreed and thus are the same
species. | d. | Their degree of relatedness cannot be evaluated. |
|
|
|
46.
|
Most of the photosynthetic activity in plants takes place in the
a. | stomata. | c. | guard cells. | b. | mesophyll. | d. | xylem. |
|
|
|
47.
|
An analysis of derived characters is used to generate a
a. | cladogram. | b. | family tree based on DNA
structure. | c. | family tree based on external appearance. | d. | traditional
classification system. |
|
|
|
48.
|
Which of the following is a characteristic of bacteria that is key to keeping
them under control?
a. | Most bacteria cannot survive high temperatures for long periods. | b. | Most bacteria do not
cause food to spoil. | c. | Most bacteria form endospores when subjected to
harsh conditions. | d. | Most bacteria are resistant to harmful
chemicals. |
|
|
|
49.
|
Which of the following is released during cellular respiration?
a. | oxygen | c. | lactic acid | b. | energy | d. | air |
|
|
|
50.
|
What triggers the aggregation of many slime mold individuals into one giant,
sluglike mass?
a. | depleted food supply | c. | invasion of a parasite | b. | lack of
water | d. | cold
weather |
|
|
|
51.
|
According to Lynn Margulis, eukaryotic cells may have evolved from
a. | chloroplasts that grew very large. | c. | mitochondria that grew very
large. | b. | a symbiosis of several cells. | d. | plants, animals, and
fungi. |
|
|
|
52.
|
Information gathered from observing a plant grow 3 cm over a two-week period
results in
a. | variables. | c. | hypotheses. | b. | inferences. | d. | data. |
|
|
|
53.
|
Scientists have found that humans and yeasts
a. | have nothing in common. | b. | cannot be evaluated for degree of
relatedness. | c. | share all aspects of cellular structure. | d. | have similar genes
for the assembly of certain proteins. |
|
|
|
54.
|
Glycolysis requires
a. | hours to produce many ATP molecules. | b. | oxygen. | c. | NADP+. | d. | an energy
input. |
|
|
|
55.
|
A seed plant is anchored in the ground by its
a. | roots. | c. | leaves. | b. | stems. | d. | trichomes. |
|
|
|
56.
|
When the body needs to exercise for longer than 90 seconds, it generates ATP by
carrying out
a. | cellular respiration. | c. | lactic acid fermentation. | b. | glycolysis. | d. | alcoholic fermentation. |
|
|
|
57.
|
According to the pressure-flow hypothesis, which of the following statements is
NOT true?
a. | Phloem is able to move sugars in either direction to meet the nutritional needs of
the plant. | b. | Water is necessary for sugars to move through phloem. | c. | The movement of
water into a nutrient-rich region of the phloem decreases the pressure in that
region. | d. | Water moves from the xylem to the phloem of a plant. |
|
|
|
58.
|
Which of the following diseases is NOT caused by a bacterium?
a. | Lyme disease | c. | tooth decay | b. | tuberculosis | d. | AIDS |
|
|
|
59.
|
Suppose Priestley repeated his experiment using many kinds of plants besides
mint, and that when different plants were placed under the jar the candle remained lighted for
different periods of time. What would be a logical conclusion from these experiments?
a. | Different plants require different amounts of light. | b. | Different plants
release different amounts of oxygen. | c. | Different plants release different amounts of
carbon dioxide. | d. | Different plants require different amounts of water. |
|
|
|
60.
|
Which of the following structures serves as the cell’s boundary from its
environment?
a. | mitochondrion | c. | channel proteins | b. | cell membrane | d. | chloroplast |
|
|
|
61.
|
Because you may come in contact with organisms you cannot see, what safety
procedure MUST be followed?
a. | Wash your hands thoroughly after completing the activity. | b. | Read over your
activity. | c. | Open the windows of the laboratory. | d. | Do not wear long
sleeves. |
|
|
|
62.
|
Plants cannot release energy from glucose using
a. | glycolysis. | c. | the Krebs cycle. | b. | cellular respiration. | d. | photosynthesis. |
|
|
|
63.
|
Unlike roots, stems
a. | are protected by epidermal cells. | c. | transport
water. | b. | may carry out photosynthesis. | d. | have ground
tissue. |
|
|
|
64.
