Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The cell theory applies to
a. | bacteria. | c. | multicellular organisms. | b. | plants and
animals. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
2.
|
Which type(s) of microscopes can produce three-dimensional images of
cells?
a. | transmission electron microscopes | c. | both A and B | b. | scanning electron
microscopes | d. | neither A nor
B |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which organelle converts the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that
are more convenient for the cell to use?
a. | chloroplast | c. | endoplasmic reticulum | b. | Golgi
apparatus | d. | mitochondrion |
|
|
|
4.
|
Which sequence correctly traces the path of a protein in the cell?
a. | rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, released from the
cell | b. | ribosome, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, chloroplast | c. | smooth endoplasmic
reticulum, lysosome, Golgi apparatus | d. | mitochondria, rough endoplasmic reticulum, cell
membrane |
|
|
|
5.
|
Diffusion occurs because
a. | molecules constantly move and collide with each other. | b. | the concentration of
a solution is never the same throughout a solution. | c. | the concentration of a solution is always the
same throughout a solution. | d. | molecules never move or collide with each
other. |
|
|
|
6.
|
When the concentration of molecules on both sides of a membrane is the same, the
molecules will
a. | move across the membrane to the outside of the cell. | b. | stop moving across
the membrane. | c. | move across the membrane in both directions. | d. | move across the
membrane to the inside of the cell. |
|
|
|
7.
|
The cells of multicellular organisms are
a. | smaller than those of unicellular organisms. | b. | simpler than those
of unicellular organisms. | c. | specialized to perform different
tasks. | d. | not dependent on one another. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which list represents the levels of organization in a multicellular organism
from the simplest level to the most complex level?
a. | cell, tissue, organ system | c. | tissue, organ, organ
system | b. | organ system, organ, tissue, cell | d. | cell, tissue, organ, organ
system |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which of the following is NOT a part of an ATP molecule?
a. | adenine | c. | chlorophyll | b. | ribose | d. | phosphate |
|
|
|
10.
|
In the overall equation for photosynthesis, six molecules of carbon dioxide
result in six molecules of
a. | glucose. | c. | oxygen. | b. | water. | d. | ATP. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Plants take in the sun’s energy by absorbing
a. | high-energy sugars. | c. | chlorophyll b. | b. | chlorophyll
a. | d. | sunlight. |
|
|
|
12.
|
A granum is a
a. | stack of chloroplasts. | c. | membrane enclosing a thylakoid. | b. | stack of
thylakoids. | d. | photosynthetic
pigment molecule. |
|
|
|
13.
|
The stroma is the region outside the
a. | thylakoids. | c. | plant cells. | b. | chloroplasts. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
14.
|
Where in the chloroplast is chlorophyll found?
a. | in the stroma | c. | in the ATP | b. | in the thylakoid | d. | in the glucose |
|
|
|
15.
|
What are the products of the light-dependent reactions?
a. | oxygen gas | c. | NADPH | b. | ATP | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
16.
|
Why does the inside of the thylakoid membrane become positively charged during
the light-dependent reactions?
a. | H+ ions are released as water splits. | b. | ATP synthase allows
H+ ions to pass through the membrane. | c. | ATP synthase produces ATP from
ADP. | d. | Carbon dioxide builds up in the stroma. |
|
|
|
17.
|
How does the Calvin cycle differ from the light-dependent reactions?
a. | It takes place in the stroma. | c. | It requires
light. | b. | It takes place in chloroplasts. | d. | It takes place in the
thylakoid. |
|
|
|
18.
|
What would you expect to happen to plants at temperatures greater than
45°C?
a. | They will have a very high rate of photosynthesis. | b. | They will have a
less than optimal rate of photosynthesis. | c. | They will have a high rate of photosynthesis if
light intensity is also great. | d. | They will have an optimal rate of
photosynthesis if water is available. |
|
|
|
Figure
8–2
|
|
|
19.
|
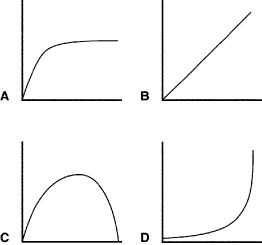
Which of the graphs in Figure 8–2 represents the effect of light intensity
on the rate of photosynthesis?
|
|
|
20.
|
What is the correct equation for cellular respiration?
a. | 6O2 + C6H12O6 ® 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy | b. | 6O2 +
C6H12O6 + Energy ® 6CO2 +
6H2O | c. | 6CO2 + 6H2O ® 6O2 +
C6H12O6 + Energy | d. | 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
® 6O2 +
C6H12O6 |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which organism is NOT likely to carry out cellular respiration?
a. | tree | c. | anaerobic bacterium | b. | mushroom | d. | tiger |
|
|
|
22.
