Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Scientists assign each type of organism a universally accepted name in the
system known as
a. | traditional classification. | c. | binomial
nomenclature. | b. | the three domains. | d. | cladistics. |
|
|
|
2.
|
In the scientific version of a species name, which of the terms is
capitalized?
a. | the first term only | c. | both the first and second terms | b. | the second term
only | d. | neither the first nor
the second term |
|
|
|
3.
|
The second part of a scientific name is unique to each
a. | order in its class. | c. | genus in its family. | b. | family in its order. | d. | species in its
genus. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Before Linnaeus, scientific names were problematic because they were
a. | too brief to be descriptive. | c. | written only in
Greek. | b. | very long and difficult to standardize. | d. | written only in
Latin. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Several different classes make up a
a. | kingdom. | c. | family. | b. | phylum. | d. | genus. |
|
|
|
6.
|
The most general and largest category in Linnaeus’s system is
a. | the phylum. | c. | the genus. | b. | the kingdom. | d. | the domain. |
|
|
|
7.
|
An analysis of derived characters is used to generate a
a. | family tree based on external appearance. | b. | family tree based on
DNA structure. | c. | cladogram. | d. | traditional classification
system. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Similar genes are evidence of
a. | binomial nomenclature. | c. | common ancestry. | b. | mutations. | d. | different
anatomy. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Scientists have found that humans and yeasts
a. | have similar genes for the assembly of certain proteins. | b. | share all aspects of
cellular structure. | c. | have nothing in common. | d. | cannot be evaluated
for degree of relatedness. |
|
|
|
10.
|
What does the presence of similar genes in very dissimilar organisms
imply?
a. | The genes were produced by different selection pressures. | b. | The organisms share
a common ancestor. | c. | The organisms do not share a common
ancestor. | d. | The genes became identical through mutation. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which kingdom contains heterotrophs with cell walls of chitin?
a. | Protista | c. | Plantae | b. | Fungi | d. | Animalia |
|
|
|
12.
|
Some scientists propose that the kingdom Protista should be broken up into
several kingdoms. Which of these statements accurately supports this idea?
a. | Protists are all very similar and easy to confuse. | b. | Protista contains
very diverse organisms that do not fit into the other kingdoms. | c. | Protists are the
most numerous organisms on Earth. | d. | Protista evolved before any other
kingdom. |
|
|
|
13.
|
The domain that corresponds to the kingdom Eubacteria is
a. | Archaea. | c. | Eukarya. | b. | Bacteria. | d. | Fungi. |
|
|
|
14.
|
The domain that contains unicellular organisms that live in extreme environments
is
a. | Eubacteria. | c. | Archaea. | b. | Eukarya. | d. | Bacteria. |
|
|
|
15.
|
The two domains composed of only unicellular organisms are
a. | Eubacteria and Archaea. | c. | Archaea and
Bacteria. | b. | Eukarya and Bacteria. | d. | Archaea and Eukarya. |
|
|
|
16.
|
Organisms in the kingdoms Eubacteria and Archaebacteria were previously grouped
in a kingdom called
a. | Animalia. | c. | Monera. | b. | Fungi. | d. | Eukarya. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following is NOT a way in which archaebacteria and eubacteria
differ?
a. | Archaebacteria lack an important carbohydrate found in the cell walls of
eubacteria. | b. | The two groups have very different membrane lipids. | c. | Archaebacteria have
gene sequences that are similar to those of eukaryotes. | d. | Archaebacteria
follow the lytic cycle, while eubacteria follow the lysogenic cycle. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following are members of the kingdom Archaebacteria?
a. | methanogens | c. | eukaryotes | b. | eubacteria | d. | E. coli |
|
|
|
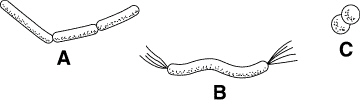
Figure
19–2
|
|
|
19.
|
Which cell shape in Figure 19–2 is called a coccus?
a. | A | c. | C | b. | B | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which of the following is(are) used to identify prokaryotes?
a. | cell shape | c. | the way prokaryotes obtain energy | b. | the way prokaryotes
move | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
21.
|
A method called Gram staining is used to tell
a. | what shape a prokaryote has. | b. | how a prokaryote obtains
energy. | c. | what kind of cell wall a prokaryote has. | d. | whether a prokaryote
has flagella. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Bacteria that break down the nutrients in dead matter into simpler substances
that are taken up by plant roots are called
a. | endospores. | c. | photoautotrophs. | b. | flagella. | d. | decomposers. |
|
|
|
23.
|
Humans use bacteria to
a. | clean up small oil spills. | c. | synthesize
drugs. | b. | mine minerals from the ground. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
24.