|
Which of the following is NOT a step in the light-dependent reactions?
a. | ATP synthase allows H+ ions to pass through the thylakoid
membrane. | b. | High-energy electrons move through the electron transport chain. | c. | Pigments in
photosystem II absorb light. | d. | ATP and NADPH are used to produce high-energy
sugars. |
|
|
|
65.
|
In the presence of oxygen, glycolysis is followed by
a. | lactic acid fermentation. | c. | photosynthesis. | b. | alcoholic
fermentation. | d. | the Krebs
cycle. |
|
|
|
66.
|
Water will move higher in a narrow glass tube than in a wide glass tube because
of
a. | capillary action. | c. | adhesion only. | b. | pressure. | d. | cohesion only. |
|
|
|
67.
|
What is the main idea behind the model of a molecular clock?
a. | that phenotypes, not genotypes, are affected by natural selection | b. | that segments of DNA
can be compared with segments of RNA | c. | that certain traits are under the pressure of
natural selection | d. | that neutral mutations accumulate at a steady
rate |
|
|
|
68.
|
Which of the following structures would NOT be found in a Euglenophyte?
a. | flagellum | b. | eyespot | c. | cell
wall | d. | pellicle |
|
|
|
69.
|
Animals that are warm-blooded, have body hair, and produce milk for their young
are grouped in the class
a. | Amphibia. | c. | Reptilia. | b. | Aves. | d. | Mammalia. |
|
|
|
70.
|
Most plants appear green because chlorophyll
a. | reflects violet light. | c. | does not absorb green light. | b. | absorbs green
light. | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
71.
|
What types of living organisms should you NOT come into contact with in your
biology laboratory?
a. | plants | b. | organisms that can be seen only with a
microscope | c. | organisms that cause disease | d. | animals |
|
|
|
72.
|
Which statement mainly explains why even well-conditioned athletes have to pace
themselves for athletic events that last several hours?
a. | Heavy breathing is needed to get rid of lactic acid. | b. | Lactic acid
fermentation can cause muscle soreness. | c. | Cellular respiration releases energy more
slowly than fermentation does. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
73.
|
Which of the following is(are) used in the overall reactions for
photosynthesis?
a. | light | c. | water | b. | carbon dioxide | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
74.
|
If some of the xylem of a young oak tree were destroyed, it would most likely
interfere with the tree’s ability to
a. | absorb water from the soil. | c. | conduct water to the
leaves. | b. | conduct sugars to the roots. | d. | absorb
sunlight. |
|
|
|
75.
|
What are the reactants in the equation for cellular respiration?
a. | glucose and oxygen | c. | water and glucose | b. | carbon dioxide and water | d. | oxygen and lactic
acid |
|
|
|
76.
|
Which sequence correctly traces the path of a protein in the cell?
a. | ribosome, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, chloroplast | b. | smooth endoplasmic
reticulum, lysosome, Golgi apparatus | c. | mitochondria, rough endoplasmic reticulum, cell
membrane | d. | rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, released from the
cell |
|
|
|
77.
|
Which of the following is a function of the cytoskeleton?
a. | surrounds the cell | c. | contains DNA | b. | helps make proteins | d. | helps a cell keep its
shape |
|
|
|
78.
|
A prophage is made of
a. | carbohydrates. | c. | capsid proteins. | b. | bacteriophages. | d. | viral DNA. |
|
|
|
79.
|
Where are you likely to find a photoautotroph?
a. | in your digestive system | b. | near the surfaces of lakes, streams, and
oceans | c. | in the darkness of the ocean | d. | in your
refrigerator |
|
|
|
80.
|
Scientists publish the details of important experiments so that
a. | their experimental procedures can be reviewed. | b. | others can try to
reproduce the results. | c. | their work can be repeated. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
81.
|
An instrument used to separate cell parts according to density is the
a. | centrifuge. | c. | blender. | b. | electron microscope. | d. | compound light
microscope. |
|
|
|
82.
|
The three-domain system arose when scientists grouped organisms according to how
long they have been
a. | going extinct. | c. | alive in their present forms. | b. | using DNA to store
information. | d. | evolving
independently. |
|
|
|
83.