|
The Krebs cycle starts with
a. | lactic acid and yields carbon dioxide. | b. | glucose and yields 32 ATPs. | c. | pyruvic acid and
yields lactic acid or alcohol. | d. | pyruvic acid and yields carbon
dioxide. |
|
|
|
23.
|
Each pair of high-energy electrons that moves down the electron transport chain
provides enough energy to
a. | transport water molecules across the membrane. | b. | convert 3 ADP
molecules into 3 ATP molecules. | c. | convert carbon dioxide into water
molecules. | d. | break glucose into pyruvic acid. |
|
|
|
24.
|
The energy of the electrons passing along the electron transport chain is used
to make
a. | lactic acid. | c. | alcohol. | b. | citric acid. | d. | ATP. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Breathing heavily after running a race is your body’s way of
a. | making more citric acid. | c. | restarting
glycolysis. | b. | repaying an oxygen debt. | d. | recharging the electron transport chain. |
|
|
|
26.
|
If you want to control your weight, how long should you exercise aerobically
each time that you exercise?
a. | at least 90 seconds | c. | 15 to 20 minutes | b. | less than 15 minutes | d. | more than 20
minutes |
|
|
|
27.
|
Before Linnaeus, scientific names were problematic because they were
a. | too brief to be descriptive. | c. | written only in
Greek. | b. | very long and difficult to standardize. | d. | written only in
Latin. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Several different classes make up a
a. | kingdom. | c. | family. | b. | phylum. | d. | genus. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which two kingdoms did Linnaeus recognize?
a. | bacteria and animals | c. | plants and animals | b. | plants and fungi | d. | protists and
animals |
|
|
|
30.
|
Animals that are warm-blooded, have body hair, and produce milk for their young
are grouped in the class
a. | Amphibia. | c. | Aves. | b. | Mammalia. | d. | Reptilia. |
|
|
|
31.
|
Traditional classifications tended to take into account primarily
a. | extinct organisms. | c. | DNA similarities. | b. | RNA similarities. | d. | general similarities in
appearance. |
|
|
|
32.
|
Sometimes, organisms that are not closely related look similar because of
a. | convergent evolution. | c. | mutations. | b. | molecular clocks. | d. | reclassification. |
|
|
|
33.
|
What kind of analysis focuses on the order in which derived characters appeared
in organisms?
a. | cladistic analysis | c. | taxonomy | b. | traditional classification | d. | anatomy |
|
|
|
34.
|
In biology, an evolutionary innovation is also referred to as a
a. | derived character. | c. | molecular clock. | b. | taxonomic group. | d. | physical
similarity. |
|
|
|
35.
|
The domain that contains unicellular organisms that live in extreme environments
is
a. | Eubacteria. | c. | Archaea. | b. | Eukarya. | d. | Bacteria. |
|
|
|
36.
|
Organisms in the kingdoms Eubacteria and Archaebacteria were previously grouped
in a kingdom called
a. | Animalia. | c. | Monera. | b. | Fungi. | d. | Eukarya. |
|
|
|
37.
|
Escherichia coli is classified as a(an)
a. | archaebacterium. | b. | eubacterium. | c. | eukaryote. | d. | virus. |
|
|
|
38.
|
Which of the following are members of the kingdom Archaebacteria?
a. | methanogens | c. | eukaryotes | b. | eubacteria | d. | E. coli |
|
|
|
Figure
19–1
|
|
|
39.
|
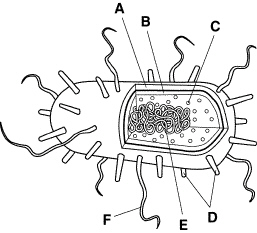
The structure in Figure 19–1 represents a(an)
a. | virus. | c. | methanogen. | b. | archaebacterium. | d. | eubacterium. |
|
|
|
40.
|
Which of the following can survive either with oxygen or without it?
a. | obligate aerobes | c. | facultative anaerobes | b. | obligate
anaerobes | d. | bacteriophages |
|
|
|
41.
|
Some bacteria are able to survive unfavorable conditions by forming
a. | photoautotrophs. | c. | coccus. | b. | capsids. | d. | endospores. |
|
|
|
42.
|
A viral capsid functions to
a. | bind the virus to the surface of a host cell. | b. | transcribe viral
genes. | c. | force a host cell to make copies of the virus. | d. | destroy a host
cell. |
|
|
|
43.
|
A prophage is made of
a. | bacteriophages. | c. | capsid proteins. | b. | carbohydrates. | d. | viral DNA. |
|
|
|
44.
|
Bacteriophages infect
a. | other viruses. | c. | any available host cell. | b. | bacteria
only. | d. | cells undergoing the
lytic cycle. |
|
|
|
45.
|
Which of the following is a way that bacteria cause disease?
a. | by capsids | c. | by conjugation | b. | by nitrogen fixation | d. | by releasing
toxins |
|
|
|
46.