|
The outer protein coat of a virus is called a
a. | DNA core. | c. | bacteriophage. | b. | capsid. | d. | tail sheath. |
|
|
|
25.
|
What is the basic structure of a virus?
a. | DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat | b. | a capsid surrounded
by a protein coat | c. | a tail sheath surrounded by tail
fibers | d. | a tiny cell surrounded by a cell wall |
|
|
|
26.
|
A lytic infection concludes with the
a. | embedding of viral DNA into the host cell’s DNA. | b. | production of a
prophage. | c. | bursting of the host cell. | d. | production of messenger
RNA. |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which of the following will NOT kill bacteria?
a. | refrigeration | c. | chemical disinfection | b. | boiling | d. | frying |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which of the following is a proper use of disinfectants?
a. | as an antibiotic | c. | to sterilize a hospital | b. | to start
conjugation | d. | to preserve
foods |
|
|
|
29.
|
Viral diseases can be
a. | treated with antibiotics and prevented with vaccines. | b. | treated with
vaccines and prevented with antibiotics. | c. | prevented with antibiotics but not treated with
vaccines. | d. | prevented with vaccines but not treated with
antibiotics. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Plant viruses have a difficult time entering the cells they infect partly
because
a. | plant viruses are weaker than animal viruses. | b. | plant cells have
tough cell walls. | c. | many plant viruses are spread by
insects. | d. | plant viruses do not have a protein coat. |
|
|
|
31.
|
Viruses cause disease by
a. | producing toxins that harm the body. | b. | reproducing independently inside the
body. | c. | forming endospores in the body. | d. | disrupting the body’s normal
equilibrium. |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of all plants?
a. | are eukaryotic | c. | produce seeds | b. | have cell walls | d. | are
multicellular |
|
|
|
33.
|
Living on land required that plants
a. | evolve photosynthetic pigments. | c. | exchange gases. | b. | conserve
water. | d. | have cell
walls. |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which of the following statements is true about bryophytes?
a. | They have specialized tissues that conduct water. | b. | They draw up water
by osmosis. | c. | They are not highly dependent on water. | d. | They are a group of
plants made up of algae and mosses. |
|
|
|
35.
|
Because bryophytes do not have vascular tissue, they
a. | obtain all their water from the surrounding air. | b. | have true roots,
stems, and leaves. | c. | show alternation of
generations. | d. | grow close to the ground. |
|
|
|
36.
|
Which of the following is true about mosses?
a. | They are the least common bryophytes. | b. | Long, thin cells called rhizoids anchor them in
the ground. | c. | They are very rare in polar regions. | d. | Some mosses form clumps of green sporophytes
growing together. |
|
|
|
37.
|
Which of the following includes all the others?
a. | xylem | c. | phloem | b. | vascular tissue | d. | tracheids |
|
|
|
38.
|
Xylem and phloem are NOT
a. | conducting tissues. | c. | present in bryophytes. | b. | vascular
tissues. | d. | present in
ferns. |
|
|
|
39.
|
Which of the following includes a plant embryo, a food supply, and a protective
covering?
a. | pollen grain | c. | seed | b. | spore | d. | gametophyte |
|
|
|
40.
|
Seed-bearing plants differ from all other plants in that
a. | they have only xylem and no phloem tissue. | b. | they have a
gametophyte generation. | c. | their gametes do not require water for
fertilization to occur. | d. | they have true roots, stems, and
leaves. |
|
|
|
41.
|
An example of a monocot is a
a. | tomato. | c. | rose. | b. | lily. | d. | daisy. |
|
|
|
42.
|
Unlike a dicot, a monocot has
a. | four or five petals per flower. | c. | taproots. | b. | two
cotyledons. | d. | parallel leaf
veins. |
|
|
|
43.
|
Flowering plants that complete a life cycle within a single growing season are
called
a. | annuals. | c. | perennials. | b. | dicots. | d. | monocots. |
|
|
|
44.
|
Which type of plant lives the longest?
a. | annual | c. | perennial | b. | biennial | d. | seasonal |
|
|
|
45.
|
Pollen grains are produced by
a. | male reproductive structures. | c. | ovules. | b. | female reproductive
structures. | d. | flowers. |
|
|
|
46.
|
In angiosperms, reproduction takes place in
a. | leaves. | c. | cones. | b. | flowers. | d. | pollen. |
|
|
|
47.
|
The sterile leaves of a flower are the
a. | carpel and stamens. | c. | stigma and style. | b. | filaments and anthers. | d. | sepals and
petals. |
|
|
|
48.
|
In an angiosperm, pollen grains are produced in the
a. | stigma. | c. | carpel. | b. | filament. | d. | anther. |
|
|
|
49.
