Multiple Choice (Value 70)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Which of the following variables present in Redi’s experiment on
spontaneous generation is NOT a controlled variable?
a. | gauze covering that keeps flies away from meat | b. | types of jars
used | c. | types of meat used | d. | temperature at which the jars were
stored |
|
|
|
2.
|
Cell specialization in multicellular organisms allows cells to
a. | reproduce. | c. | respond to their environment. | b. | perform different
functions. | d. | be less
complex. |
|
|
|
3.
|
To observe a small, living organism, a scientist might use a(an)
a. | electronic balance. | c. | compound light microscope. | b. | TEM. | d. | electron microscope. |
|
|
|
4.
|
An instrument that allows light to pass through the specimen and uses two
lenses to form an image is a(an)
a. | compound light microscope. | c. | TEM. | b. | electron
microscope. | d. | SEM. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells?
a. | Anton van Leeuwenhoek | c. | Matthias Schleiden | b. | Robert Hooke | d. | Rudolf Virchow |
|
|
|
6.
|
The work of Schleiden and Schwann can be summarized by saying that
a. | all plants are made of cells. | b. | all animals are made of
cells. | c. | plants and animals have specialized cells. | d. | all plants and
animals are made of cells. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which type(s) of microscopes can produce three-dimensional images of
cells?
a. | transmission electron microscopes | c. | both A and B | b. | scanning electron
microscopes | d. | neither A nor
B |
|
|
|
8.
|
Looking at a cell under a microscope, you note that it is a prokaryote. How do
you know?
a. | The cell lacks cytoplasm. | c. | The cell lacks a
nucleus. | b. | The cell lacks a cell membrane. | d. | The cell lacks genetic
material. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which of the following is NOT found in the nucleus?
a. | cytoplasm | c. | chromatin | b. | nucleolus | d. | DNA |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which of the following statements explains the importance of the
nucleus to the cell?
a. | Only eukaryotes have nuclei. | b. | Only prokaryotes have
nuclei. | c. | The nucleus contains coded instructions for making proteins. | d. | The nucleus is
surrounded by a nuclear envelope. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which organelles help provide cells with energy?
a. | mitochondria and chloroplasts | c. | smooth endoplasmic
reticulum | b. | rough endoplasmic reticulum | d. | Golgi apparatus and ribosomes |
|
|
|
12.
|
The main function of the cell wall is to
a. | support and protect the cell. | c. | direct the activities of the
cell. | b. | store DNA. | d. | help the cell move. |
|
|
|
13.
|
The cell membrane contains channels and pumps that help move materials from one
side to the other. What are these channels and pumps made of?
a. | carbohydrates | c. | bilipids | b. | lipids | d. | proteins |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which means of particle transport requires input of energy from the
cell?
a. | diffusion | c. | facilitated diffusion | b. | osmosis | d. | active transport |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following is NOT a part of an ATP molecule?
a. | adenine | c. | chlorophyll | b. | ribose | d. | phosphate |
|
|
|
16.
|
A student is collecting the gas given off from a plant in bright sunlight
at a temperature of 27°C. The gas being collected is probably
a. | oxygen. | c. | ATP. | b. | carbon dioxide. | d. | vaporized
water. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide
into
a. | oxygen. | b. | high-energy sugars and
starches. | c. | ATP and oxygen. | d. | oxygen and high-energy sugars and
starches. |
|
|
|
18.
|
A granum is a
a. | stack of chloroplasts. | c. | membrane enclosing a thylakoid. | b. | stack of
thylakoids. | d. | photosynthetic
pigment molecule. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Where do the light-dependent reactions take place?
a. | in the stroma | c. | within the thylakoid membranes | b. | in the
mitochondria | d. | only in
chlorophyll molecules |
|
|
|
20.
|
If carbon dioxide is completely removed from a plant’s environment, what
would you expect to happen to the plant’s production of high-energy sugars?
a. | More sugars will be produced. | b. | No sugars will be produced. | c. | The same number of
sugars will be produced but without carbon dioxide. | d. | Carbon dioxide does not affect the production
of high-energy sugars in plants. |
|
|
|
21.
|
What is the correct equation for cellular respiration?
a. | 6O2 + C6H12O6 ® 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy | b. | 6O2 +
C6H12O6 + Energy ® 6CO2 +
6H2O | c. | 6CO2 + 6H2O ® 6O2 +
C6H12O6 + Energy | d. | 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
® 6O2 +
C6H12O6 |
|
|
|
22.
|
What are the reactants in the equation for cellular
respiration?
a. | oxygen and lactic acid | c. | glucose and oxygen | b. | carbon dioxide and water | d. | water and
glucose |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of these is a product of cellular respiration?