|
Which of the following diseases is NOT caused by a bacterium?
a. | tooth decay | c. | AIDS | b. | tuberculosis | d. | Lyme disease |
|
|
|
47.
|
A vaccine would be useful if given to
a. | a potato farmer whose entire crop is infected with a potato virus. | c. | a teenager who has
strep throat. | b. | a nurse who works around people infected with tuberculosis. | d. | a cow that probably has mad cow
disease. |
|
|
|
48.
|
Food stored in a refrigerator will keep longer because the bacteria that spoil
food
a. | die at low temperatures. | b. | take longer to multiply at low
temperatures. | c. | require light to live. | d. | grow more slowly in the
dark. |
|
|
|
49.
|
Which of the following will NOT kill bacteria?
a. | refrigeration | c. | chemical disinfection | b. | boiling | d. | frying |
|
|
|
50.
|
The sporozoan Plasmodium causes the disease known as
a. | African sleeping sickness. | c. | malaria. | b. | amebic
dysentery. | d. | algal
bloom. |
|
|
|
51.
|
What effect does a red tide have on humans?
a. | All the fish in the area die, causing local fishermen to lose
money. | b. | It is unhealthy to swim in the ocean during a red tide. | c. | The protists help
clean up wastes discharged by local sewage pipes. | d. | Eating poisoned shellfish from affected waters
can cause sickness and death to humans. |
|
|
|
52.
|
What characteristic of plants is shared by green algae?
a. | cell wall composition | c. | multicellularity | b. | photosynthetic pigments | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
53.
|
The green alga Chlamydomonas reproduces asexually by producing
a. | gametophytes. | c. | zygotes. | b. | sporophytes. | d. | zoospores. |
|
|
|
54.
|
Funguslike protists get nutrients by
a. | photosynthesis. | b. | living as an animal
parasite. | c. | absorbing them from dead or decaying matter. | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
55.
|
A mushroom is a fungal
a. | fruiting body. | c. | mycorrhiza. | b. | lichen. | d. | yeast. |
|
|
|
56.
|
Dark fuzz that grows on bread is an example of
a. | toadstool. | c. | yeast. | b. | spore. | d. | mold. |
|
|
|
57.
|
Which of the following ingredients is NOT added to bread dough in order to make
it rise?
a. | sugar | c. | water | b. | yeast | d. | oxygen |
|
|
|
58.
|
The common name for members of the phylum Basidiomycota is derived from the
shape of their
a. | spores. | c. | basidia. | b. | hyphae. | d. | stalks. |
|
|
|
59.
|
Each of the following is a basidiomycete EXCEPT
a. | shelf fungi. | c. | puffballs. | b. | mushrooms. | d. | cup fungi. |
|
|
|
60.
|
Fungi that absorb food from decaying organic matter are
a. | parasites. | c. | mutualists. | b. | saprobes. | d. | autotrophs. |
|
|
|
61.
|
Fungi feed on
a. | only living organisms. | c. | both living and dead organisms. | b. | only dead
organisms. | d. | only other
fungi. |
|
|
|
Figure
21–2
|
|
|
62.
|
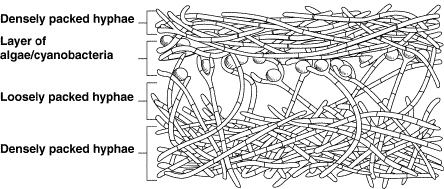
Figure 21–2 illustrates an association of a(an)
a. | cyanobacterium and a plant. | c. | plant and a
fungus. | b. | alga or cyanobacterium and a fungus. | d. | alga and a
plant. |
|
|
|
63.
|
The first plants evolved from
a. | mosses that lived in the water. | b. | an organism similar to multicellular green
algae. | c. | a protist that lived on land. | d. | prokaryotes that carried on
photosynthesis. |
|
|
|
64.
|
The number of seed leaves distinguishes
a. | club mosses from mosses. | c. | two classes of
angiosperms. | b. | angiosperms from gymnosperms. | d. | seed plants from seedless
plants. |
|
|
|
65.
|
Which of the following statements is true?
a. | The roots of a perennial die at the end of the growing season. | b. | A biennial is
smaller during its first growing season. | c. | The stems of all perennials live from one year
to the next. | d. | A biennial flowers in both years. |
|
|
|
66.
|
A seed plant is anchored in the ground by its
a. | stems. | c. | leaves. | b. | roots. | d. | trichomes. |
|
|
|
67.
|
Ground tissue is found in a plant’s
a. | stems only. | c. | roots and stems only. | b. | stems and leaves
only. | d. | roots, stems, and
leaves. |
|
|
|
68.
|
What type of tissue is the first tissue in a plant seedling?
a. | ground | c. | meristematic | b. | vascular | d. | dermal |
|
|
|
69.