|
The Calvin cycle takes place in the
a. | thylakoid membranes. | c. | stroma. | b. | photosystems. | d. | chlorophyll
molecules. |
|
|
|
84.
|
Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells?
a. | Rudolf Virchow | c. | Robert Hooke | b. | Matthias Schleiden | d. | Anton van
Leeuwenhoek |
|
|
|
85.
|
The electron transport chain can be found in
a. | prokaryotes. | c. | plants. | b. | animals. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
86.
|
Which of the following acts as an electron carrier in cellular
respiration?
a. | NAD+ | c. | ATP | b. | ADP | d. | pyruvic acid |
|
|
|
87.
|
A protist is any organism that is not a plant, an animal, a fungus, or
a(an)
a. | prokaryote. | c. | eubacterium. | b. | eukaryote. | d. | archaebacterium. |
|
|
|
88.
|
Biologists use a classification system to group organisms in part because
organisms
a. | share too many derived characters. | c. | are very numerous and
diverse. | b. | are too much alike. | d. | are going extinct. |
|
|
|
89.
|
Which of the following is inside the thylakoid membrane?
a. | ATP synthase | c. | electron transport chain | b. | photosystem
I | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
90.
|
Which organelle breaks down food into molecules the cell can use?
a. | endoplasmic reticulum | c. | lysosome | b. | mitochondrion | d. | Golgi apparatus |
|
|
|
91.
|
How are cellular respiration and photosynthesis almost opposite
processes?
a. | Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and cellular respiration
puts it back. | b. | Photosynthesis releases energy, and cellular respiration stores
energy. | c. | Photosynthesis removes oxygen from the atmosphere, and cellular respiration puts it
back. | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
92.
|
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from
a. | an area of equilibrium to an area of high concentration. | b. | an area of high
concentration to an area of low concentration. | c. | an area of low concentration to an area of high
concentration. | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
93.
|
Which kingdom contains heterotrophs with cell walls of chitin?
a. | Fungi | c. | Protista | b. | Animalia | d. | Plantae |
|
|
|
94.
|
Viral diseases can be
a. | treated with antibiotics and prevented with vaccines. | b. | prevented with
vaccines but not treated with antibiotics. | c. | prevented with antibiotics but not treated with
vaccines. | d. | treated with vaccines and prevented with antibiotics. |
|
|
|
95.
|
During a lytic infection, the host cell is
a. | destroyed. | c. | prepared for the lysogenic cycle. | b. | copied many times
over. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
96.
|
Many algae switch back and forth between diploid and haploid stages during their
life cycle in a process known as
a. | asexual reproduction. | c. | fusion of opposite mating types. | b. | sexual
reproduction. | d. | alternation
of generations. |
|
|
|
97.
|
In biology, an evolutionary innovation is also referred to as a
a. | molecular clock. | c. | derived character. | b. | taxonomic group. | d. | physical
similarity. |
|
|
|
98.
|
In an amoeba, a small cavity within the cytoplasm that stores food is called
a
a. | gullet. | c. | contractile vacuole. | b. | pseudopod. | d. | food vacuole. |
|
|
|
99.
|
One of the main functions of stems is to
a. | store water. | b. | carry out photosynthesis. | c. | store
carbohydrates. | d. | transport substances between roots and leaves. |
|
|
|
100.
|
A theory
a. | is always true. | b. | may be revised or replaced. | c. | is the opening
statement of an experiment. | d. | is a problem to be
solved. |
|
|
|
101.
|
Which of the following describes the heartwood of a tree?
a. | produces protective layers of cork | b. | old, nonfunctioning phloem | c. | active xylem that
transports water and minerals | d. | old, nonfunctioning
xylem |
|
|
|
102.
|
In oomycetes, sexual reproduction takes place in the
a. | sporangium. | c. | migrating colony. | b. | zoosporangium. | d. | antheridium and
oogonium. |
|
|
|
103.
|
Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse in and out of a leaf through the
a. | palisade mesophyll. | c. | stomata. | b. | phloem. | d. | guard cells. |
|
|
|
104.