a. | oxygen | c. | glucose | b. | water | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
24.
|
Lactic acid fermentation occurs in
a. | bread dough. | c. | muscle cells. | b. | any environment containing
oxygen. | d. | mitochondria. |
|
|
|
25.
|
One cause of muscle soreness is
a. | alcoholic fermentation. | c. | lactic acid
fermentation. | b. | glycolysis. | d. | the Krebs cycle. |
|
|
|
26.
|
The Krebs cycle does not occur if
a. | oxygen is present. | c. | glycolysis occurs. | b. | fermentation occurs. | d. | carbon dioxide is
present. |
|
|
|
27.
|
The Krebs cycle produces
a. | oxygen. | c. | electron carriers. | b. | lactic acid. | d. | glucose. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Photosynthesis is to chloroplasts as cellular respiration is to
a. | chloroplasts. | c. | mitochondria. | b. | cytoplasm. | d. | nuclei. |
|
|
|
29.
|
The products of photosynthesis are the
a. | products of cellular respiration. | c. | products of
glycolysis. | b. | reactants of cellular respiration. | d. | reactants of
fermentation. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following is a valid hypothesis for why a plant appears to be
dying?
a. | The plant is not being watered enough. | b. | The plant is being watered too
much. | c. | The plant is receiving too much sunlight. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
31.
|
A student suggests that a certain species of bacteria grows better in the light
than in the dark. The student has 10 culture plates on which to grow the bacteria. Which
of the following would be the best experiment to test this idea?
a. | Grow 10 plates in the dark. | b. | Grow 10 plates in the light.
| c. | Grow 5 plates in the dark and 5 plates in the light. | d. | Grow 10 plates in
the light, with extra water. |
|
|
|
32.
|
A controlled experiment allows the scientist to isolate and test
a. | a conclusion. | c. | several variables. | b. | a mass of information. | d. | a single
variable. |
|
|
|
33.
|
Which of the following is NOT a principle of the cell
theory?
a. | Cells are the basic units of life. | b. | All living things are made of
cells. | c. | Very few cells reproduce. | d. | All cells are produced by existing
cells. |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which of the following contain a nucleus?
a. | prokaryotes | c. | eukaryotes | b. | bacteria | d. | organelles |
|
|
|
35.
|
Which of the following is a function of the nucleus?
a. | stores DNA | b. | controls most of the cell’s
processes | c. | contains the information needed to make proteins | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
36.
|
Which organelle would you expect to find in plant cells but not animal
cells?
a. | mitochondrion | c. | chloroplast | b. | ribosome | d. | smooth endoplasmic
reticulum |
|
|
|
37.
|
Which of the following is NOT a function of the
cytoskeleton?
a. | helps the cell maintain its shape | b. | helps the cell move | c. | prevents chromosomes
from separating | d. | helps organelles within the cell move |
|
|
|
38.
|
You will NOT find a cell wall in which of these kinds of
organisms?
a. | plants | c. | fungi | b. | animals | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
39.
|
Which of the following is a function of the cell membrane?
a. | breaks down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins from foods | b. | stores water, salt,
proteins, and carbohydrates | c. | keeps the cell wall in
place | d. | regulates which materials enter and leave the cell |
|
|
|
40.
|
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from
a. | an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. | b. | an area of high
concentration to an area of low concentration. | c. | an area of equilibrium to an area of high
concentration. | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
41.
|
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called
a. | osmotic pressure. | c. | facilitated diffusion. | b. | osmosis. | d. | active transport. |
|
|
|
42.
|
An animal cell that is surrounded by fresh water will burst because the osmotic
pressure causes
a. | water to move into the cell. | c. | solutes to move into the
cell. | b. | water to move out of the cell. | d. | solutes to move out of the
cell. |
|
|
|
43.
|
Energy is released from ATP when
a. | a phosphate group is added. | c. | ATP is exposed to
sunlight. | b. | adenine bonds to ribose. | d. | a phosphate group is removed. |
|
|
|
44.
|
The stroma is the region outside the
a. | thylakoids. | c. | plant cells. | b. | chloroplasts. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
45.
|
Where in the chloroplast is chlorophyll found?
a. | in the stroma | c. | in the ATP | b. | in the thylakoid | d. | in the glucose |
|
|
|
46.
|
What are the products of the light-dependent reactions?
a. | oxygen gas | c. | NADPH | b. | ATP | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
47.
|
The Calvin cycle is another name for
a. | light-independent reactions. | c. | photosynthesis. | b. | light-dependent
reactions. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
48.
|
The Calvin cycle takes place in the
a. | stroma. | c. | thylakoid membranes. | b. | photosystems. | d. | chlorophyll
molecules. |
|
|
|
49.