|
In plants, mitosis occurs only in
a. | apical meristem of stems. | c. | apical meristem and
cambium. | b. | pith and parenchyma. | d. | parenchyma and cambium. |
|
|
|
70.
|
Which of the following should a student examine under a compound microscope to
observe cell reproduction?
a. | epidermis of a leaf | c. | xylem from a tree trunk | b. | tip of a
shoot | d. | phloem from the leaf
of a plant |
|
|
|
71.
|
Which of the following are found mainly in monocots?
a. | taproots | c. | extensive root systems | b. | long, thick primary
roots | d. | small secondary
roots |
|
|
|
72.
|
The soil around a lilac bush was watered with a solution containing radioactive
phosphorus. Several hours later, radiation was detected in its stems. Through which cells did the
radioactive phosphorus travel to the stems?
a. | sieve tube elements | c. | tracheids and vessel elements | b. | companion
cells | d. | cells of the
cortex |
|
|
|
73.
|
One of the main functions of stems is to
a. | carry out photosynthesis. | b. | transport substances between roots and
leaves. | c. | store carbohydrates. | d. | store water. |
|
|
|
74.
|
Which of the following describes the heartwood of a tree?
a. | active xylem that transports water and minerals | b. | old, nonfunctioning
xylem | c. | old, nonfunctioning phloem | d. | produces protective layers of
cork |
|
|
|
Figure
23–2
|
|
|
75.
|
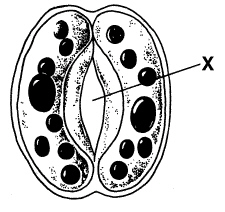
In Figure 23–2, the X points to a
a. | guard cell. | c. | vein. | b. | mesophyll cell. | d. | stoma. |
|
|
|
76.
|
Through which plant cells does water move by capillary action?
a. | phloem cells | c. | mesophyll cells | b. | guard cells | d. | xylem cells |
|
|
|
77.
|
The closing of a plant’s stomata will
a. | increase capillary action in the plant’s stem. | b. | increase
transpiration pull. | c. | cause wilting. | d. | cause less water to
be pulled up from the plant’s roots. |
|
|
|
78.
|
Only 5 percent of all animals have
a. | eukaryotic cells. | c. | vertebral columns. | b. | a protostome development
pattern. | d. | cell
membranes. |
|
|
|
79.
|
How do some sponges play an important role in the primary productivity of coral
reefs?
a. | They provide food for sponge-eating sea stars. | b. | They attract light
with their antennae. | c. | They are harvested for sale as bath
sponges. | d. | They have symbiotic relationships with photosynthetic
organisms. |
|
|
|
80.
|
A characteristic of cnidarians is that they are
a. | found only in warm, tropical waters. | b. | carnivorous animals. | c. | named for their body
symmetry. | d. | attached to a surface throughout life. |
|
|
|
81.
|
In jellyfish,
a. | both polyp and medusa are diploid. | b. | both polyp and medusa are
haploid. | c. | the medusa is diploid and the polyp is haploid. | d. | the medusa is
haploid and the polyp is diploid |
|
|
|
82.
|
The class Scyphozoa contains
a. | jellyfishes. | c. | corals. | b. | hydras. | d. | sea anemones. |
|
|
|
83.
|
The Portuguese man-of-war is a member of what class of cnidarians?
a. | Hydrozoa | c. | Anthozoa | b. | Scyphozoa | d. | Porifera |
|
|
|
84.
|
Some flatworms have clusters of nerve cells that control the nervous system.
Each cluster is called a(an)
a. | ganglion. | c. | eyespot. | b. | brain. | d. | flame cell. |
|
|
|
85.
|
Free-living flatworms, most of which live in marine environments or fresh water,
are
a. | flukes. | c. | tapeworms. | b. | turbellarians. | d. | roundworms. |
|
|
|
86.
|
An adult tapeworm uses its scolex to
a. | attach itself to the intestinal wall of its host. | b. | digest
food. | c. | store sperm. | d. | store fertilized
eggs. |
|
|
|
87.
|
A pseudocoelom forms between the mesoderm and
a. | endoderm. | c. | true coelom. | b. | ectoderm. | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
88.
|
The nervous system of a roundworm includes
a. | a simple brain. | c. | a single ganglion. | b. | a complex brain. | d. | several
ganglia. |
|
|
|
89.
|
What causes the disease called elephantiasis?
a. | flukes | c. | hookworms | b. | filarial worms | d. | ascarid worms |
|
|
|
90.
|
A person who has trichinosis likely contracted it from
a. | walking barefoot on soil infested with Trichinella worms. | b. | eating undercooked
meat containing Trichinella cysts. | c. | being bitten by mosquitoes. | d. | coming in contact
with Trichinella-infested snails. |
|
|
|
91.