|
Cellular respiration is called an aerobic process because it requires
a. | exercise. | c. | oxygen. | b. | light. | d. | glucose. |
|
|
|
105.
|
Which of the following contain a nucleus?
a. | bacteria | c. | prokaryotes | b. | organelles | d. | eukaryotes |
|
|
|
106.
|
A vaccine would be useful if given to
a. | a potato farmer whose entire crop is infected with a potato virus. | c. | a nurse who
works around people infected with tuberculosis. | b. | a teenager who has strep
throat. | d. | a cow that probably
has mad cow disease. |
|
|
|
107.
|
What kind of analysis focuses on the order in which derived characters appeared
in organisms?
a. | traditional classification | c. | taxonomy | b. | anatomy | d. | cladistic analysis |
|
|
|
108.
|
Which of the following characteristics of living things best explains why birds
fly south for the winter?
a. | Living things maintain internal balance. | b. | Living things
respond to their environment. | c. | Living things are made up of units called
cells. | d. | Living things are based on a universal genetic code. |
|
|
|
109.
|
Which of the following are members of the kingdom Archaebacteria?
a. | eubacteria | c. | eukaryotes | b. | E. coli | d. | methanogens |
|
|
|
110.
|
The air bubbles and spongy texture of bread are due to which process?
a. | glycolysis | c. | lactic acid fermentation | b. | the Krebs
cycle | d. | alcoholic
fermentation |
|
|
|
111.
|
Which of the following is false?
a. | A stroma contains a thylakoid. | c. | A thylakoid contains
chlorophyll. | b. | A chloroplast contains stroma. | d. | A granum contains several
thylakoids. |
|
|
|
112.
|
A genus is composed of a number of related
a. | species. | c. | orders. | b. | phyla. | d. | kingdoms. |
|
|
|
113.
|
Which of the following is a way that bacteria cause disease?
a. | by nitrogen fixation | c. | by capsids | b. | by conjugation | d. | by releasing
toxins |
|
|
|
114.
|
For many species, there are often regional differences in their
a. | common names. | c. | scientific names. | b. | taxa. | d. | binomial
nomenclature. |
|
|
|
115.
|
The movement of sugars in a plant can be explained by
a. | root pressure. | c. | capillary action. | b. | the pressure-flow
hypothesis. | d. | transpiration
pull. |
|
|
|
116.
|
Bacteria that cause disease are called
a. | viruses. | c. | endospores. | b. | antibiotics. | d. | pathogens. |
|
|
|
117.
|
How many meters are in 2.4 km?
a. | 24,000 | c. | 2,400 | b. | 240,000 | d. | 240 |
|
|
|
118.
|
A group of similar cells that perform a particular function is called
a(an)
a. | division of labor. | c. | tissue. | b. | organ system. | d. | organ. |
|
|
|
119.
|
The cell theory applies to
a. | multicellular organisms. | c. | plants and
animals. | b. | bacteria. | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
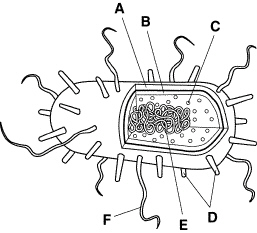
Figure
19–1
|
|
|
120.
|
Which structure or structures shown in Figure 19–1 have key differences in
eubacteria and archaebacteria?
a. | A, B, C | c. | A only | b. | D only | d. | A, B, E |
|
Modified True/False
Indicate
whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
statement true.
|
|
|
121.
|
Paleontologists study dinosaurs and other ancient life.
_________________________
|
|
|
122.
|
Protists are a diverse group of mainly multicellular eukaryotes.
_________________________
|
|
|
123.
|
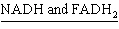 carry electrons from the Krebs cycle to the
electron transport chain. _________________________
|
|
|
124.
|
Slime molds are funguslike protists that play key roles in recycling
organic matter. _________________________
|
|
|
125.
|
Ultimately, the energy that a carnivore, such as a wolf, uses comes from
sunlight. _________________________
|
|
|
126.
|
The bacterium Rhizobium, which grows on the roots of legumes, helps
“fix” the carbon in the air by forming ammonium.