|
What is a product of the Calvin cycle?
a. | oxygen gas | c. | high-energy sugars | b. | ATP | d. | carbon dioxide
gas |
|
|
|
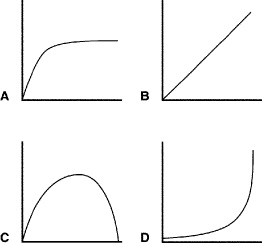
Figure
8–2
|
|
|
50.
|
Which of the graphs in Figure 8–2 represents the effect of temperature on
the rate of photosynthesis?
|
|
|
51.
|
Which of the graphs in Figure 8–2 represents the effect of light intensity
on the rate of photosynthesis?
|
|
|
52.
|
Which of the following is the correct sequence of events in cellular
respiration?
a. | glycolysis ® fermentation ® Krebs cycle | b. | Krebs cycle ®
electron transport ® glycolysis | c. | glycolysis ® Krebs cycle ® electron
transport | d. | Krebs cycle ® glycolysis ® electron transport |
|
|
|
53.
|
Which of these processes takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell?
a. | glycolysis | c. | Krebs cycle | b. | electron transport | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
54.
|
The starting molecule for glycolysis is
a. | ADP. | c. | citric acid. | b. | pyruvic acid. | d. | glucose. |
|
|
|
55.
|
Which of the following is NOT a product of glycolysis?
a. | NADH | c. | ATP | b. | pyruvic acid | d. | glucose |
|
|
|
56.
|
Which of the following acts as an electron carrier in cellular
respiration?
a. | NAD+ | c. | ADP | b. | pyruvic acid | d. | ATP |
|
|
|
57.
|
The two main types of fermentation are called
a. | alcoholic and aerobic. | c. | alcoholic and lactic acid. | b. | aerobic and
anaerobic. | d. | lactic acid and
anaerobic. |
|
|
|
58.
|
Cellular respiration is called an aerobic process because it requires
a. | light. | c. | oxygen. | b. | exercise. | d. | glucose. |
|
|
|
59.
|
The starting molecule for the Krebs cycle is
a. | glucose. | c. | pyruvic acid. | b. | NADH. | d. | coenzyme A. |
|
|
|
60.
|
How are cellular respiration and photosynthesis almost opposite
processes?
a. | Photosynthesis releases energy, and cellular respiration stores
energy. | b. | Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and cellular respiration
puts it back. | c. | Photosynthesis removes oxygen from the atmosphere, and cellular respiration puts it
back. | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
61.
|
Based on their names, you know that the baboons Papio annubis and
Papio cynocephalus do NOT belong to the same
a. | class. | c. | genus. | b. | family. | d. | species. |
|
|
|
62.
|
The second part of a scientific name is unique to each
a. | order in its class. | c. | genus in its family. | b. | family in its order. | d. | species in its
genus. |
|
|
|
63.
|
Traditional classifications tended to take into account primarily
a. | extinct organisms. | c. | DNA similarities. | b. | RNA similarities. | d. | general similarities in
appearance. |
|
|
|
64.
|
The domain that corresponds to the kingdom Eubacteria is
a. | Archaea. | c. | Eukarya. | b. | Bacteria. | d. | Fungi. |
|
|
|
65.
|
The domain that contains unicellular organisms that live in extreme environments
is
a. | Eubacteria. | c. | Archaea. | b. | Eukarya. | d. | Bacteria. |
|
|
|
66.
|
What is thought to be true about the three domains of living things?
a. | They diverged from a common ancestor fairly recently. | b. | They diverged from a
common ancestor before the evolution of the main groups of eukaryotes. | c. | They did not have a
common ancestor. | d. | Domains Bacteria and Archaea evolved after the main groups of
eukaryotes. |
|
|
|
67.
|
Which structure of a paramecium is analogous to a “reserve copy” of
all the cell’s genes?
a. | the micronucleus | c. | the trichocysts | b. | the gullet | d. | the
macronucleus |
|
|
|
68.
|
Chlorophyll a is best at absorbing
a. | blue light. | c. | yellow and green light. | b. | green
light. | d. | red and violet
light. |
|
|
|
69.
|
Red algae lack flagella and
a. | nuclei. | c. | accessory pigments. | b. | centrioles. | d. | chlorophyll. |
|
|
|
70.
|
In oomycetes, sexual reproduction takes place in the
a. | migrating colony. | c. | antheridium and oogonium. | b. | sporangium. | d. | zoosporangium. |
|
Modified True/False (Value 20)
Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false,
change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true.
|
|
|
71.
|
Scientists try to organize living things into groups that have economic
significance. _________________________
|
|
|
72.
|
In binomial nomenclature, each species is assigned a two-part scientific
name. _________________________
|
|
|
73.
|
Evidence shows that the same gene that codes for a particular protein in human
muscle also codes for that protein in yeasts, indicating common ancestry.