|
In earthworms, inability to produce offspring might be associated with
a. | lack of a true coelom. | b. | the inability of a worm to fertilize its own
eggs. | c. | a malfunction of the nephridia. | d. | a malfunction of the
clitellum. |
|
|
|
92.
|
The muscular extension of a leech that penetrates the tissue of its host is
the
a. | septum. | c. | proboscis. | b. | radula. | d. | ganglion. |
|
|
|
93.
|
Earthworms benefit gardeners because their tunnels provide passageways
for
a. | leeches. | c. | plant roots and water. | b. | polychaetes. | d. | planarians. |
|
|
|
94.
|
The larvae of many marine annelids are ecologically important because
they
a. | poison coral reefs. | b. | are eaten by fishes and other marine
animals. | c. | feed on earthworms. | d. | aerate the mud on the
seafloor. |
|
|
|
95.
|
The spade-shaped burrowing structure of one group of mollusks and the tentacles
of another group are both modifications of the
a. | foot. | c. | shell. | b. | mantle. | d. | visceral mass. |
|
|
|
96.
|
Bivalve communities that live near undersea volcanic vents obtain their food
mostly from
a. | symbiotic bacteria. | c. | detritus. | b. | symbiotic algae. | d. | filter-feeding. |
|
|
|
97.
|
Filter-feeding bivalves can be used to monitor the environmental health of a
habitat because
a. | the bivalves reproduce rapidly in polluted water. | b. | the bivalves
concentrate pollutants and microorganisms in their tissues. | c. | the bivalves live
near deep-sea vents. | d. | some bivalves never get
cancer. |
|
|
|
98.
|
The appendages of arthropods are
a. | found only on the head. | b. | hard and immovable. | c. | jointed and extend
from the body wall. | d. | divided into six
branches. |
|
|
|
99.
|
Which of these events is the first to happen when an arthropod molts?
a. | The animal fills with air or fluids. | b. | A new skeleton is secreted. | c. | The animal pulls
itself out of the original skeleton. | d. | Skin glands digest the inner part of the
skeleton. |
|
|
|
100.
|
Which of the following invertebrates is NOT a crustacean?
a. | horseshoe crab | c. | barnacle | b. | fiddler crab | d. | crayfish |
|
|
|
101.
|
Honeybees use dances to
a. | lure insects of other species. | b. | signal the death of a member of the
colony. | c. | attract mates. | d. | convey information about food
sources. |
|
|
|
102.
|
The water vascular system of echinoderms is involved with each of the following
body functions EXCEPT
a. | respiration. | c. | movement. | b. | circulation. | d. | reproduction. |
|
|
|
103.
|
Which structure is part of an echinoderm’s water vascular system?
a. | skin gill | c. | madreporite | b. | anus | d. | stomach |
|
|
|
104.
|
The plates of the endoskeleton are reduced and contained inside a soft, muscular
body wall in
a. | sand dollars. | c. | sea urchins. | b. | sea cucumbers. | d. | brittle stars. |
|
|
|
105.
|
Which of the following is NOT a type of blood vessel?
a. | artery | c. | lymphatic cell | b. | vein | d. | capillary |
|
|
|
106.
|
Which organ helps to regulate blood pressure?
a. | spleen | c. | liver | b. | kidney | d. | gall bladder |
|
|
|
107.
|
Which of the following is NOT a function of blood?
a. | regulate filtration | c. | transport nutrients | b. | regulate body temperature | d. | fight infection |
|
|
|
108.
|
The nicotine in cigarette smoke causes
a. | blood pressure to decrease. | c. | blood pressure to
increase. | b. | heart rate to increase. | d. | both b and c. |
|
|
|
109.
|
The energy available in food can be measured by
a. | first determining which nutrients the body needs. | b. | burning the
food. | c. | tracing chemical pathways. | d. | all of the
above. |
|
|
|
110.
|
Substances that are needed by the body for growth, repair, and maintenance are
called
a. | enzymes. | c. | ATP. | b. | nutrients. | d. | Calories. |
|
|
|
111.
|
Inorganic nutrients that the body needs are called
a. | lipids. | c. | vitamins. | b. | proteins. | d. | minerals. |
|
|
|
112.
|
The raw materials that the body needs for growth and repair come from
a. | proteins. | c. | carbohydrates. | b. | unsaturated fats. | d. | water. |
|
|
|
113.
|
The Food Guide Pyramid advises a person to eat more
a. | meat than dairy products. | c. | dairy products than
vegetables. | b. | grains than meat. | d. | dairy products than grains. |
|
|
|
114.
|
The trend of the Food Guide Pyramid is that the majority of the food in your
diet should be from
a. | the group(s) at the top. | b. | the group(s) at the bottom. | c. | the group(s) in the
middle. | d. | all of the groups in the same proportion. |
|
|
|
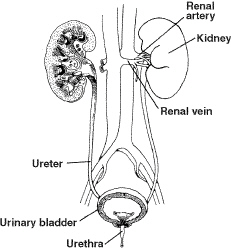
Figure
38–1
|
|
|
115.