_________________________
|
|
|
127.
|
Once equilibrium is reached, roughly equal numbers of molecules move in
either direction across a semipermeable membrane, and there is no further change in concentration on
either side of the membrane. _________________________
|
|
|
128.
|
The main function of the cell wall is to provide support and protection.
_________________________
|
|
|
129.
|
Either cellular respiration or fermentation can be used to release energy,
depending on the presence of carbohydrates. _________________________
|
|
|
130.
|
Blooms of dinoflagellates can cause red tides.
_________________________
|
|
|
131.
|
If a plant is placed in a greenhouse held at 40°C, the plant will probably
increase its normal rate of photosynthesis. _________________________
|
|
|
132.
|
If you grind up the chloroplasts found in spinach leaves into a liquid solution,
the solution will have a green color. _________________________
|
|
|
133.
|
The principal organs in which plants carry out photosynthesis are leaves.
_________________________
|
|
|
134.
|
The secondary growth of a dicot stem results from cell divisions in the
stem’s vascular cambium and xylem. _________________________
|
|
|
135.
|
If you swim aerobically for 30 minutes, your body has probably started to break
down stored molecules, such as fats, for energy. _________________________
|
|
|
136.
|
ATP synthesis depends directly on the availability of light energy.
_________________________
|
|
|
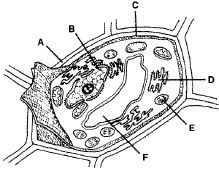
Figure
7–1
|
|
|
137.
|
The cell represented in Figure 7–1 is a eukaryote.
_________________________
|
|
|
138.
|
A disinfectant is a chemical solution that kills bacteria.
_________________________
|
|
|
139.
|
During the course of a long race, a person’s muscle cells will use both
cellular respiration and lactic acid fermentation to produce ATP.
_________________________
|
|
|
140.
|
During the light-dependent reactions, plants use the energy in ATP and
NADPH to build high-energy sugars. _________________________
|
|
|
141.
|
An important goal of a scientist is to use evidence to learn about the
natural world. _________________________
|
|
|
142.
|
The nuclear envelope regulates which substances enter and leave a cell.
_________________________
|
|
|
143.
|
Transpiration from leaves occurs because of the osmosis of water from the
leaf to the environment. _________________________
|
|
|

Figure
8–1
|
|
|
144.
|
The substance represented in Figure 8–1 is called ATP.
_________________________
|
|
|
145.
|
In binomial nomenclature, each species is assigned a two-part scientific
name. _________________________
|
|
|
146.
|
Scientists reason that archaebacteria may be the ancestors of eukaryotes.
If this is true, then archaebacteria and eukaryotes share a common ancestor that is more
recent than the common ancestor of archaebacteria and eubacteria. _________________________
|
|
|
147.
|
The Krebs cycle releases energy in the form of ATP.
_________________________
|
|
|
148.
|
Unlike many others in the same phylum, the spores of the Myxomycota that
caused potato blight in nineteenth-century Ireland are airborne. _________________________
|
|
|
149.
|
A major difference between archaebacteria and eubacteria is the presence of
peptidoglycan in the cell membrane of eubacteria._________________________
|
|
|
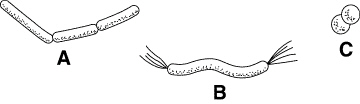
Figure
19–2
|
|
|
150.
|
Figure 19–2 shows the three shapes of viruses.
_________________________
|
|
|
151.
|
Dried Porphyran, called nori in Japanese, is a green alga.
_________________________
|
|
|
152.
|
Cladistic analysis considers characteristics that have arisen as lineages
have evolved over time. _________________________
|
|
|
153.
|
The variable that is deliberately changed is called the responding
variable. _________________________
|
|
|
154.
|
Scientists often look for similar genes in very dissimilar organisms.
_________________________
|
|
|
155.
|
An order is a broad taxonomic category composed of similar phyla.