_________________________
|
|
|
74.
|
The older kingdom Monera contains the same organisms as the two domains Bacteria
and Archaea. _________________________
|
|
|
75.
|
The kingdom Eubacteria contains the same organisms as the domain
Animalia. _________________________
|
|
|
76.
|
Ciliates use flagella for feeding and movement.
_________________________
|
|
|
77.
|
If the people in a town contracted amebic dysentery or infections by the
animallike protist, Giardia, the most likely cause would be contaminated drinking
water. _________________________
|
|
|
78.
|
Blooms of dinoflagellates can cause red tides.
_________________________
|
|
|
79.
|
The holdfast of a brown alga helps keep it upright in the water.
_________________________
|
|
|
80.
|
Members of the phylum Rhodophyta contain the accessory pigment
phycobilin. _________________________
|
|
|
81.
|
An important goal of a scientist is to use evidence to learn about the
natural world. _________________________
|
|
|
82.
|
Scientists are persuaded by logical arguments that are supported by
evidence. _________________________
|
|
|
83.
|
In a laboratory, you are responsible for your own safety, as well as the safety
of your teacher and classmates. _________________________
|
|
|
84.
|
Once equilibrium is reached, roughly equal numbers of molecules move in
either direction across a semipermeable membrane, and there is no further change in concentration on
either side of the membrane. _________________________
|
|
|
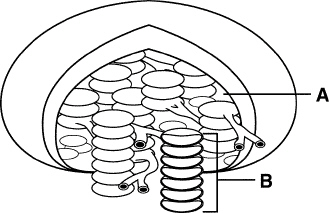
Figure
8–3
|
|
|
85.
|
If you were to isolate the structure shown in Figure 8–3, it would appear
green. _________________________
|
|
|
86.
|
Cellular respiration releases energy by breaking down glucose in the presence of
carbon dioxide. _________________________
|
|
|
87.
|
An organism may have different common names that vary from area to area
and language to language. _________________________
|
|
|
88.
|
Biologists attempt to group organisms into categories that represent lines of
evolutionary descent. _________________________
|
|
|
89.
|
Cladistic analysis considers characteristics that have arisen as lineages
have evolved over time. _________________________
|
|
|
90.
|
Protists are a diverse group of mainly multicellular eukaryotes.
_________________________
|
Completion (Value 10)
Complete
each statement.
|
|
|
91.
|
Evidence shows that very dissimilar organisms, such as yeasts and humans, have
some genes in common, indicating that they share a common ____________________.
|
|
|
92.
|
The domain ____________________ is composed of the kingdom Eubacteria.
|
|
|
93.
|
Chlorophyll and accessory pigments allow algae to harvest and use the energy of
____________________.
|
|
|
94.
|
A fish-eating bear indirectly relies on _________________________ protists for
food.
|
|
|
95.
|
____________________ protists are heterotrophs that absorb nutrients from dead
or decaying organic matter.
|
|
|
96.
|
In a eukaryote, the material between the cell membrane and the nucleus is called
the ____________________.
|
|
|
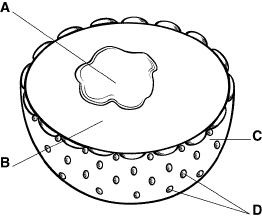
Figure
7–3
|
|
|
97.
|
RNA and other molecules leave the nucleus through the structure labeled
____________________ in Figure 7–3.
|
|
|
98.
|
Molecules tend to move from an area where they are more concentrated to an area
where they are less concentrated. This process is called ____________________.
|
|
|
99.
|
The cells in a multicellular organism have specific jobs. This is called cell
_________________________.
|
|
|

Figure
8–3
|
|
|
100.
|
The area in Figure 8–3 labeled A is called the
____________________.
|
Essay: Complete two of the following essay questions (Value
10)
|
|
|
101.
|
What is the goal of science?
|
|
|
102.
|
Identify the electron carriers of cellular respiration. Discuss the relationship
between the electron carriers and the electron transport chain.
|
|
|
103.
|
What effect might the common use of the microscope by biologists have had on
Linnaeus’s original system of taxonomy? Explain.
|
|
|
104.
|
How does traditional classification differ from evolutionary
classification?
|
|
|
105.
|
Describe the structure of the diploid zygote of Chlamydomonas, and
explain under what conditions it forms and the adaptive advantage of the process of zygote
formation.
|
|
|
106.
|
Contrast the asexual and sexual phases in the life cycle of a water mold.
|