|
Look at Figure 38–1. Clean, filtered blood is returned to circulation
through the
a. | renal artery. | c. | urinary bladder. | b. | renal vein. | d. | urethra. |
|
|
|
116.
|
The main organs of the excretory system are the
a. | kidneys. | c. | intestines. | b. | lungs. | d. | ureters. |
|
|
|
117.
|
How are infectious diseases spread?
a. | through coughing, sneezing, or physical contact | b. | through contaminated
water and food | c. | by infected animals | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
118.
|
Antibiotics fight infections by
a. | preventing viruses from replicating. | b. | killing bacteria. | c. | killing infected
cells. | d. | growing green mold that inhibits bacterial growth. |
|
|
|
119.
|
The body’s nonspecific defenses against invading pathogens include
a. | antibiotics. | c. | antibodies. | b. | mucus, sweat, and tears. | d. | killer T cells. |
|
|
|
120.
|
A person who has received a vaccine against polio
a. | is able to produce antibodies against polio. | b. | is more susceptible
to the polio virus than someone who has not had the vaccine. | c. | has polio antibodies
in the bloodstream. | d. | has antipolio killer T cells in the
bloodstream. |
|
|
|
121.
|
The symptoms of allergies include
a. | runny nose and a fever. | b. | sneezing, runny nose, and watery
eyes. | c. | unusual infections of the lungs, mouth, throat, and skin. | d. | formation of a
tumor. |
|
|
|
122.
|
An example of an autoimmune disease is
a. | asthma. | c. | multiple sclerosis. | b. | allergies. | d. | strep throat. |
|
|
|
123.
|
HIV weakens the immune system by killing
a. | antibodies. | c. | helper T cells. | b. | B cells. | d. | killer T cells. |
|
|
|
124.
|
Which of the following presents a risk of spreading HIV?
a. | abstaining from sex | b. | giving blood | c. | kissing someone on
the cheek | d. | using a contaminated needle to receive an injection |
|
|
|
125.
|
Cancer cells affect other cells in the body by
a. | taking in nutrients needed by other cells. | b. | increasing nerve
connections. | c. | forming benign tumors throughout the body. | d. | all of the
above |
|
Modified True/False
Indicate
whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
statement true.
|
|
|
126.
|
The cytoskeleton helps to move organelles within the cell.
_________________________
|
|
|
127.
|
Water, carbon dioxide, oxygen, and some other substances can pass through
the cell wall. _________________________
|
|
|
128.
|
Heterotrophs require oxygen. _________________________
|
|
|
129.
|
A plant whose leaves are naturally yellow probably contains chlorophyll as well
as other light-absorbing pigments. _________________________
|
|
|
130.
|
If you grind up the chloroplasts found in spinach leaves into a liquid solution,
the solution will have a green color. _________________________
|
|
|
131.
|
The Krebs cycle releases energy in the form of ATP.
_________________________
|
|
|
132.
|
If you swim aerobically for 30 minutes, your body has probably started to break
down stored molecules, such as fats, for energy. _________________________
|
|
|
133.
|
During photosynthesis, energy is stored in the form of fats.
_________________________
|
|
|
134.
|
An organism may have different common names that vary from area to area
and language to language. _________________________
|
|
|
135.
|
Biologists attempt to group organisms into categories that represent lines of
evolutionary descent. _________________________
|
|
|
136.
|
Cladistic analysis considers characteristics that have arisen as lineages
have evolved over time. _________________________
|
|
|
137.
|
Evidence shows that the same gene that codes for a particular protein in human
muscle also codes for that protein in yeasts, indicating common ancestry.
_________________________
|
|
|
138.
|
The six kingdoms of life are Eubacteria, Monera, Protista, Plantae,
Fungi, and Animalia. _________________________
|
|
|
139.
|
Many archaebacteria live in extreme environments, such as in Utah’s
Great Salt Lake. _________________________
|
|
|
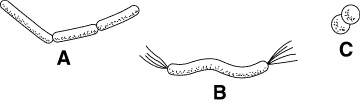
Figure
19–2
|
|
|
140.
|
The spiral-shaped organism labeled B in Figure 19–2 is an example of a
spirillum. _________________________
|
|
|
141.
|
In a lysogenic infection, host cells can make copies of virus DNA for
many generations. _________________________
|
|
|
142.
|
Insects often help spread viruses from one plant to another.
_________________________
|
|
|
143.
|
Funguslike protists are autotrophs. _________________________
|
|
|
144.
|
Generally, in order for sexual reproduction to occur in fungi, the spores
of opposite mating types must meet. _________________________
|
|
|
145.
|
Basidiomycetes resemble other fungal phyla but do not have a sexual
cycle. _________________________
|
|
|
146.
|
Fungi recycle nutrients in all ecosystems.