_________________________
|
|
|
156.
|
Members of the phylum Rhodophyta contain the accessory pigment
phycobilin. _________________________
|
|
|
157.
|
The older kingdom Monera contains the same organisms as the two domains Bacteria
and Archaea. _________________________
|
|
|
158.
|
Many archaebacteria live in extreme environments, such as in Utah’s
Great Salt Lake. _________________________
|
|
|
159.
|
The high concentration of mineral ions in the plant cells causes water molecules
to move into the plant by diffusion. _________________________
|
|
|
160.
|
In cell fractionation, the first step is to place the cells into a
centrifuge. _________________________
|
Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
161.
|
The use of a two-part scientific name for organisms is called
____________________ nomenclature.
|
|
|
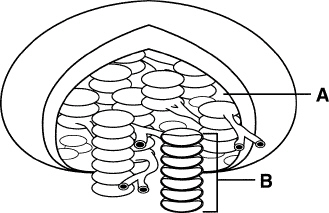
Figure
8–3
|
|
|
162.
|
The area in Figure 8–3 labeled A is called the
____________________.
|
|
|
163.
|
The information you gather during an experiment is called your
____________________.
|
|
|
Figure
7–3
|
|
|
164.
|
The structure labeled ____________________ in Figure 7–3 consists of DNA
bound to protein.
|
|
|
165.
|
Chlorophyll and accessory pigments allow algae to harvest and use the energy of
____________________.
|
|
|
166.
|
The electrons that chlorophyll loses to the electron transport chain are
replenished by ____________________ molecules.
|
|
|
167.
|
Large molecules such as glucose that cannot cross the lipid bilayer can still
move across the membrane with a concentration gradient by _________________________.
|
|
|
168.
|
Because algae undergo ________________________, they produce much of
Earth’s atmospheric oxygen.
|
|
|
169.
|
A fish-eating bear indirectly relies on _________________________ protists for
food.
|
|
|
170.
|
The three main stages of cellular respiration are _____________________, the
Krebs cycle, and ________________________.
|
|
|
171.
|
The layer of growing tissue that surrounds the expanding phloem tissue in trees
is the _________________________.
|
|
|
172.
|
Ingenhousz found that plants produce oxygen only in the presence of
____________________.
|
|
|
173.
|
The roots of grasses are a type of root called a(an) ____________________
root.
|
|
|
174.
|
A membrane protein called _____________________ allows H+ ions to
pass through the thylakoid membrane out of the thylakoids.
|
|
|
175.
|
During an experiment, measuring the height of a plant in centimeters would be an
example of collecting ____________________ data.
|
|
|
176.
|
As the relative concentration of mineral ions in a root’s epidermal cells
increases, the relative concentration of water molecules ____________________.
|
|
|
177.
|
In taxonomy, the class Mammalia is grouped with the classes Aves, Reptilia,
Amphibia, and several classes of fishes into the phylum ____________________.
|
|
|
178.
|
The cell takes in food and water and eliminates wastes through the
_________________________.
|
|
|
179.
|
Photosynthesis requires light, water, carbon dioxide, and
____________________.
|
|
|
180.
|
The first protists evolved approximately ___________________ years ago.
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
181.
|
What three kinds of tissues does meristematic tissue develop into?
|
|
|
182.
|
Cellular respiration is able to extract about 38 percent of the potential energy
from glucose. What happens to the rest of the energy? Give an example.
|
|
|
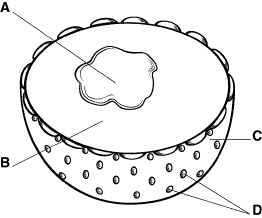
Figure
23–3
|
|
|
183.
|
In Figure 23–3, what is structure C, and what tissues is it made up
of?
|
|
|
184.
|
List the two types of viral infections. Explain what happens to the host
cell.
|
|
|
185.
|
What does the cell theory say?
|
|
|
186.
|
Root pressure causes guttation, the exuding of water droplets seen in the
morning on blades of grass and on the leaf edges of some monocots. Why does guttation not occur in
the leaves of trees?
|
|
|
187.
|
What are the energy totals produced by one molecule of pyruvic acid entering the
Krebs cycle?
|
|
|
188.
|
What is the difference between a theory and a hypothesis?
|
|
|
189.
|
Explain how heterotrophs get their energy from the sun even though they cannot
make their own food.
|
|
|
190.
|
Why might a particular kind of organism have more than one common name?
|