|
The tough outer layer of a seed is called the
a. | seed coat. | c. | nut. | b. | fruit. | d. | embryo wall. |
|
|
|
50.
|
What fruit-eating animal likely would ensure the widest dispersal of a
plant’s seeds?
a. | a rat | c. | a bird | b. | a raccoon | d. | a squirrel |
|
|
|
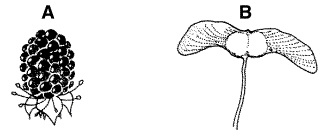
Figure
24–1
|
|
|
51.
|
The seed type shown in Figure 24–1 that is generally dispersed by animals
is(are)
a. | only A. | c. | both A and B. | b. | only B. | d. | neither A nor
B. |
|
|
|
52.
|
Seeds that are dispersed by wind and water typically are
a. | lightweight. | c. | nutritious. | b. | large. | d. | sweet and
fleshy. |
|
|
|
53.
|
An animal that has an imaginary plane passing through the middle and produce
equalt left and right sides shows
a. | radial symmetry. | c. | several planes of symmetry. | b. | segmentation. | d. | bilateral symmetry. |
|
|
|
54.
|
Organisms that spend their entire adult lives attached to one spot are said to
be
a. | sessile. | c. | flagellated. | b. | heterotrophic. | d. | symmetric. |
|
|
|
55.
|
Many sponges protect themselves from predators by producing
a. | larvae. | c. | nematocysts. | b. | choanocytes. | d. | toxins. |
|
|
|
56.
|
The body symmetry of a cnidarian is
a. | bilateral. | b. | radial . | c. | asymmetry | d. | sphercial |
|
|
|
57.
|
How do polyps differ from medusas?
a. | Polyps have a mesoglea, and medusas do not. | b. | Medusas are
cylindrical and usually sessile, and polyps are bell-shaped and motile. | c. | Medusas are
carnivorous, and polyps are not. | d. | Polyps are cylindrical and usually sessile, and
medusas are bell-shaped and motile. |
|
|
|
58.
|
The nerve cells of cnidarians make up a(an)
a. | brain. | c. | hydrostatic skeleton. | b. | ocelli. | d. | nerve net. |
|
|
|
59.
|
A cnidarian’s gastrovascular cavity is specialized for
a. | reproduction. | c. | digestion. | b. | capturing prey. | d. | sensing the
environment. |
|
|
|
60.
|
Flatworms belong to the phylum?
a. | Annelida | b. | Chordata | c. | Playthelminthes | d. | Nemotoda |
|
|
|
61.
|
The nervous system of a roundworm includes
a. | a simple brain. | c. | a single ganglion. | b. | a complex brain. | d. | several
ganglia. |
|
|
|
62.
|
The body of an annelid has
a. | a backbone. | c. | segments. | b. | an external shell. | d. | stinging
tentacles. |
|
|
|
63.
|
Which of these animals has a true coelom?
a. | filarial worm | c. | planarian | b. | tapeworm | d. | earthworm |
|
|
|
64.
|
A type of worm that is an external parasite is the
a. | tapeworm. | c. | leech. | b. | polychaete. | d. | earthworm. |
|
|
|
65.
|
Mollusks have a
a. | foot. | b. | mantle | c. | shell | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
66.
|
The tubelike structure through which water enters and leaves a mollusk’s
body is the
a. | sinus. | c. | coelom. | b. | siphon. | d. | mantle cavity. |
|
|
|
67.
|
The mollusks that would move the most are the
a. | gastropods. | c. | bivalves. | b. | cephalopods. | d. | nudibranchs. |
|
|
|
68.
|
Which of the following invertebrates is NOT a crustacean?
a. | spider | c. | barnacle | b. | lobster | d. | crayfish |
|
|
|
69.
|
An example of an arachnid is a
a. | lobster. | c. | crayfish. | b. | centipede. | d. | spider. |
|
|
|
70.
|
Echinoderms are like vertebrates in that echinoderms
a. | are bilaterally symmetrical as larvae and as adults. | b. | are
deuterostomes. | c. | have cephalization. | d. | have an anterior end and a posterior
end. |
|
|
|
71.
|
The skeleton of an echinoderm is an
a. | exoskeleton made of calcium carbonate. | b. | exoskeleton made of chitin. | c. | endoskeleton made of
calcium carbonate. | d. | endoskeleton made of
chitin. |
|
|
|
72.
|
In an echinoderm, the structure that operates like a living suction cup is
the
a. | madreporite. | c. | stomach. | b. | tube foot. | d. | nerve ring. |
|
|
|
73.
|
An example of an echinoderm is
a. | squid | c. | sand dollar | b. | clam | d. | sponge |
|
|
|
74.