_________________________
|
|
|
147.
|
Losing excessive amounts of water through evaporation may affect a plant’s
ability to carry out photosynthesis. _________________________
|
|
|
148.
|
Biennials are pollinated during their first year of growth.
_________________________
|
|
|
149.
|
Phloem consists of vessel elements and companion cells.
_________________________
|
|
|
150.
|
Transpiration from leaves occurs because of the osmosis of water from the
leaf to the environment. _________________________
|
|
|
151.
|
Cells called gemmules move water currents through a sponge.
______________________________
|
|
|
152.
|
In the Portuguese man-of-war, a single tentacle acts as a balloonlike
float. _________________________
|
|
|
153.
|
A flatworm’s eyespots can detect chemicals.
_________________________
|
|
|
154.
|
An unidentified worm specimen that has a one-way digestive tract suspended in a
pseudocoelom is likely to be a(an) annelid. _________________________
|
|
|
155.
|
The type of body cavity shared by all mollusks is a pseudocoelom.
_________________________
|
|
|
156.
|
Around active deep-sea vents, symbiotic bacteria provide food for bivalve
communities. _________________________
|
|
|
157.
|
The three major groups of arthropods are crustaceans, chelicerates, and
uniramians. _________________________
|
|
|
158.
|
When a honeybee performs the round dance, it indicates that a food source has a
low energy value by changing direction less frequently than it would if the food were high
quality. _________________________
|
|
|
159.
|
An adult starfish has radial symmetry. _________________________
|
|
|
160.
|
When an echinoderm exerts a pulling force on an object, muscles pull the centers
of the tube feet upward. _________________________
|
|
|
161.
|
Humans have an open circulatory system. _________________________
|
|
|
162.
|
Flaps of connective tissue called valves are located between the atria
and the ventricles. _________________________
|
|
|
163.
|
Lymph nodes act as filters, trapping bacteria and other microorganisms
that cause disease. _________________________
|
|
|
164.
|
The process by which oxygen and carbon monoxide are exchanged between
cells, the blood, and air in the lungs is known as respiration. _________________________
|
|
|
165.
|
The pharynx is a piece of cartilage that covers the entrance to the
trachea when you swallow. _________________________
|
|
|
166.
|
Simple and complex carbohydrates are the main source of energy for the
body. _________________________
|
|
|
167.
|
The Food Guide Pyramid classifies food into five groups.
_________________________
|
|
|
168.
|
Gravity allows food to travel through your esophagus into the stomach.
_________________________
|
|
|
169.
|
If too little water is absorbed from the large intestine, constipation
results. _________________________
|
|
|
170.
|
As the amount of water in the blood increases, the rate of water reabsorption in
the kidneys increases. _________________________
|
|
|
171.
|
Washing your hands frequently can prevent the spread of many vectors.
_________________________
|
|
|
172.
|
Antibiotics are an effective treatment for a viral disease such as
measles. _________________________
|
|
|
173.
|
The immune response is triggered by antibodies.
_________________________
|
|
|
174.
|
Histamines can reduce the symptoms of an allergic reaction.
_________________________
|
|
|
175.
|
Benign tumors are not cancerous. _________________________
|
Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
176.
|
Eukaryotes contain specialized structures that perform important cellular
functions. These structures are called ____________________.
|
|
|
177.
|
Enzymes in the _________________________ attach carbohydrates and lipids to
proteins.
|
|
|
178.
|
Cells keep only a small amount of ____________________ on hand and regenerate it
as needed by using carbohydrates.
|
|
|
179.
|
If you separate the pigments found in a typical plant cell’s chloroplasts,
you will find ____________________, orange, and red pigments.
|
|
|
180.
|
The electrons that chlorophyll loses to the electron transport chain are
replenished by ____________________ molecules.
|
|
|
181.
|
The body gets rid of lactic acid in a chemical pathway that requires
____________________.
|
|
|
182.
|
A high level of lactic acid in the blood is a sign that
______________________________ has occurred.
|
|
|
183.
|
Traditional classification is based on general similarities of
_________________________ among organisms.
|
|
|
184.
|
The domain ____________________ contains plants, fungi, protists, and
animals—which are all eukaryotes.
|
|
|

Figure
19–2
|
|
|
185.
|
The organism labeled A in Figure 19–2 is an example of a(an)
____________________.
|
|
|
186.
|
By breaking down the nutrients from dead organisms in an ecosystem, bacteria act
as ____________________.
|
|
|
187.
|
The germ theory of disease was first proposed by ____________________.
|
|
|
188.
|
A chemical solution that is used in hospitals to kill bacteria is called a(an)
____________________.
|
|
|
189.
|
Certain viruses called ____________________ viruses cause cancer in
animals.
|
|
|
190.