|
In chordates, the long supporting rod that runs through the body is called
the
a. | nerve cord. | c. | pharyngeal pouch. | b. | notochord. | d. | tail. |
|
|
|
75.
|
Which of these chordate characteristics exists as paired structures?
a. | tail | c. | pharyngeal pouch | b. | notochord | d. | nerve cord |
|
|
|
76.
|
A vertebrate is any chordate that has a
a. | backbone. | c. | hollow nerve cord. | b. | notochord. | d. | tail that extends beyond the
anus. |
|
|
|
77.
|
Any animal with a spinal cord must be a(an)
a. | fish. | c. | vertebrate. | b. | amphibian. | d. | nonvertebrate
chordate. |
|
|
|
78.
|
The first vertebrates to evolve were
a. | amphibians. | c. | tunicates. | b. | lancelets. | d. | fishes. |
|
|
|
79.
|
Three body parts,
jointed legs and a tough exoskeleton are characteristics of which phylum? a. | Cnidaria | c. | arthropoda | b. | mollusca | d. | nemotoda |
|
|
|
80.
|
Soft, thin, flat bodies are characteristics of
which phylum?
a. | Cnidaria | c. | Arthropoda | b. | Mollusca | d. | Platyheliminthes |
|
|
|
81.
|
Soft-bodied animals which usually have a shell is
a characteristic of which phylum? a. | Cnidaria | c. | Arthropoda | b. | Mollusca | d. | Nemotoda |
|
|
|
82.
|
Roundworms with evolution of body cavity belong to
which phylum? a. | Cnidaria | c. | Arthropoda | b. | Mollusca | d. | Nemotoda |
|
|
|
83.
|
Jelly like animals
that have a bell or umbrella shape belong to which phylum? a. | Cnidaria | c. | Porifera | b. | Platyhelminthes | d. | Nemotoda |
|
|
|
84.
|
The simplest animals
which gain nutrients by filtering water, are part of what phylum? a. | Cnidaria | c. | Porifera | b. | Platyhelminthes | d. | Nemotoda |
|
|
|
85.
|
Animals that have a backbone that supports the
body are part of which phylum? a. | Chordata | c. | Arthropoda | b. | Annelida | d. | Nemotoda |
|
|
|
86.
|
Long animals which
are divided into segments are part of which phylum? a. | Chordata | c. | Arthropoda | b. | Annelida | d. | Nemotoda |
|
|
|
87.
|
Fish that have no true teeth are in class
a. | Chondrichthyes | c. | Agnatha | b. | Osteichthyes | d. | Aves |
|
|
|
88.
|
Animals that can have gills and lungs at different stages of their life are in
class
a. | Reptilia | c. | Aves | b. | Amphibia | d. | Mammalia |
|
|
|
89.
|
Warm-blooded animals that have mammary glands to produce their own milk are in
class
a. | Agnatha | c. | Aves | b. | Reptilia | d. | Mammalia |
|
|
|
90.
|
Animals that have feathers and wings are in class
a. | Aves | c. | Reptilia | b. | Agnatha | d. | Osteichthyes |
|
|
|
91.
|
Lizards, snakes, and alligators are examples of class
a. | Reptilia | c. | Aves | b. | Amphibia | d. | Agnatha |
|
|
|
92.
|
A shark is an example of class
a. | Agnatha | c. | Chondrichthyes | b. | Osteichthyes | d. | Aves |
|
|
|
93.
|
A fish that has skeleton made of bone is in class
a. | Agnatha | c. | Amphibia | b. | Chondrichthyes | d. | Osteichthyes |
|
|
|
94.
|
All of the phyla are invertebrates EXCEPT
a. | Echinoderms | c. | Mollusks | b. | Chordata | d. | Porifera |
|
|
|
95.
|
All of the following are example of arthropods EXCEPT
a. | insects | c. | arachnids | b. | crustaceans | d. | bivalves |
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
96.
|
Differenciate between: (Value 22)
a) prokaryotic and eukaryotic
b)
autotrophic and heterotropic
c) multicellular and unicellular
d) fungi and plants
e) plants
and animals
f) prion and viroid
g) eubacteria and archeabacteria
h) binary fission and
conjugation
i) antibiotics and vaccines
j) lytic cycle and lysogenic cycle
k) mosses and
ferns
l) gymnosperms and angiosperms
m) stamen and carpel
n) xylem and phloem
o) monocots
and dicots
p) annual and perennial
q) sporophyte and gametophyte
r) invertebrates and
vertebrates
s) protosome and deutrosome
t) bilateral and radial symmetry
u) cephalization
and coelom
v) flatworms and annelids
|