|
The first protists evolved approximately ___________________ years ago.
|
|
|
191.
|
Animal-like protists that use structures called ____________________ for
movement and for feeding are members of the phylum Sarcodina.
|
|
|
192.
|
In the human body, Plasmodium first infects liver cells, then
____________________ cells, causing them to burst.
|
|
|
193.
|
A multicellular protist that efficiently absorbs blue light, collects calcium
carbonate in its cell walls, and lives in the ocean would be classified in the phylum
_________________________.
|
|
|
194.
|
Close examination of a colony of individuals of the phylum Acrasiomycota would
reveal that they retain their ____________________, unlike organisms of the phylum Myxomycota.
|
|
|
195.
|
In ascomycetes, the structure in which a diploid zygote forms is called a(an)
_________________________.
|
|
|
196.
|
Unicellular ascomycetes are commonly known as
_________________________.
|
|
|
197.
|
A serious fungal disease of ____________________ needs two different plants to
complete its life cycle.
|
|
|
198.
|
Plants need to exchange ______________________________ with the atmosphere in
order to carry out the processes of photosynthesis and respiration.
|
|
|
199.
|
Photosynthesis takes place in the _________________stage of the moss life
cycle.
|
|
|
200.
|
The process by which bryophytes draw water into their cells from the environment
is called ____________________.
|
|
|
201.
|
Water moves from cell to cell in the rhizoids of a moss by the process of
____________________.
|
|
|
202.
|
Ferns can live in shaded areas of a forest most likely because they have
____________________.
|
|
|
203.
|
The phloem cells called ___________________ are arranged end to end to form a
long pipeline.
|
|
|
204.
|
Root hairs take in water from the soil through the process of
____________________.
|
|
|
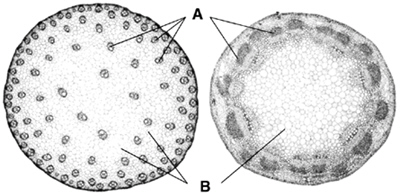
Figure
23–1
|
|
|
205.
|
In Figure 23–1, B is pointing to _________________________.
|
|
|
206.
|
The layer of growing tissue that surrounds the expanding phloem tissue in trees
is the _________________________.
|
|
|
207.
|
The front end of an organism is the ____________________ end.
|
|
|
208.
|
The internal space of a cnidarian is called a(an)
______________________________.
|
|
|
209.
|
Cnidarians have a(an) ____________________ that enables them to respond to touch
by pulling their tentacles inside their bodies.
|
|
|
210.
|
Many free-living roundworms are ____________________, which are animals that eat
other animals.
|
|
|
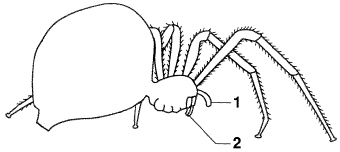
Figure
28–2
|
|
|
211.
|
On the chelicerate in Figure 28–2, the appendage labeled 1 is a(an)
____________________.
|
|
|
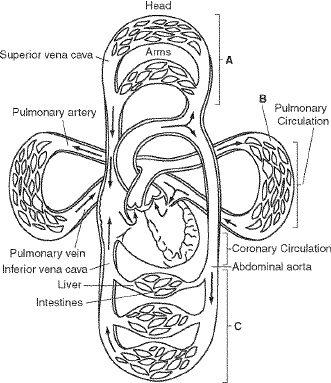
Figure
37–2
|
|
|
212.
|
In Figure 37–2, the area labeled B represents the capillaries of a
____________________.
|
|
|
213.
|
The iron-containing protein called ____________________ binds to oxygen in the
lungs and transports it to tissues throughout the body where the oxygen is released.
|
|
|
214.
|
The phrase “swollen glands” refers to swelling of the
_________________________.
|
|
|
215.
|
Inhaled air passes from the trachea to one of the two
____________________.
|
|
|
216.
|
Breathing is such an important function that your ____________________ system
will not let you have complete control over it.
|
|
|
217.
|
Contractions known as ____________________ squeeze food through the length of
the esophagus into the stomach.
|
|
|
218.
|
If a part of the stomach wall digests itself, a(an) ____________________
develops.
|
|
|
219.
|
The functioning units of the kidneys are the ____________________.
|
|
|
220.
|
To a large extent, the activity of kidneys is controlled by the composition of
____________________.
|
|
|
221.
|
A ____________________ is any disease-causing organism.
|
|
|
222.
|
Chickenpox, tetanus, and malaria are all examples of ____________________
diseases.
|
|
|
223.
|
Any opening in the skin is a potential entrance for ____________________.
|
|
|
224.
|
A ____________________ T cell activates other T cells and B cells, whereas a
killer T cell binds to infected cells.
|
|
|
225.
|
A person who has ____________________ is likely to suffer from a number of other
rare infections because this virus attacks the immune system.
|